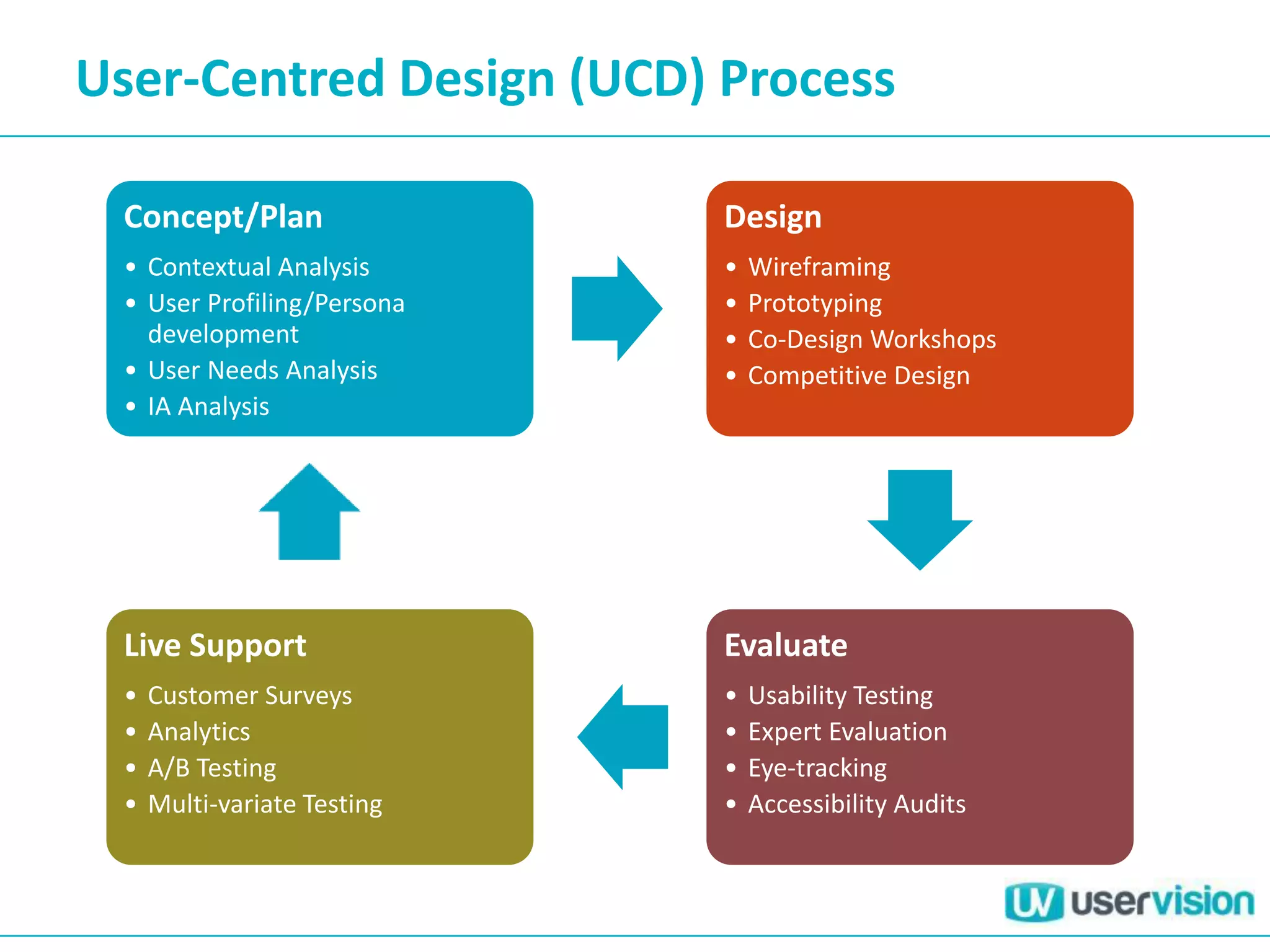
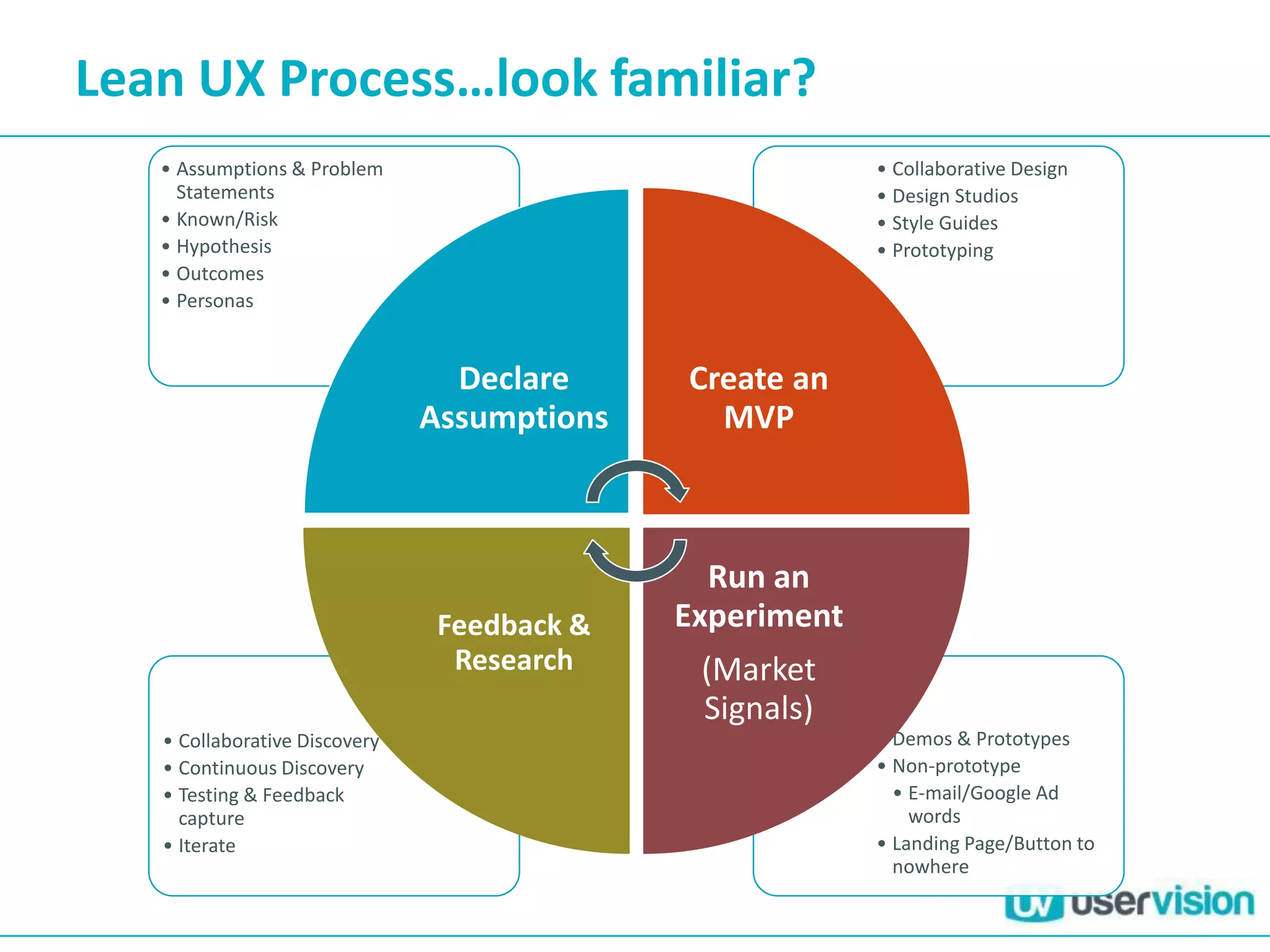
