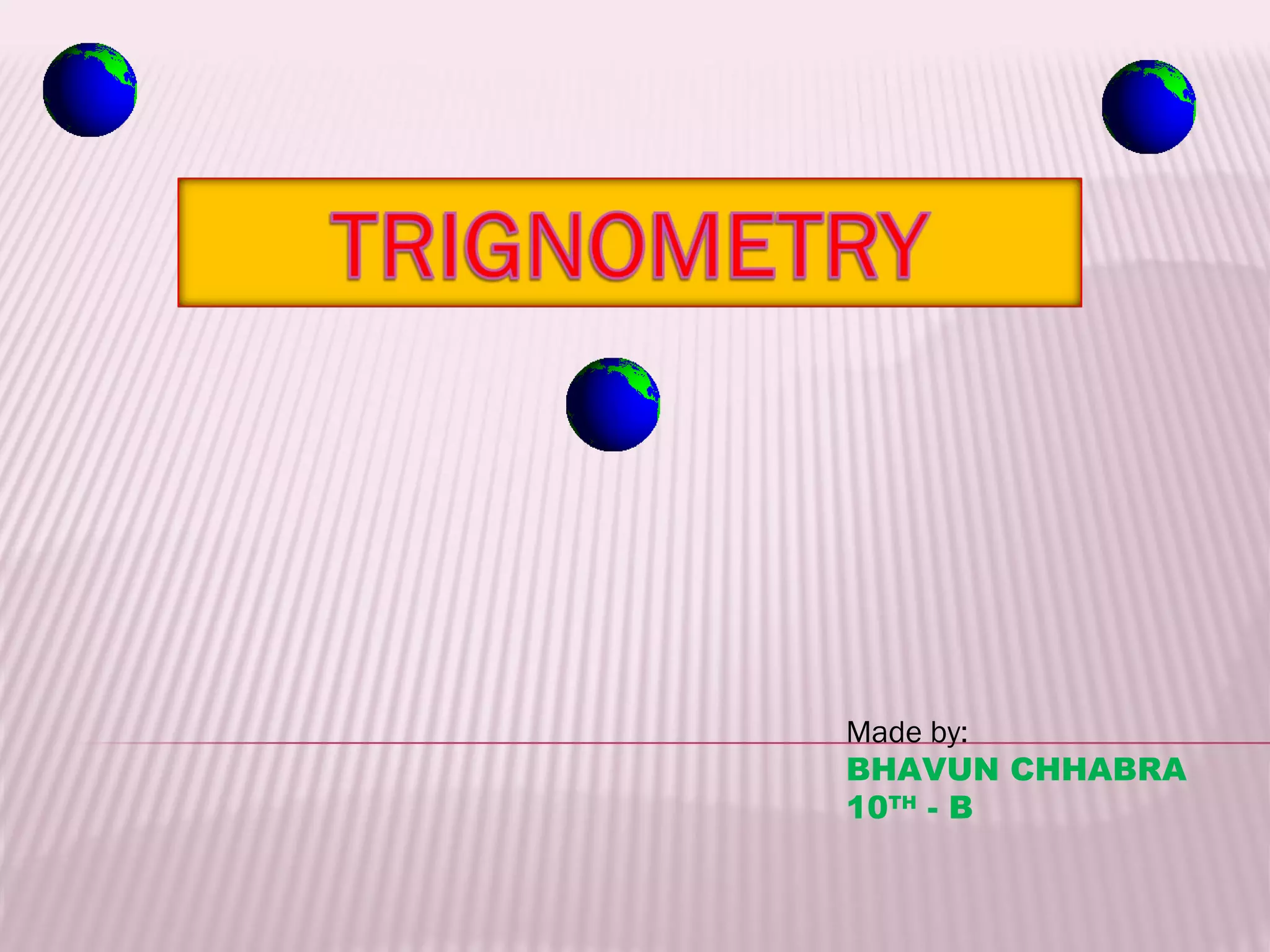
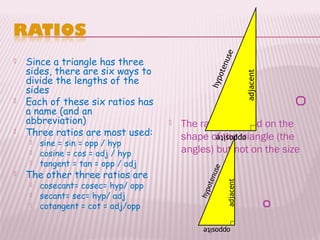
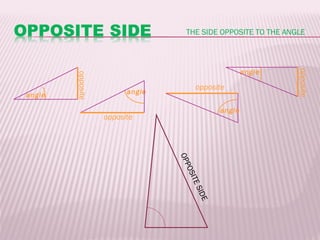
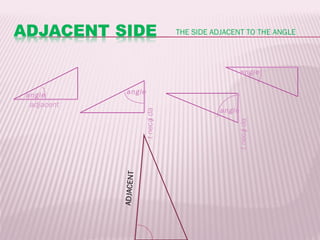
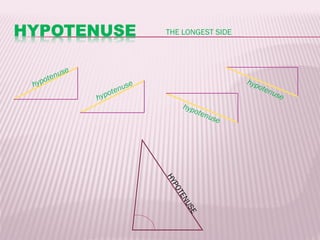
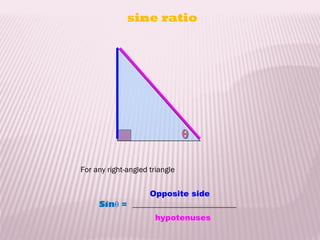
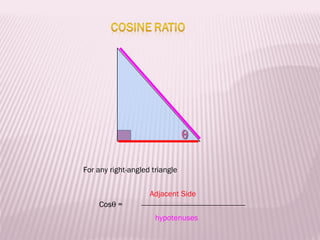
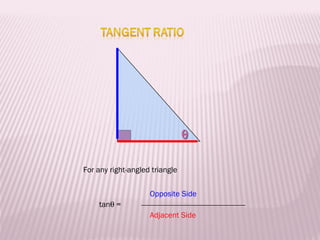
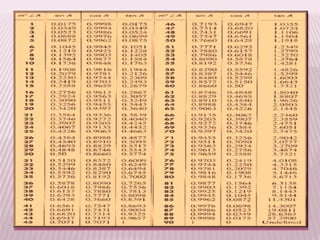
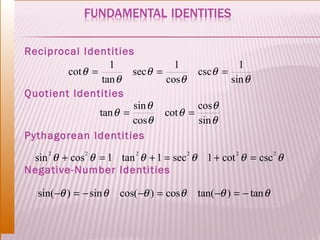
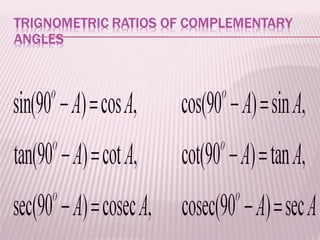
This document discusses trigonometric ratios and identities. It defines the three main trigonometric ratios - sine, cosine, and tangent - as ratios of the lengths of sides of a right triangle. It also introduces six trigonometric functions defined as reciprocals or quotients of the main ratios. The document provides examples of using trigonometric identities to verify relationships between functions through algebraic manipulation.