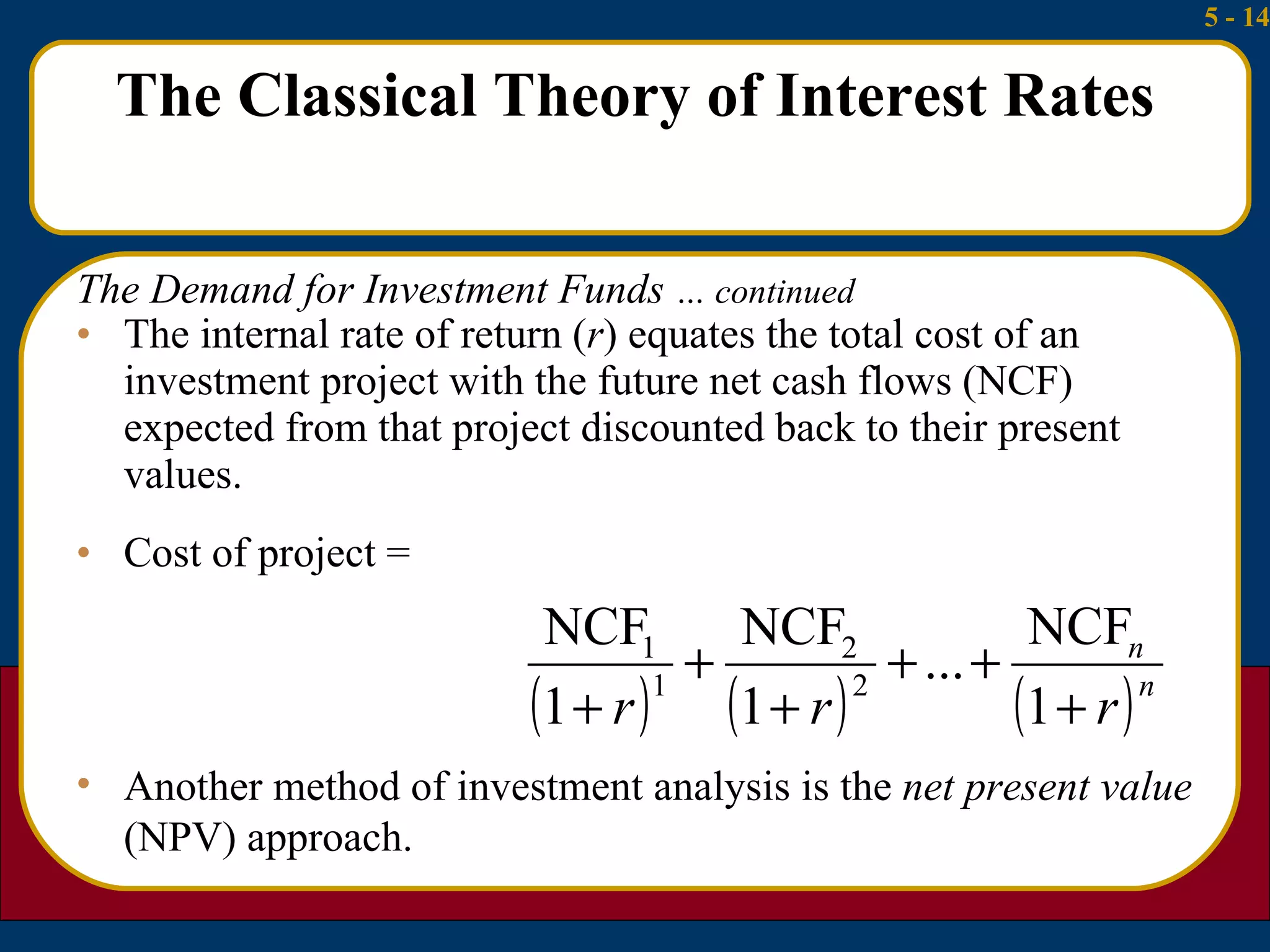
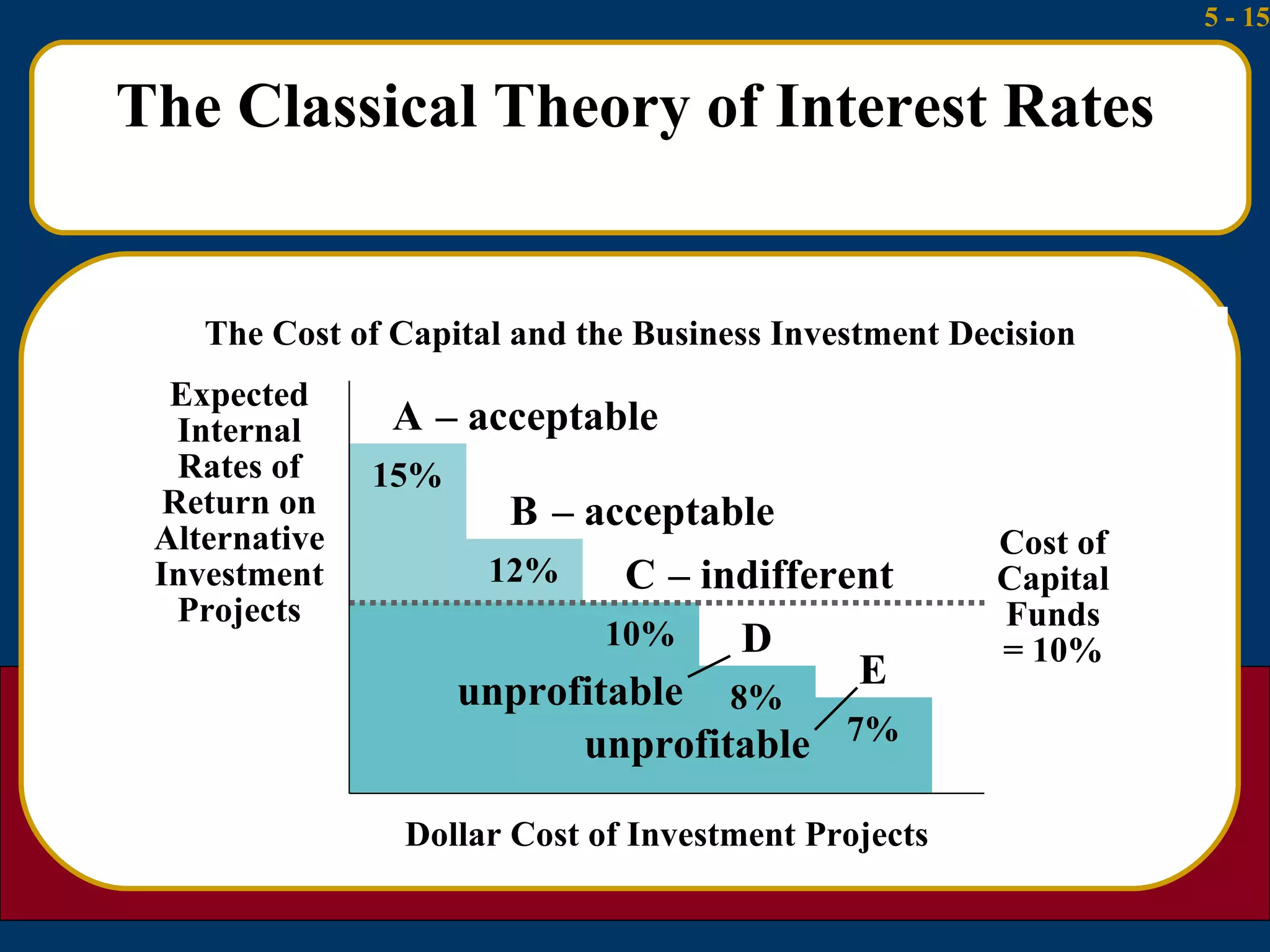
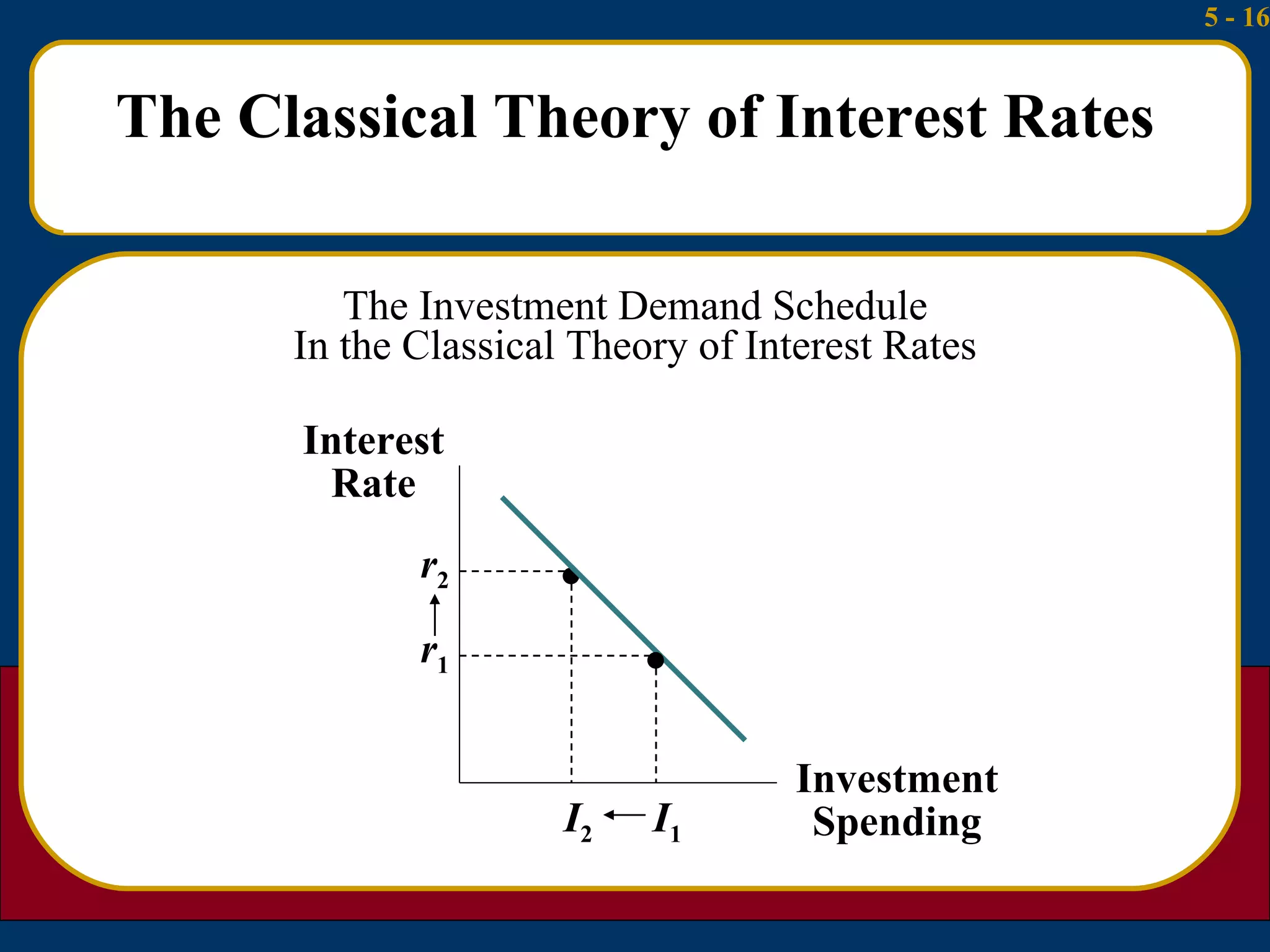
