The document covers essential financial concepts including financial markets, institutions, and intermediaries, as well as stocks and bonds, explaining their pros and cons. It discusses the federal government's budget deficit, the value of money, and various strategies for dealing with financial risks. Additionally, it includes information on topics such as present and future value, compound interest, and the implications of currency depreciation.












![References
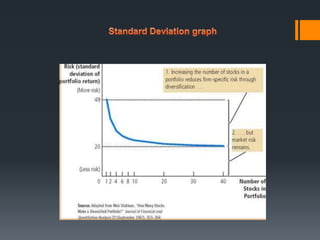
Mankiw, N. (Producer). (2014). FIGURE 2 Diversification Reduces
Risk [Print Graphic]. Retrieved from
http://digitalbookshelf.southuniversity.edu/
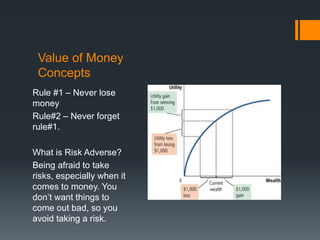
Mankiw,N. (Producer). (2014). Figure 1- The Utility Function [Web
Graphic]. Retrieved from http://digitalbookshelf.southuniversity.edu/
Norstad, J. (1999). An introduction to utility theory., Retrieved from:
http://www.norstad.org/finance/util.pdf
The Huffington Post. (Producer). (2013, October 14). Confused
About The Deficit? This 2-Minute Video Can Help [Web Video].
Retrieved from Confused About The Deficit? This 2-Minute Video
Can Help
Valderramo, D. (2004, August 13). Does a fall in the dollar mean
higher u.s. consumer prices? Retrieved from
http://www.frbsf.org/economic-research/publications/economic-
letter/2004/august/does-a-fall-in-the-dollar-mean-higher-us-
consumer-prices/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialconcepts-140824155007-phpapp01/85/Financial-concepts-15-320.jpg)
