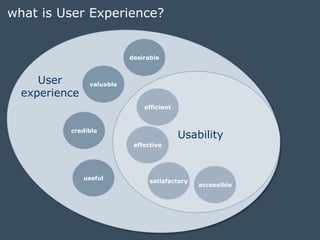
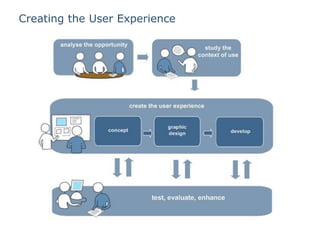
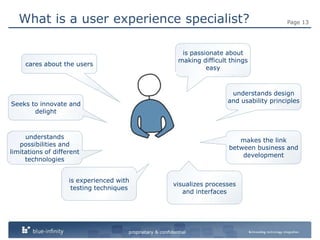
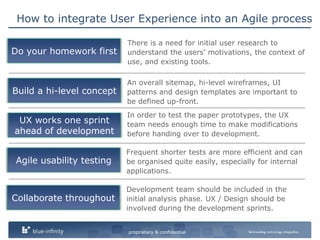
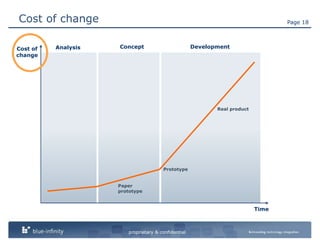
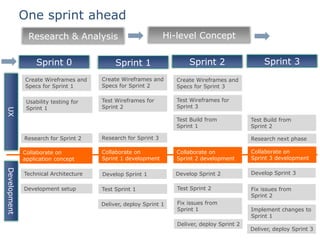
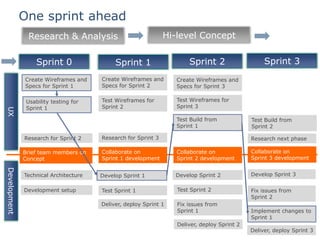
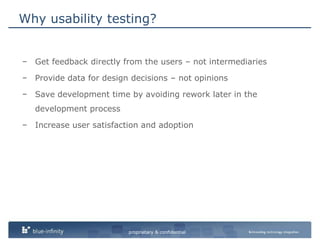
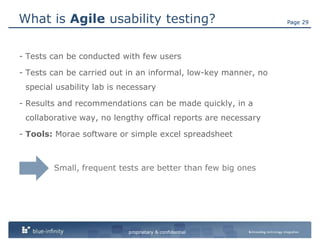
The document discusses integrating user experience (UX) design into an agile development process. It recommends doing initial user research, creating a high-level concept upfront with sitemaps, wireframes and templates. The UX team should work one sprint ahead of development to test prototypes and pass designs to developers. Frequent short usability tests are more efficient than long tests. Development and UX teams should collaborate throughout with UX involved in analysis and development sprints. Challenges include resource availability, working on multiple sprints, and client demands and involvement.