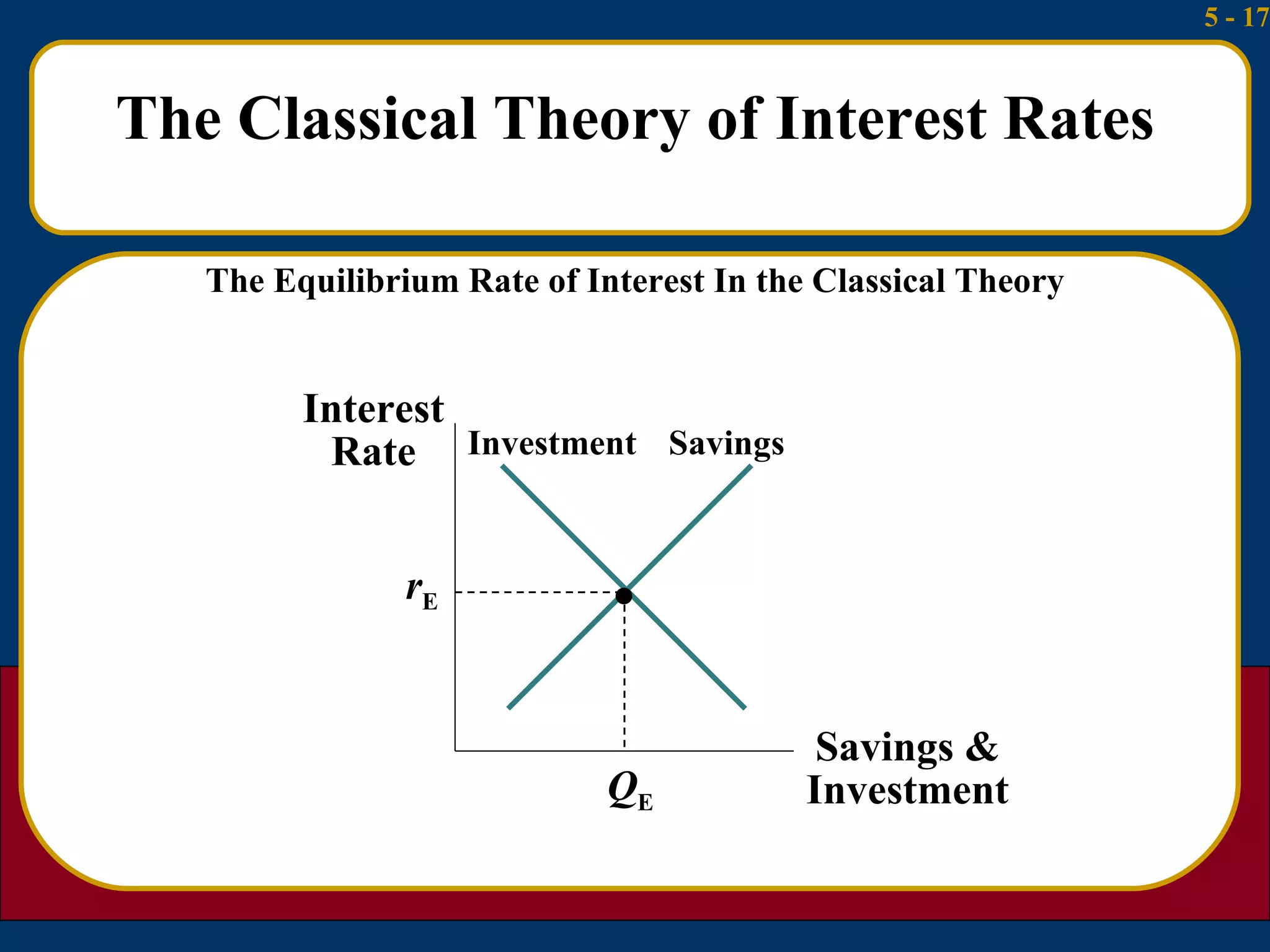
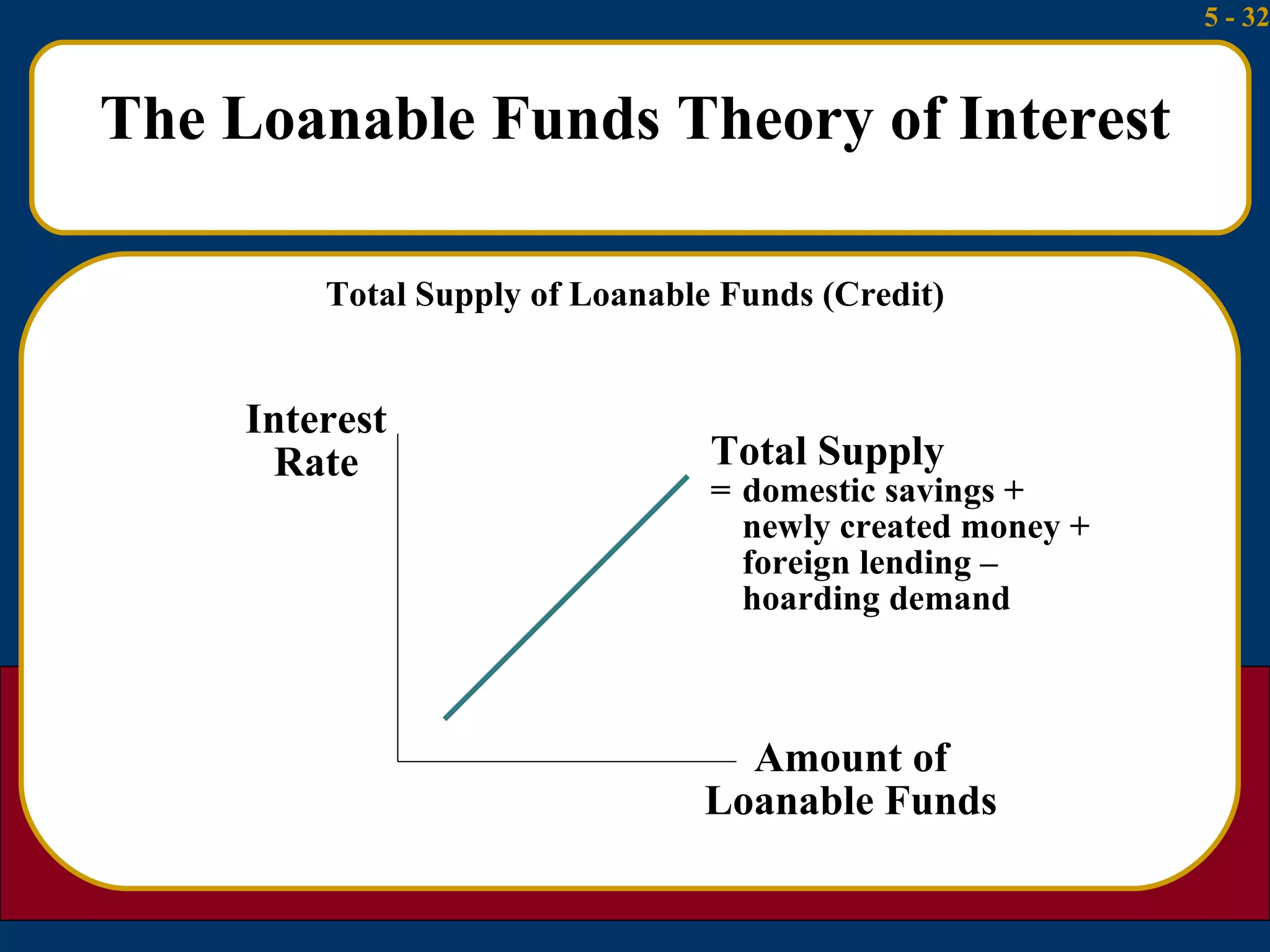
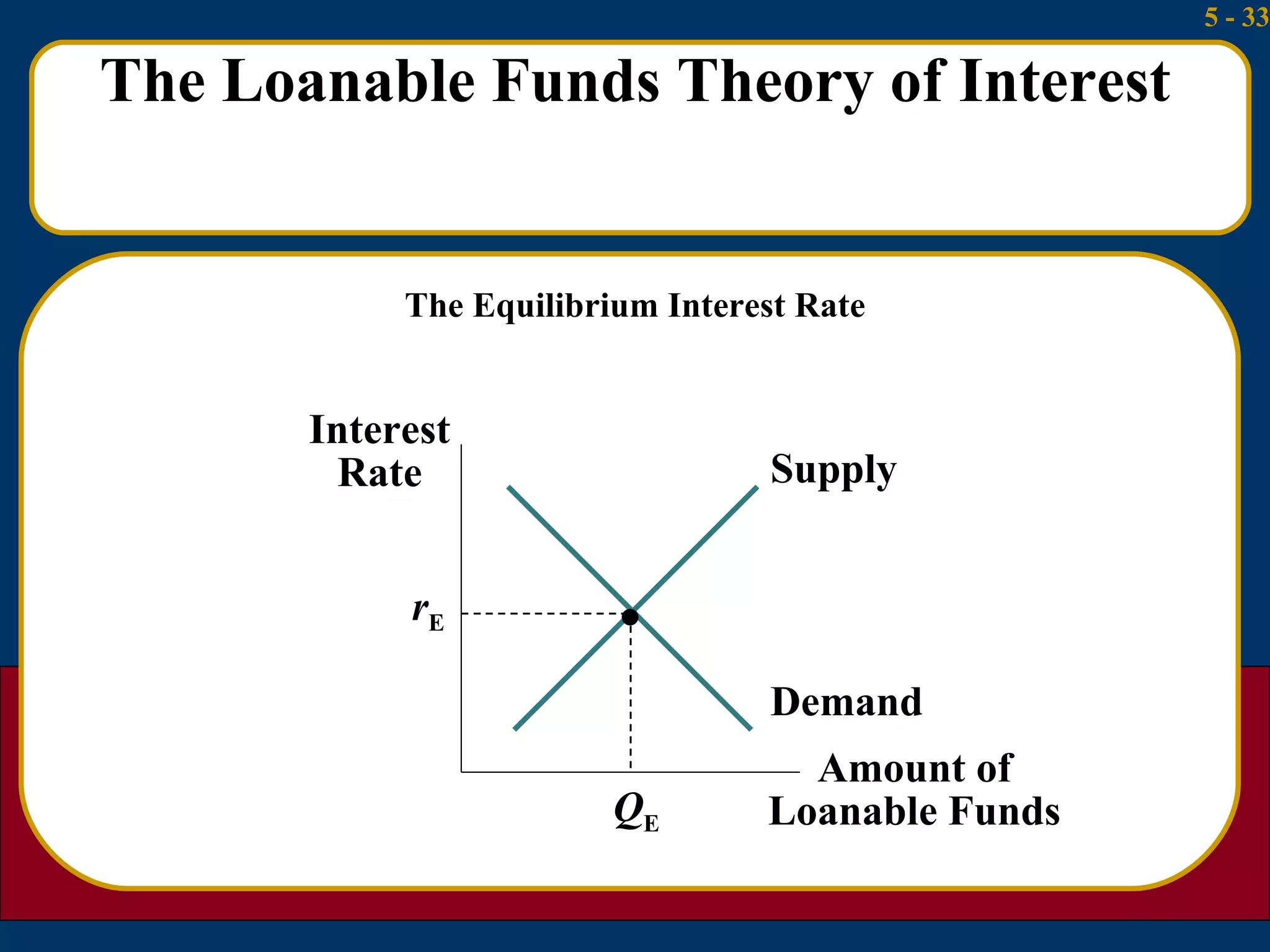
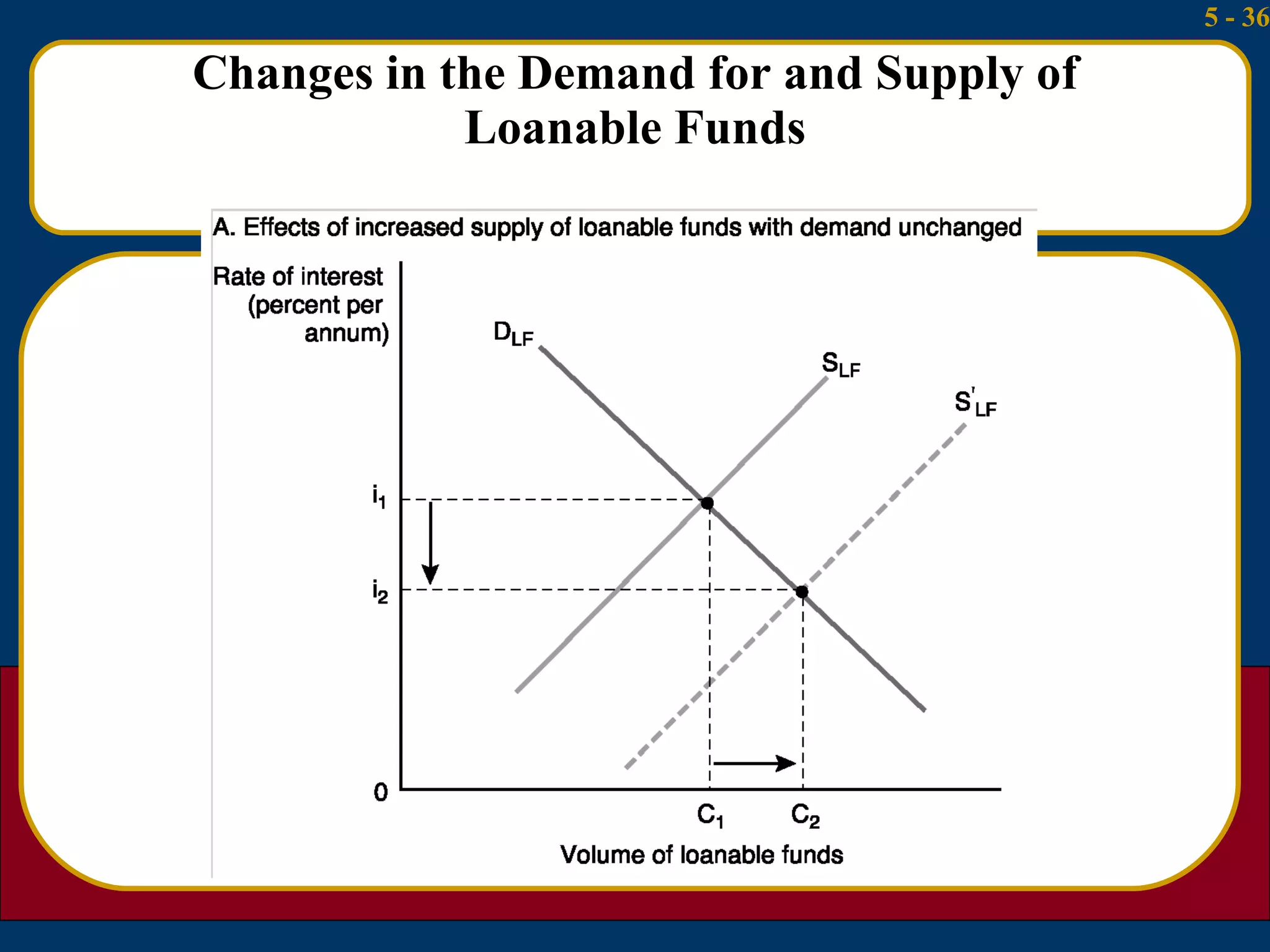
