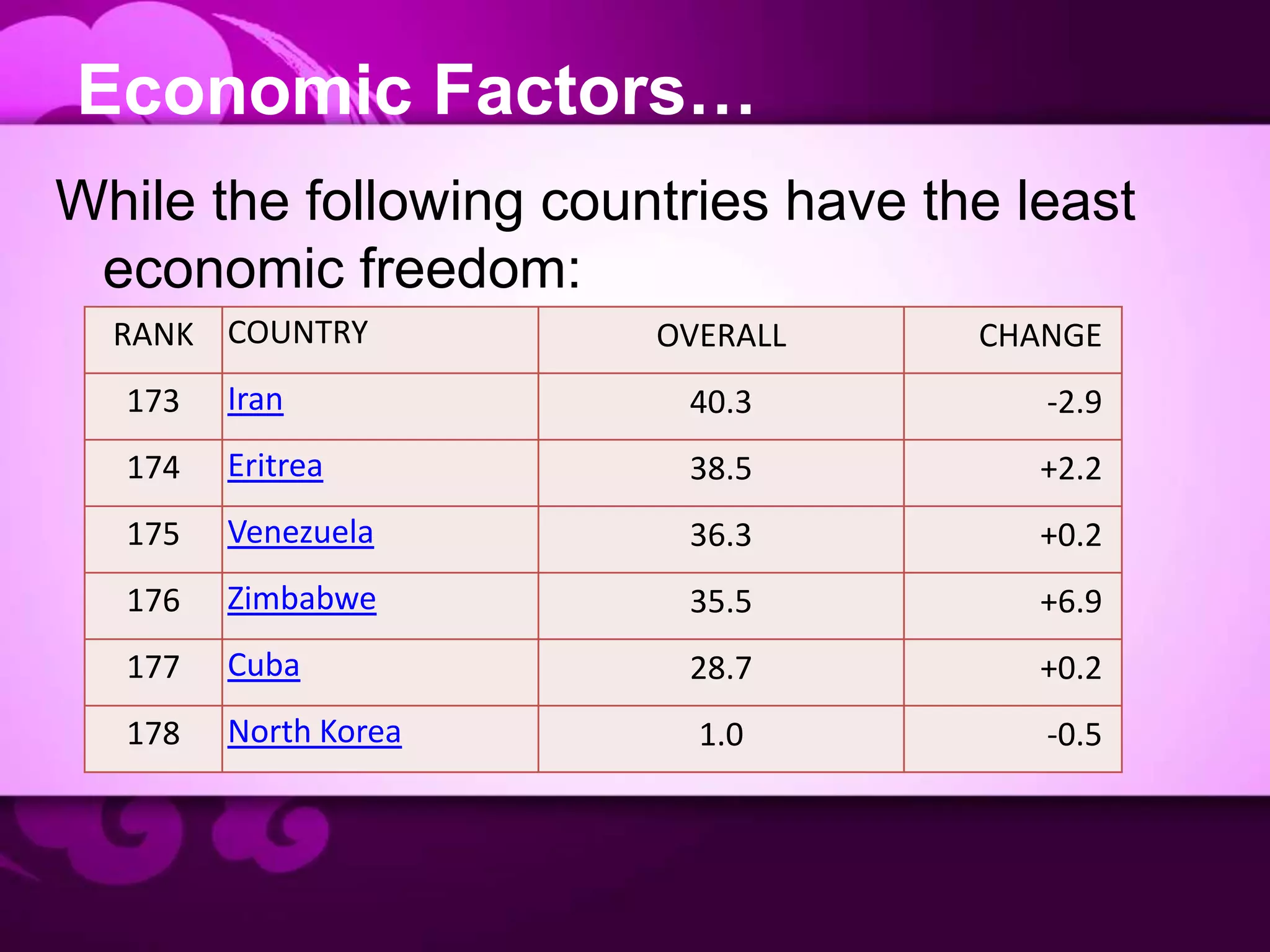
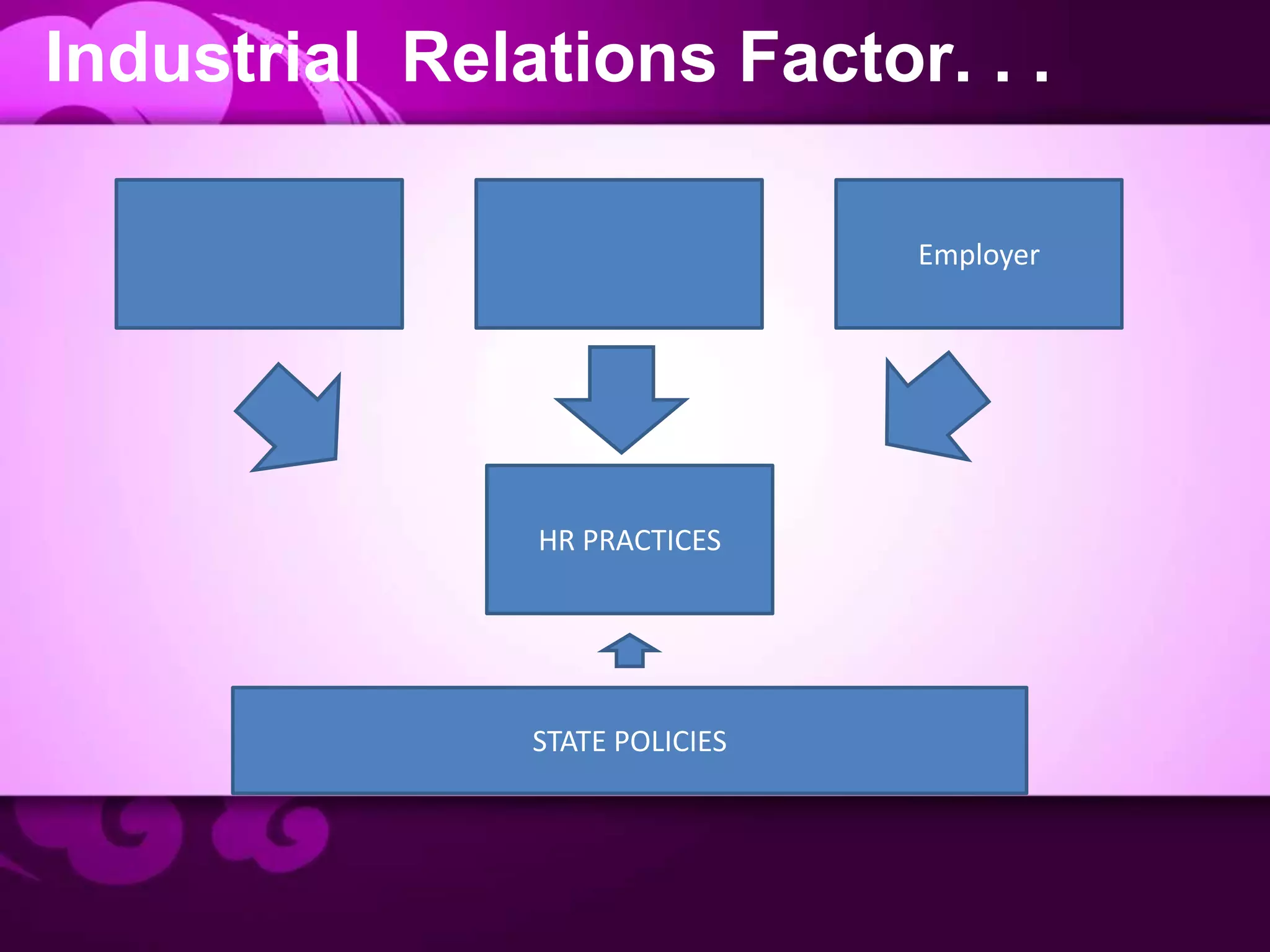
Globalization and advances in technology have increased the need for companies to operate internationally and manage a global workforce. However, intercountry differences across many factors like culture, economics, labor costs, and industrial relations present significant challenges to human resource management practices. Cultural factors like power distance, individualism, and concepts of time vary widely between countries. Economic systems, labor costs, and the power of labor unions also differ dramatically in different parts of the world. Effective international HR requires understanding these differences and adapting practices accordingly instead of exporting domestic biases globally.