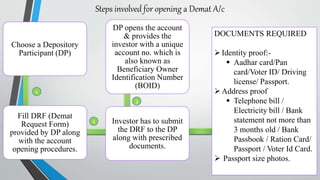
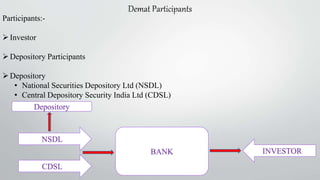
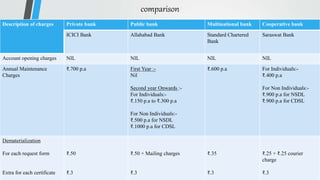
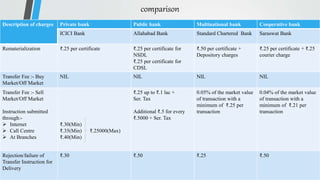
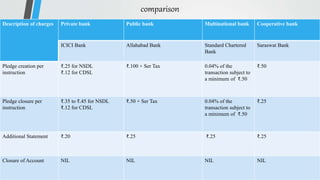
Demat accounts allow investors to hold securities like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds in electronic form instead of physical certificates. Opening a demat account involves choosing a Depository Participant and submitting account opening documents. Demat accounts provide benefits like safe and convenient transfer of securities, reduction in paperwork, and risk elimination. National Securities Depository Limited and Central Depository Services Limited are the two depositories in India that work with Depository Participants like banks to provide demat services. Dematerialization is the process of converting physical securities like share certificates into electronic form in a demat account, while rematerialization is the reverse process of converting electronic securities back into physical form.