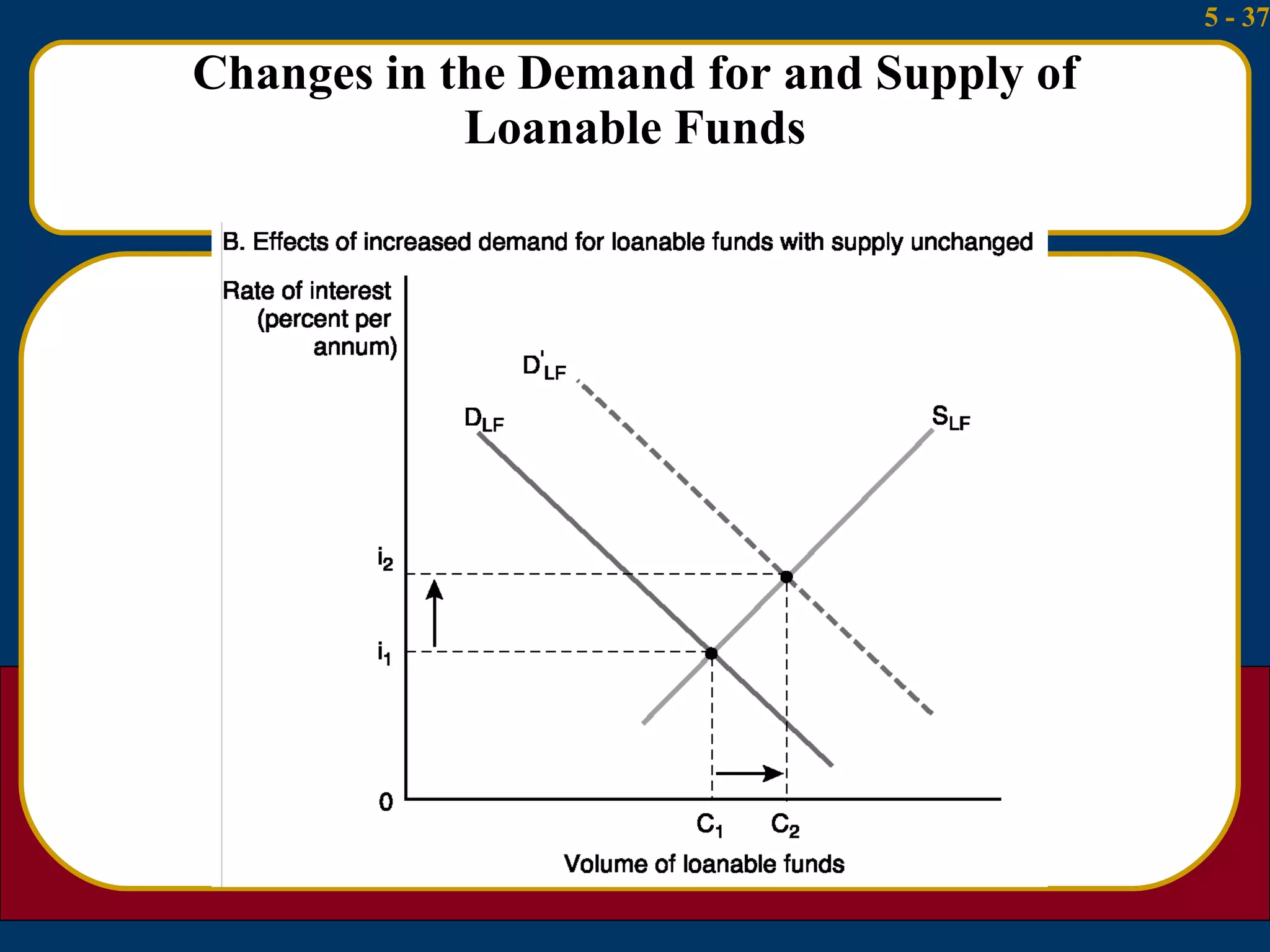
The document summarizes several theories about what determines interest rates:
