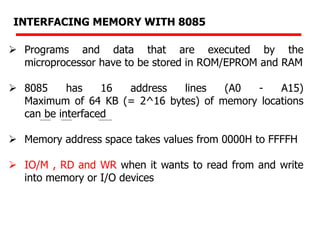
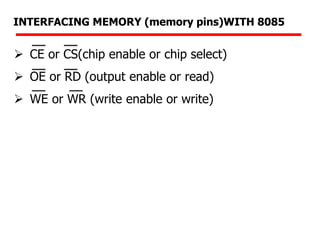
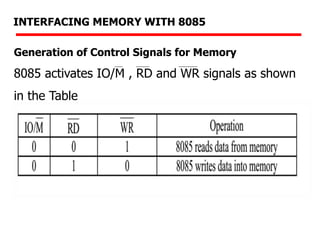
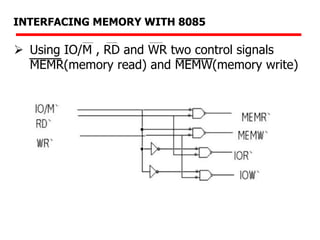
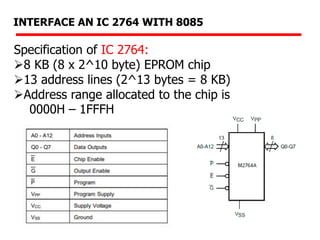
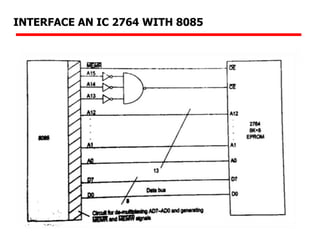
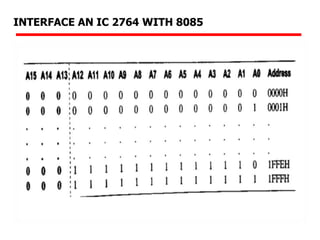
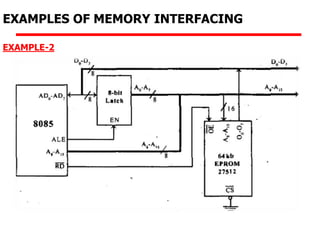
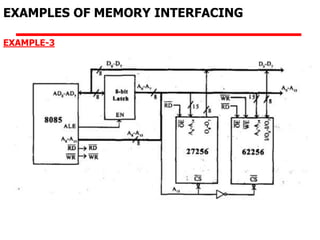
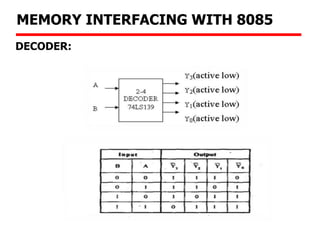
The document details memory interfacing with the 8085 microprocessor, highlighting the role of ROM, EPROM, and RAM in memory storage and control signals used for memory operations. It provides various examples of interfacing different memory configurations, including full EPROM usage and equal division between EPROM and RAM, specifying address lines and chip select management. Additionally, it describes specific ICs and their allocation within the memory address space.