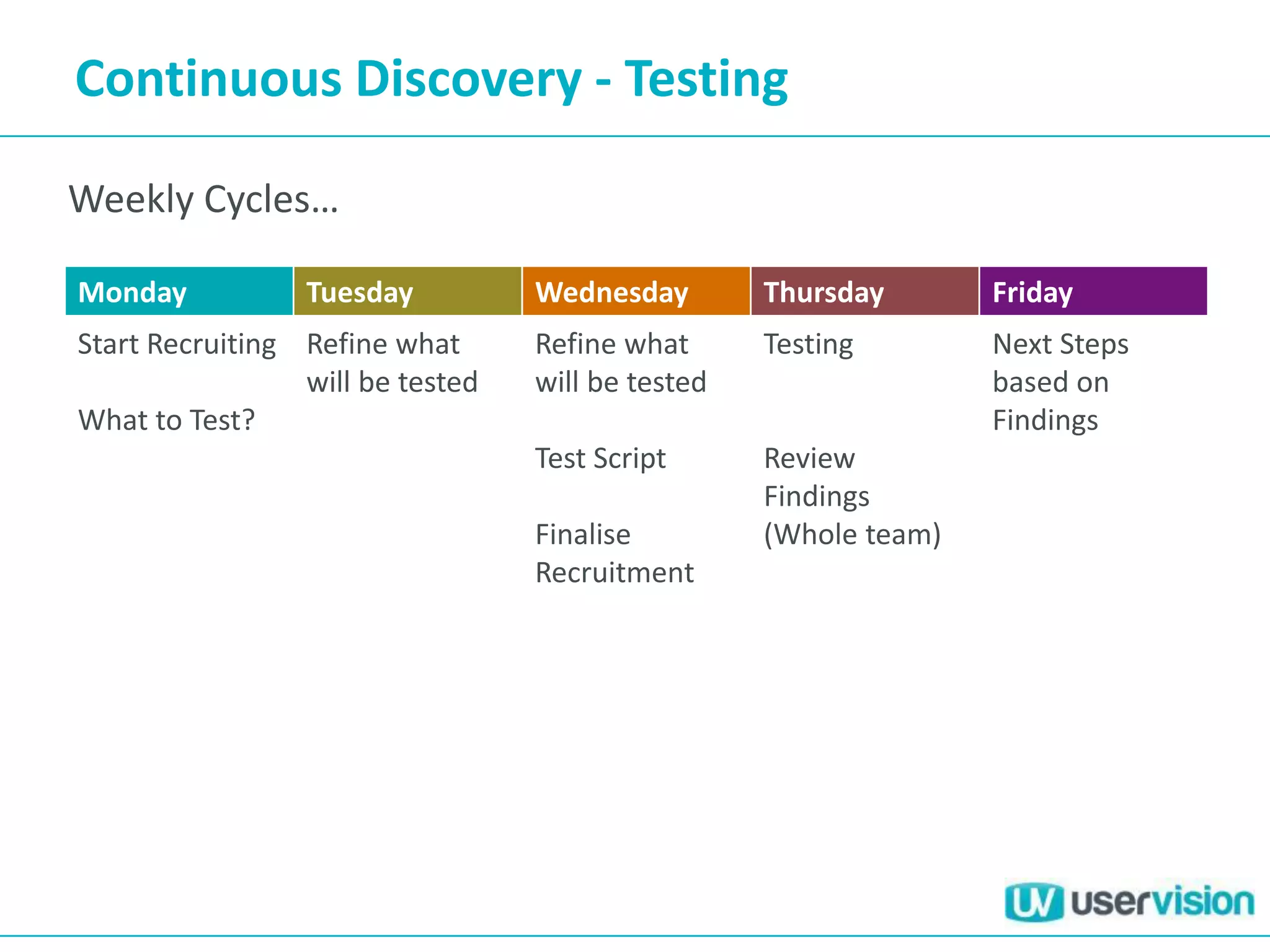
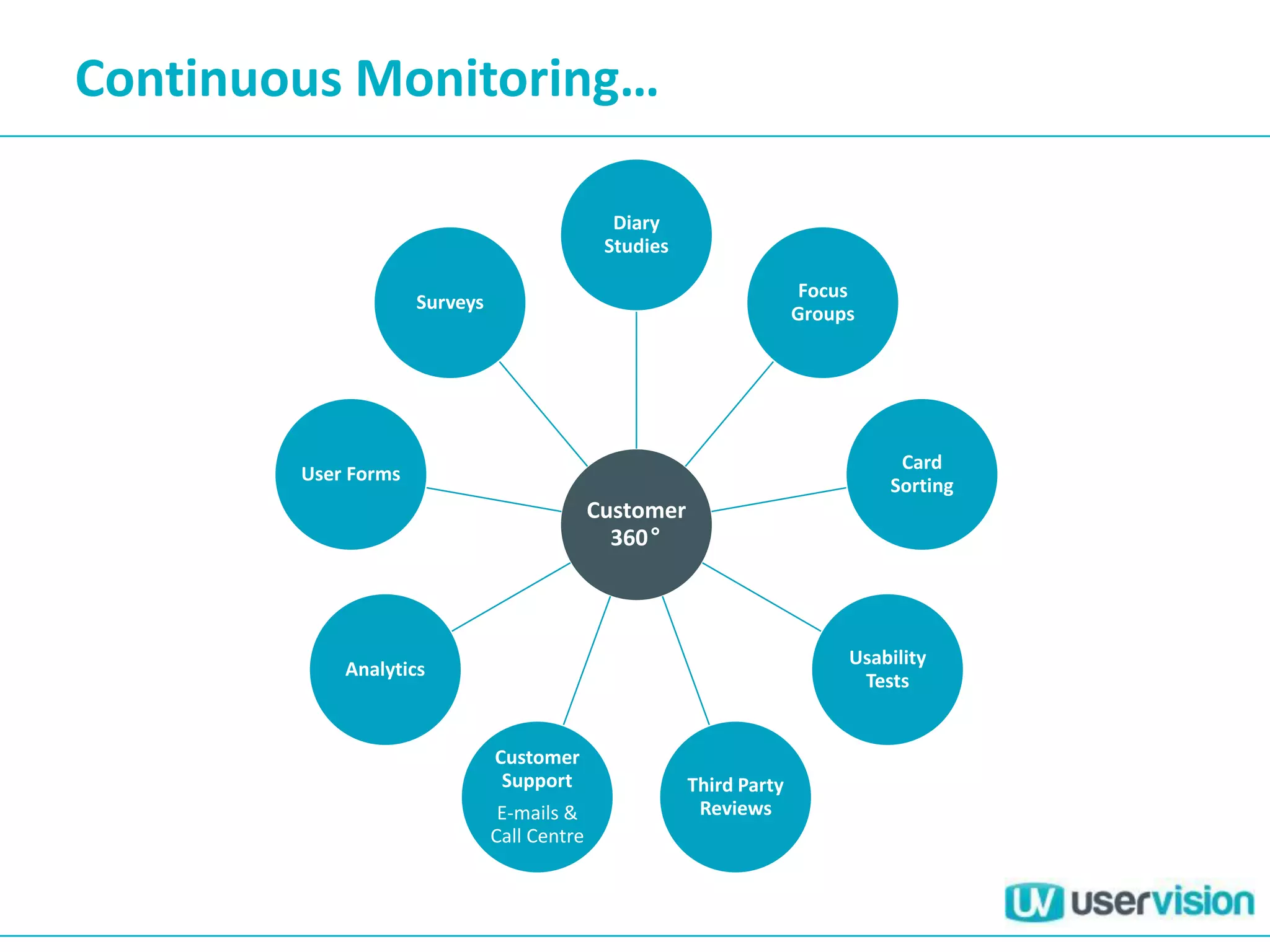