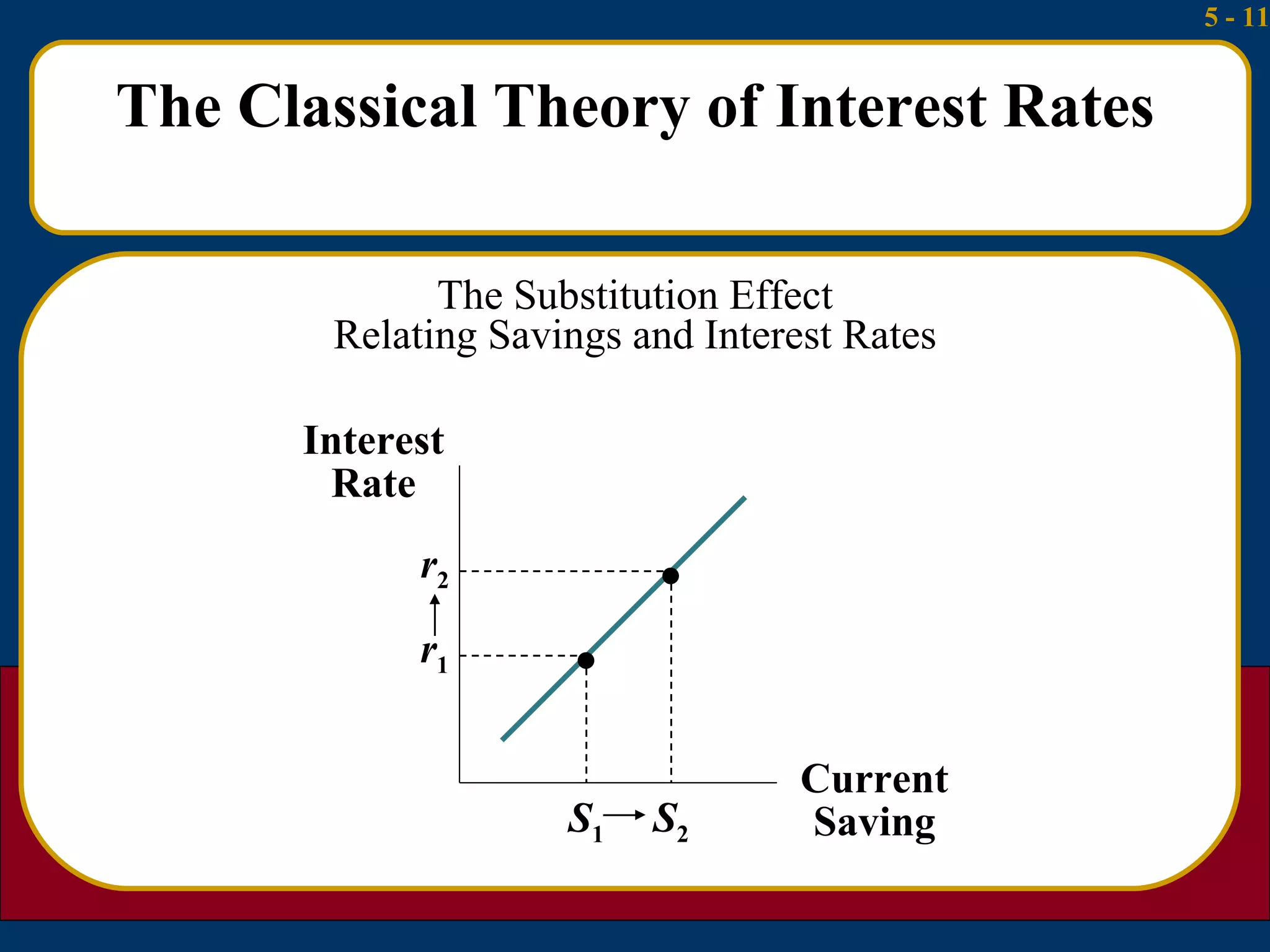
1) The classical theory argues that interest rates are determined by the supply of household savings and the demand