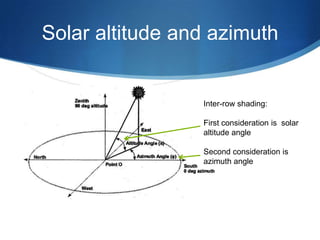
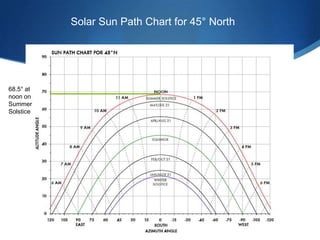
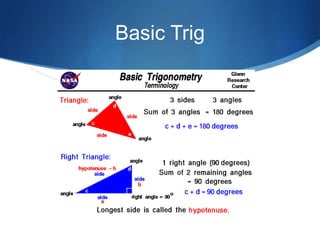
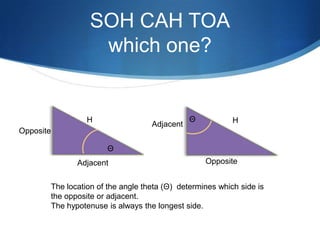
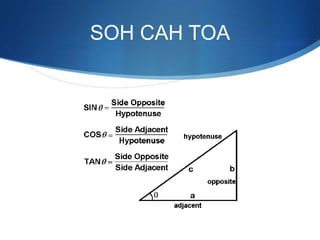
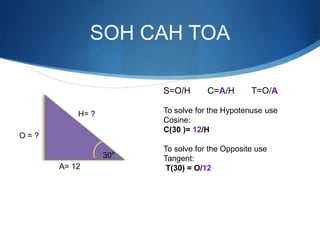
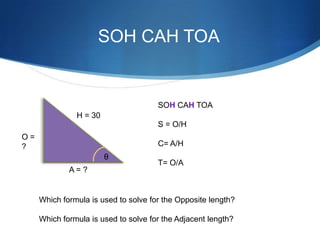
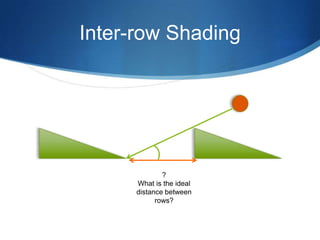
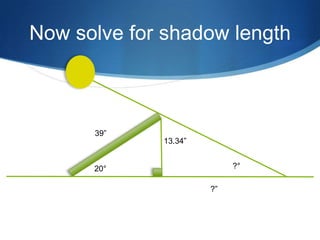
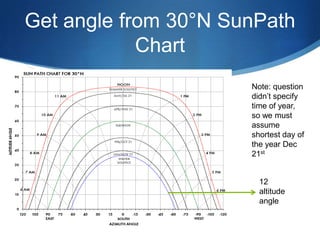
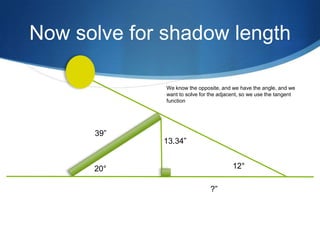
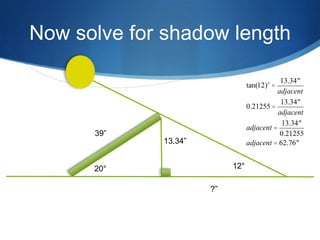
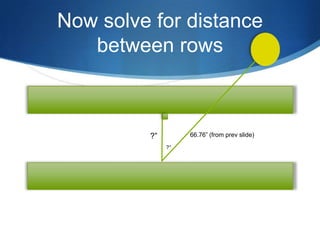
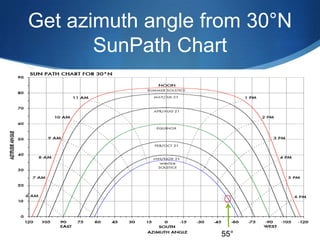
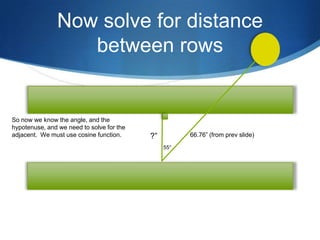
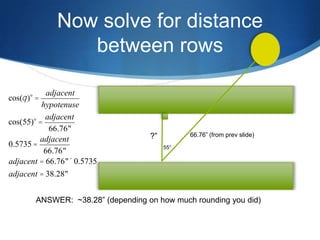
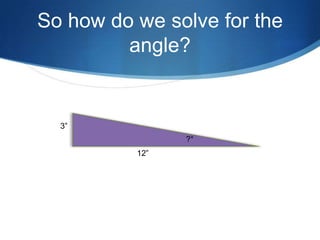
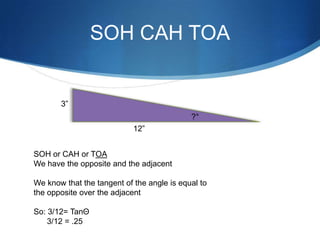
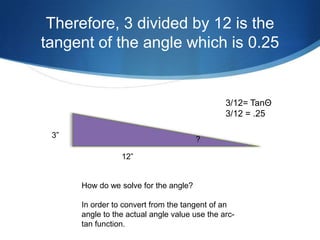
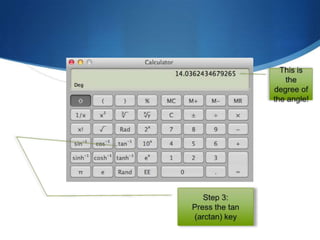
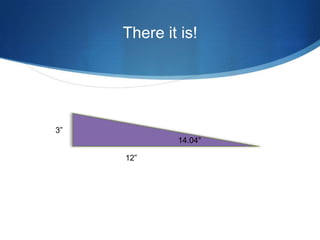
The document details advanced concepts for calculating inter-row shading in solar design, focusing on solar altitude and azimuth angles. It includes the use of trigonometric functions to determine the height and distance needed to avoid shading in solar panel installations. Additionally, practical examples illustrate how to apply these calculations for specific conditions, such as latitude and time of year.