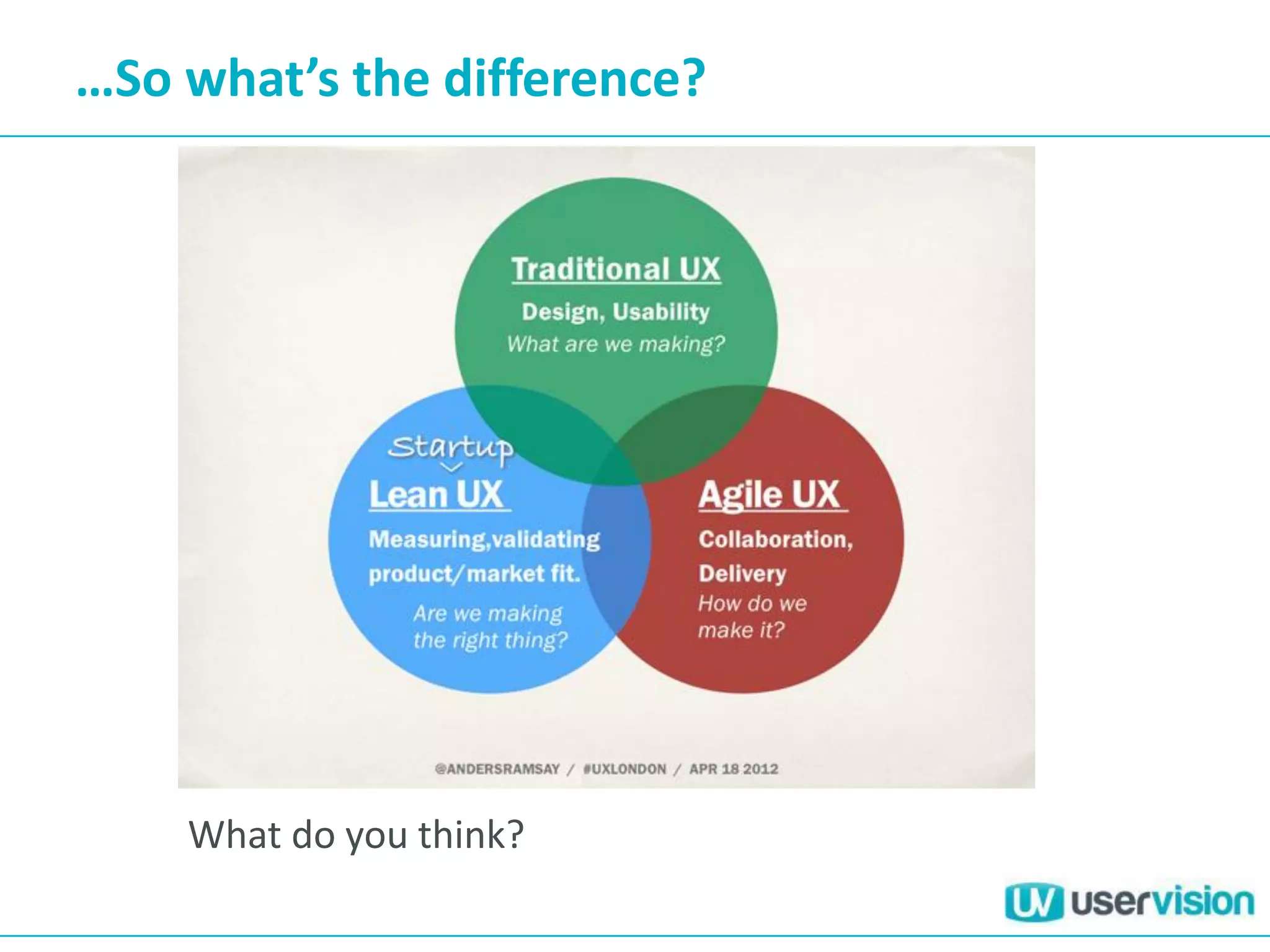
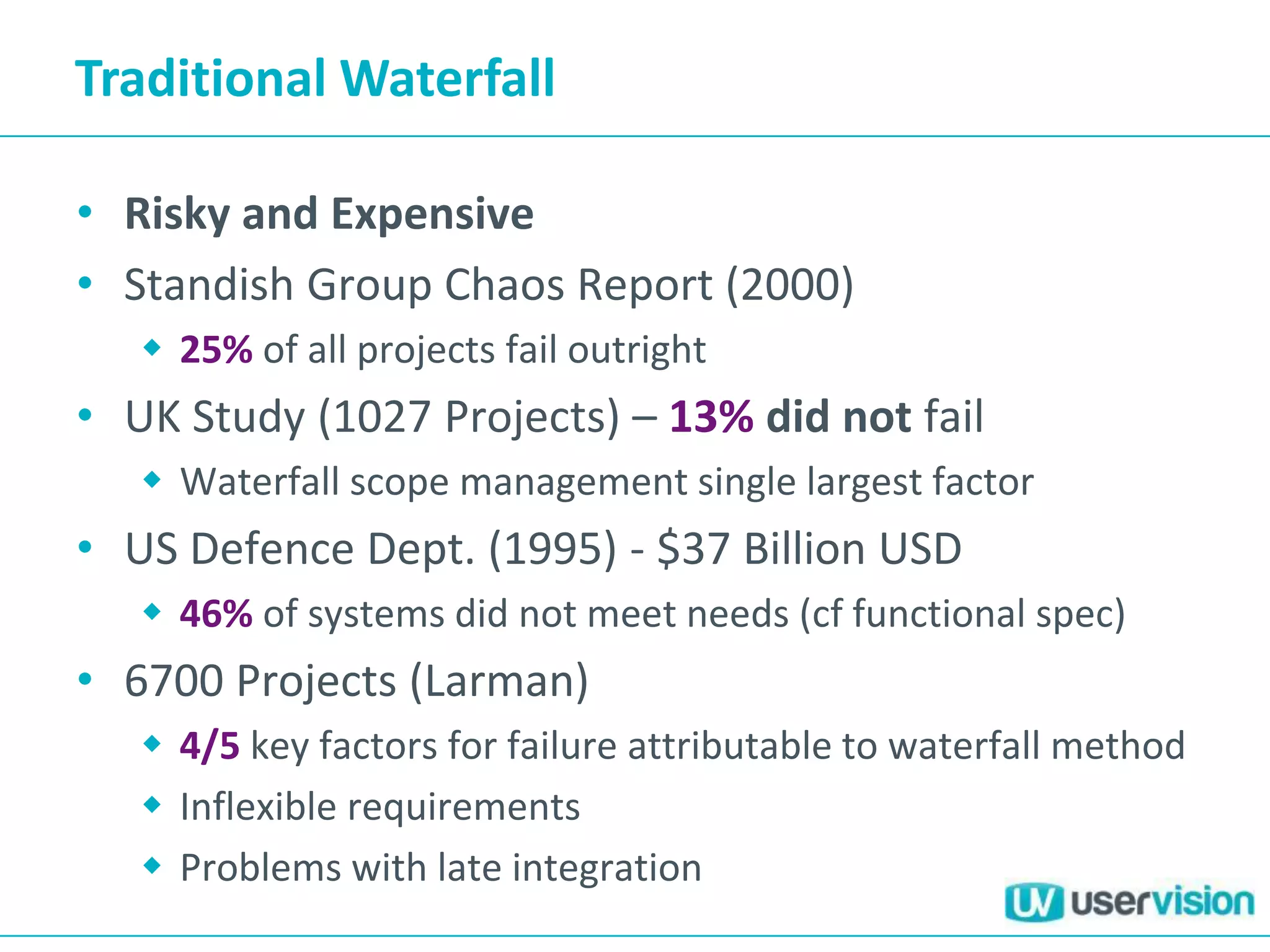
