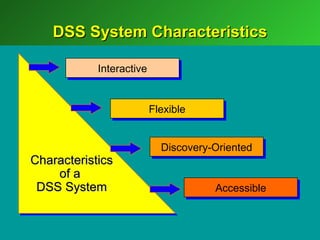
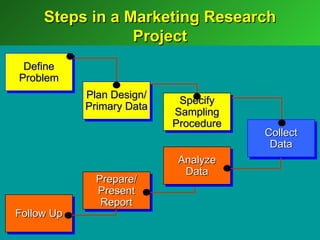
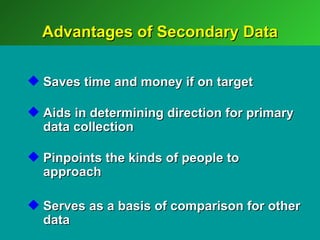
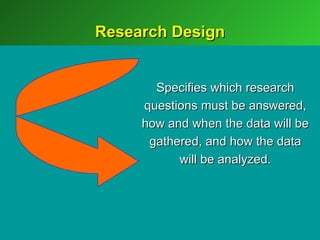
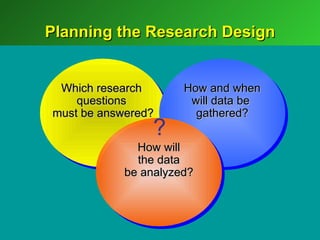
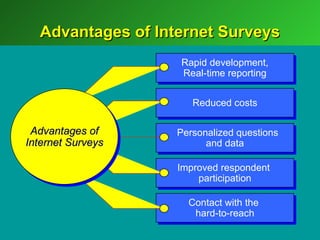
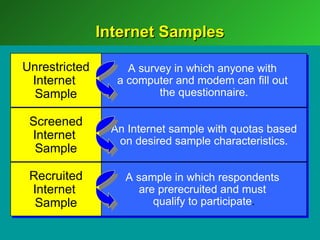
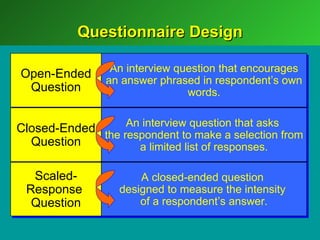
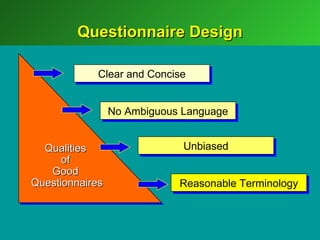
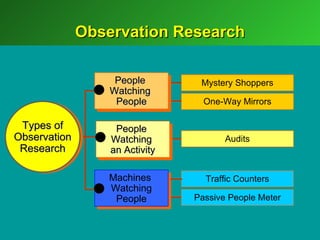
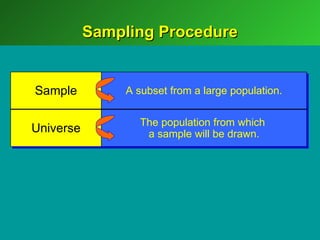
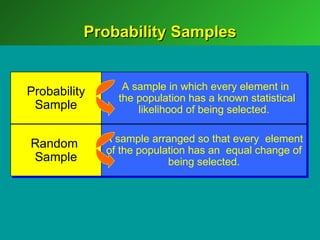
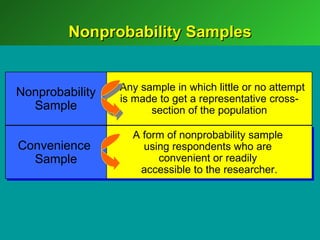
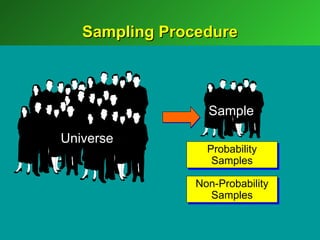
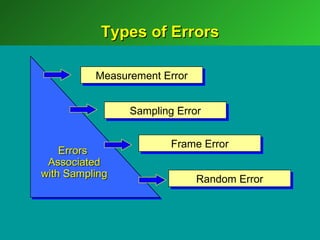
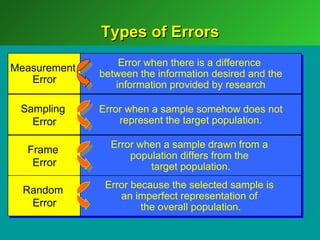
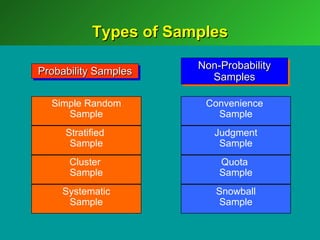
A marketing decision support system (DSS) helps managers obtain and manipulate information to make decisions. Marketing research involves collecting and analyzing data relevant to marketing decisions. It follows steps such as defining problems, planning research design, collecting primary or secondary data, and analyzing and reporting results. Marketing research is important for decision-making, product development, and understanding customers.