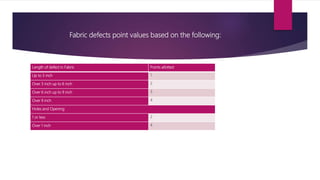
A warehouse is a commercial building used for storage of goods by manufacturers, importers, exporters and others. Warehouses are usually large plain buildings located in industrial areas of cities. The document then provides information about the management staff and total employees in different sections of a garment factory including store/warehouse, sample, cutting, sewing, quality inspection, and finishing. It discusses the processes, terminology, and responsibilities in each section.