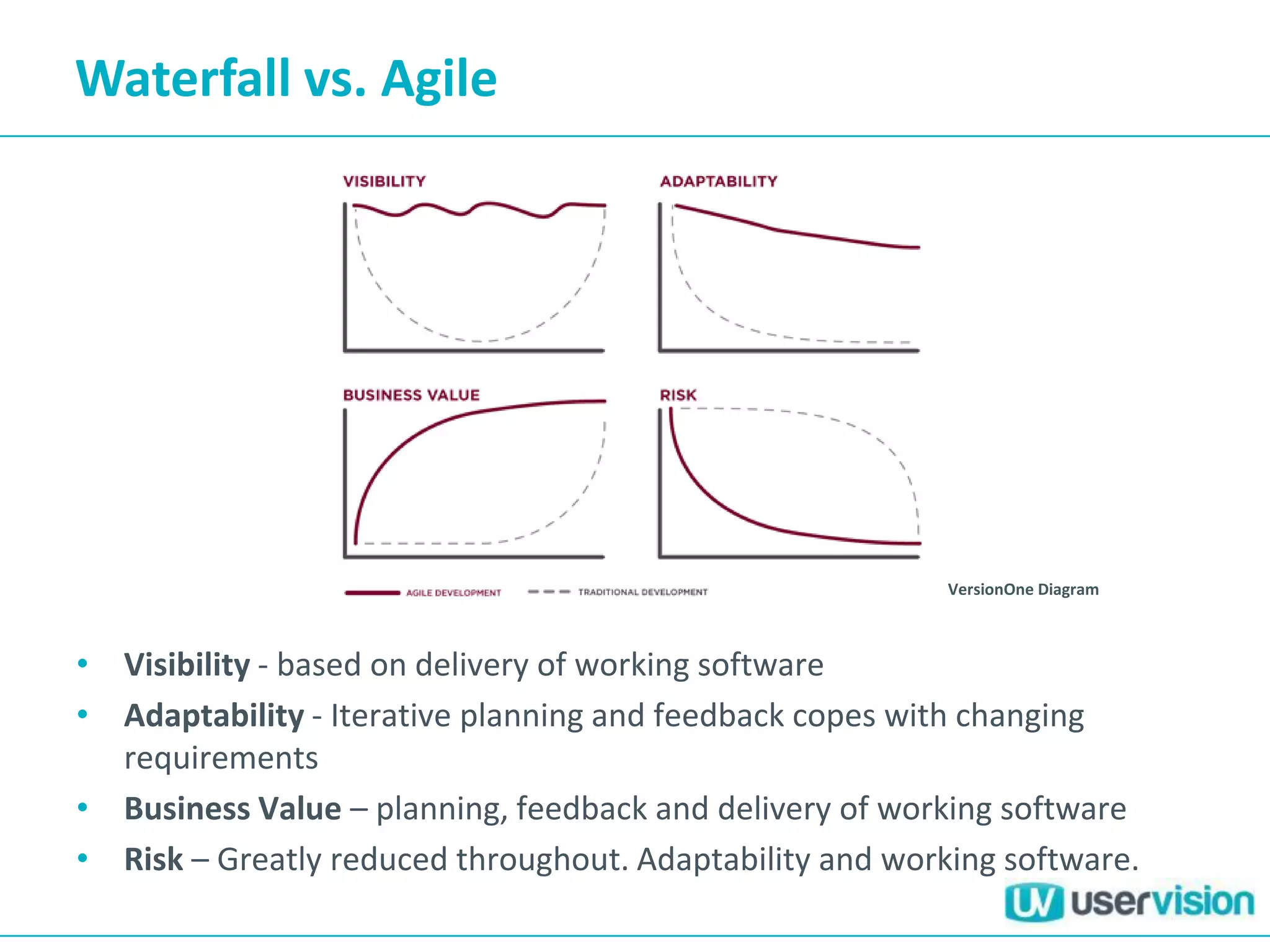
