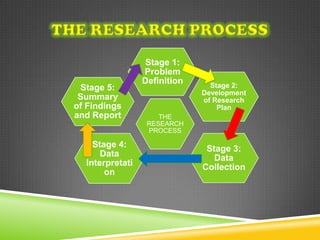
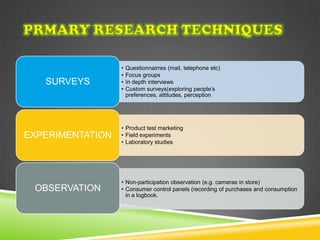
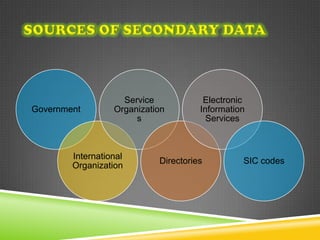
The document discusses the significance of information in market orientation and performance, distinguishing between primary and secondary research types. It outlines strategic and tactical levels of research relevant to international marketing, emphasizing data collection methods and considerations for selecting research agencies. The information gathered should be relevant, useful, and timely to aid marketing decision-making and reduce risks.