for business investment.
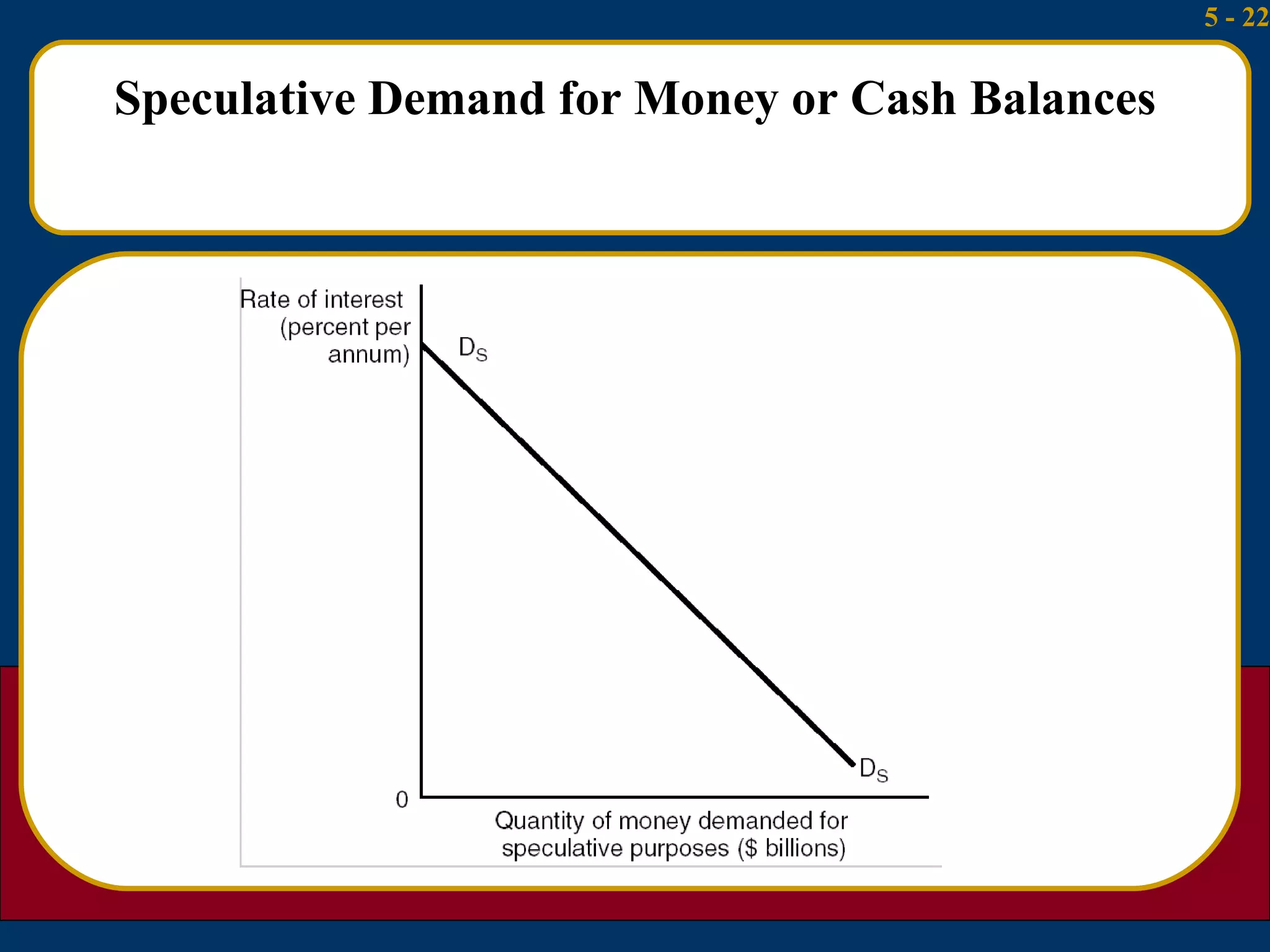
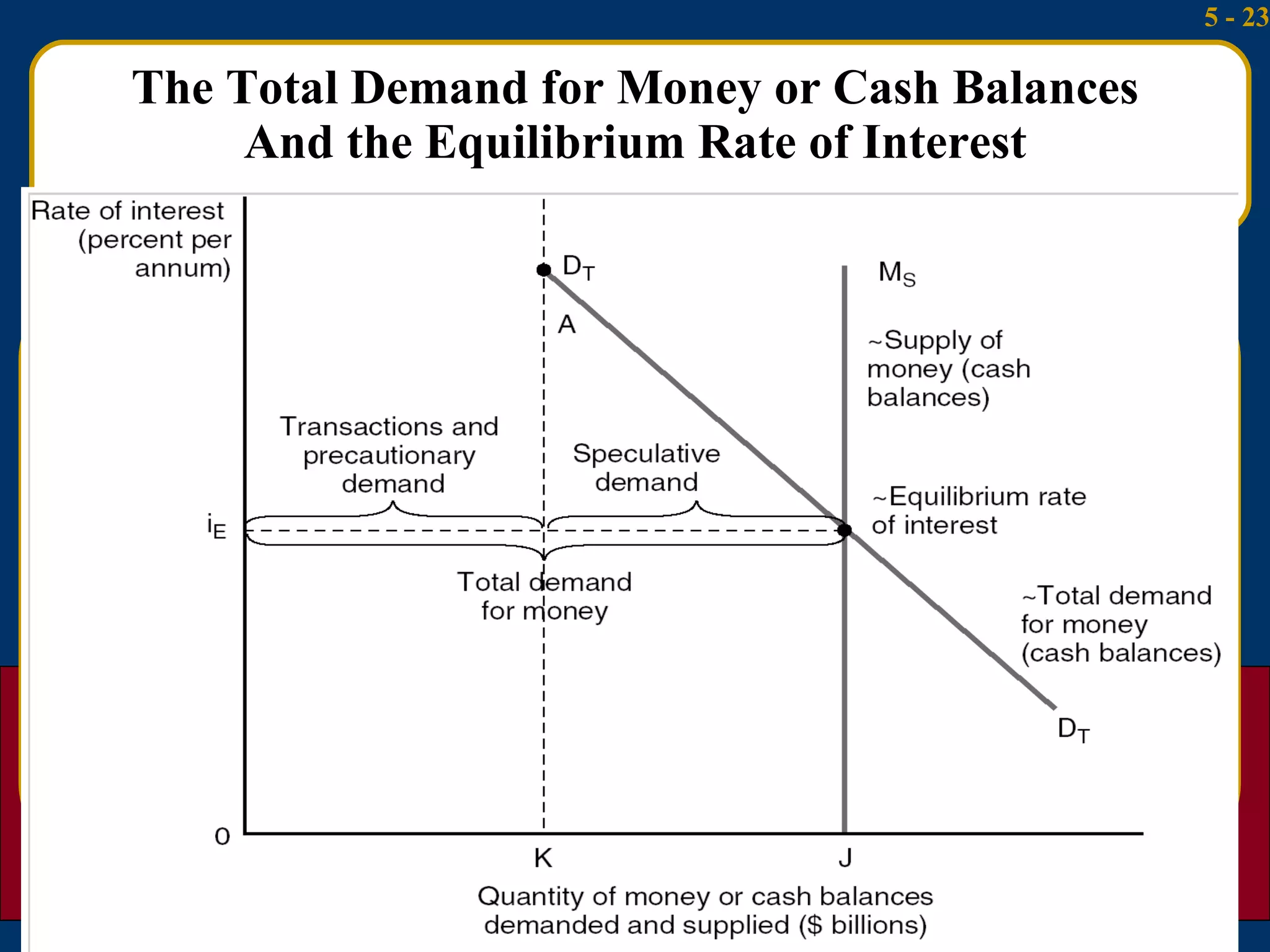
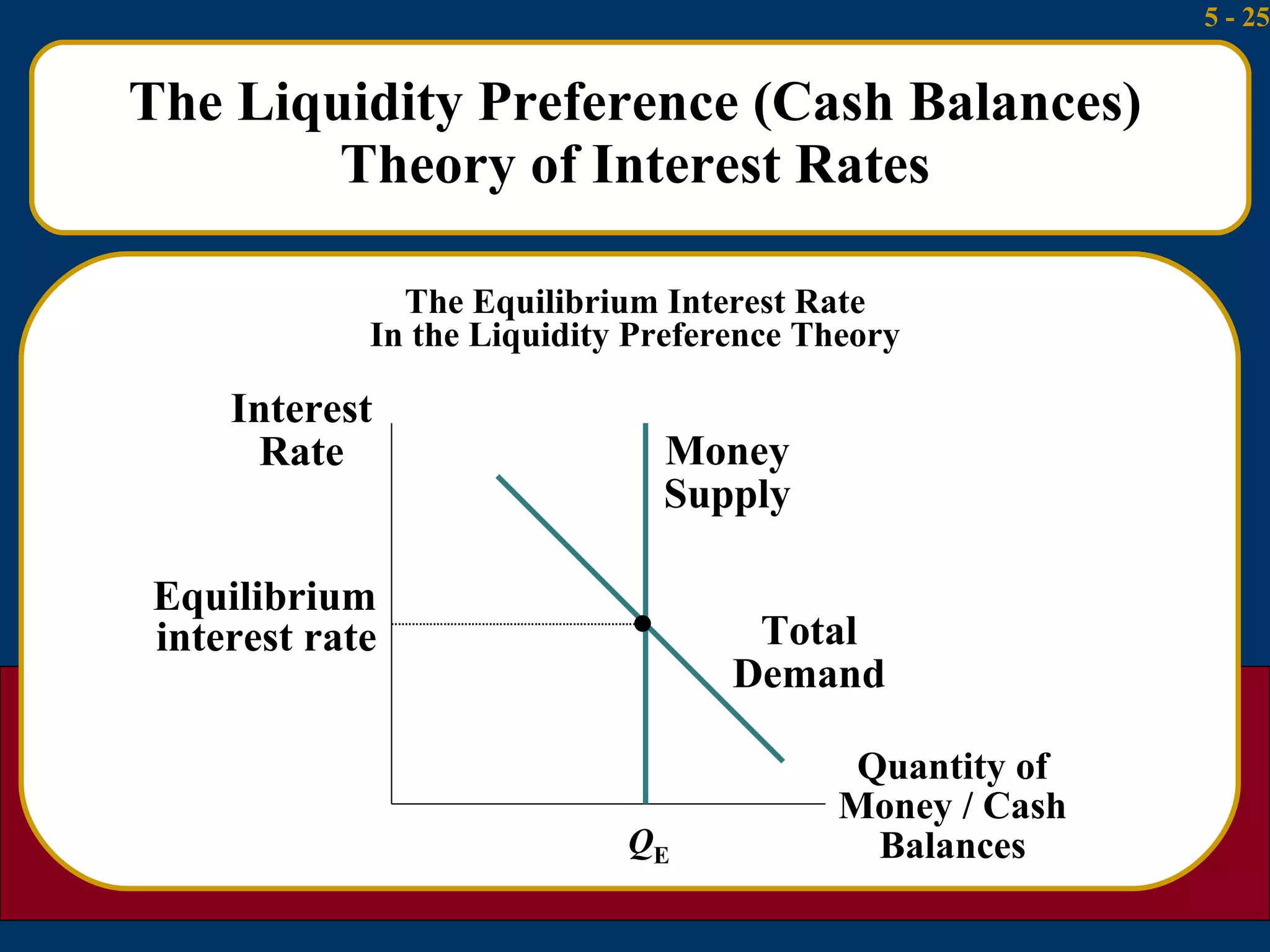
2) The liquidity preference theory views interest rates as the price that induces people to hold cash rather than bonds given transactions, precautionary, and speculative demands for money.
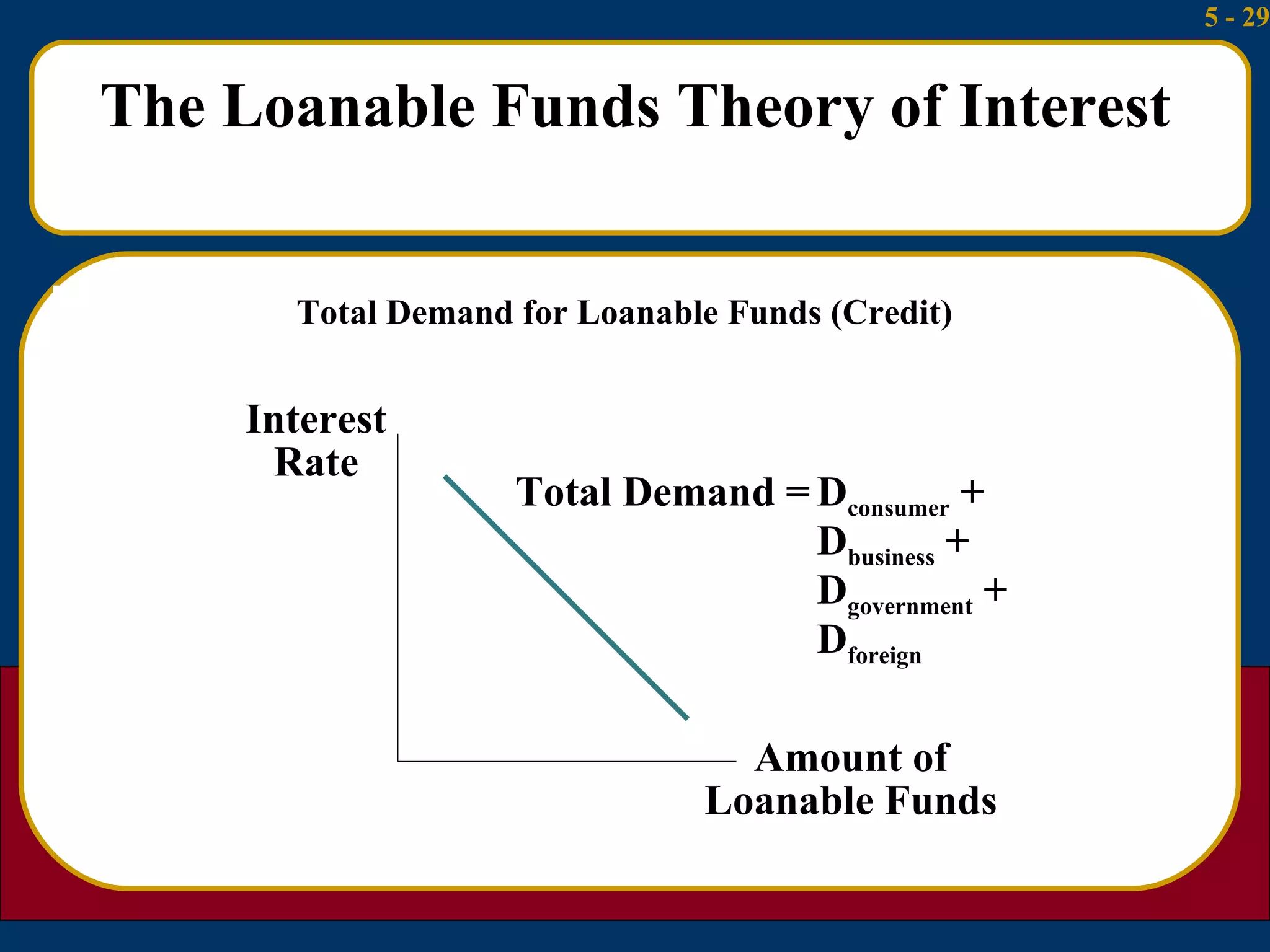
3) The loanable funds theory sees interest rates as set by the overall demand for and supply of credit from various sources like domestic savings, money creation, and foreign lending.