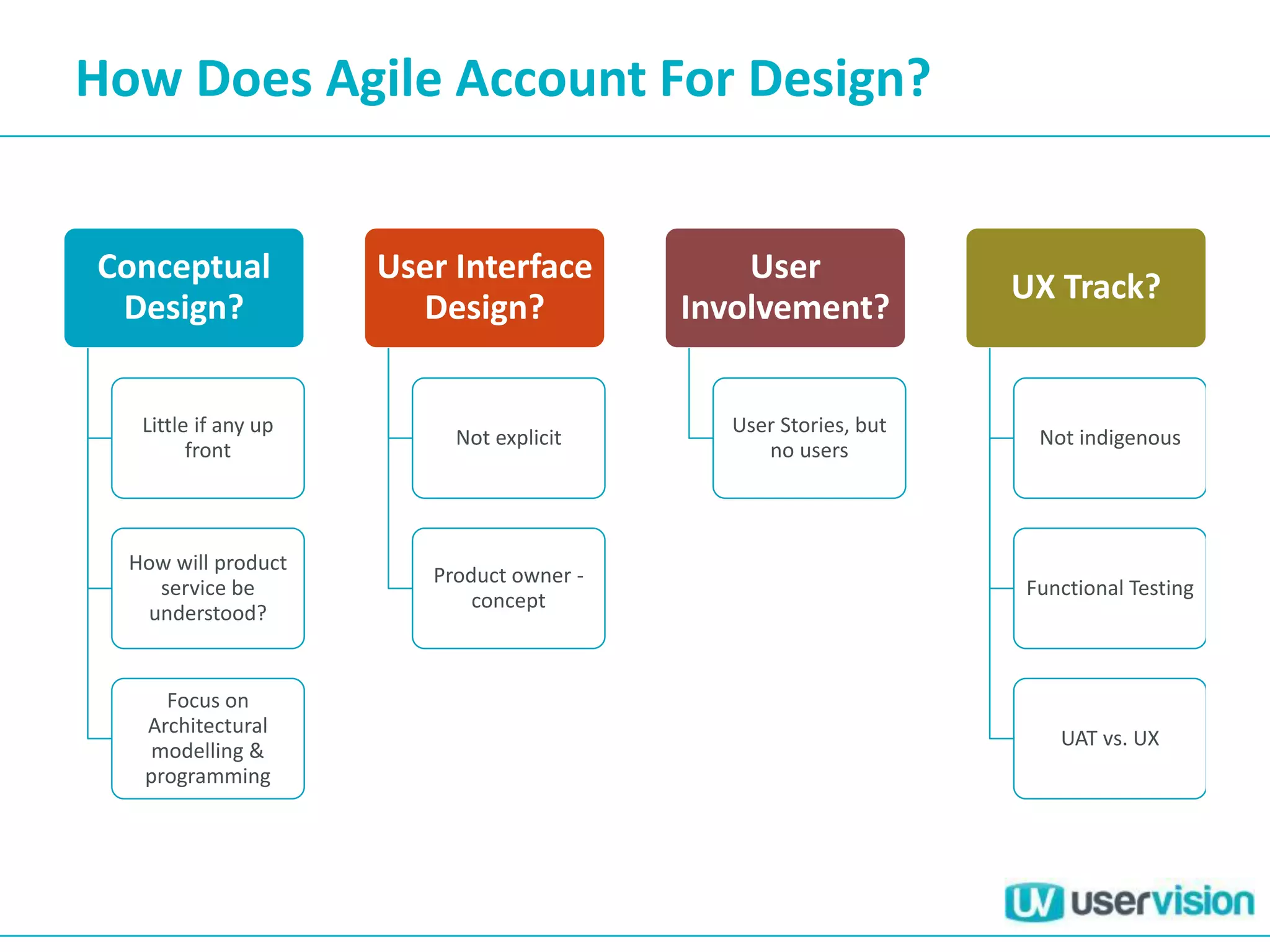
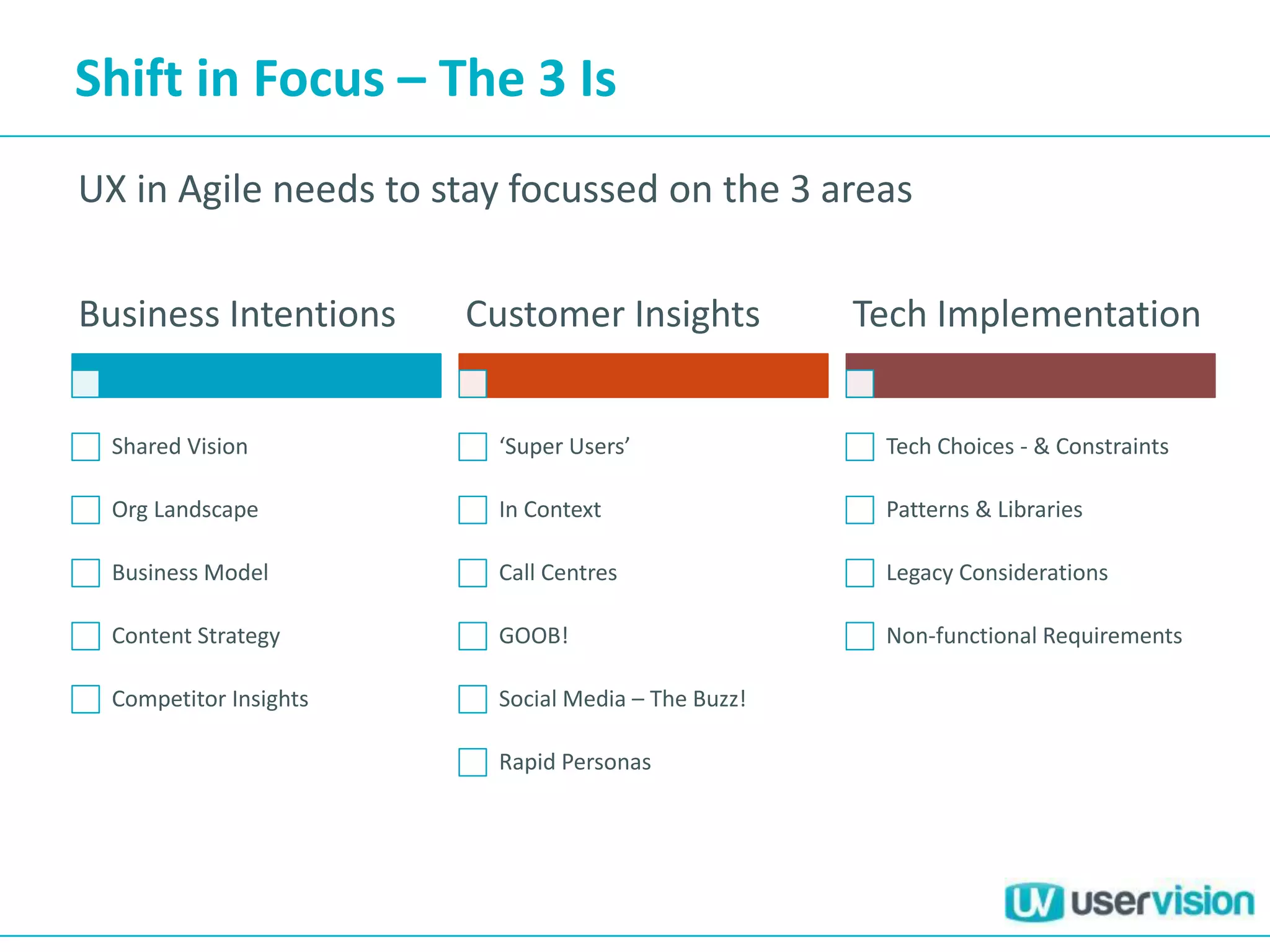
This document discusses adapting UX practices for agile development. It begins by explaining the limitations of traditional waterfall development and benefits of agile. It then outlines challenges UX faces in agile, like lack of big upfront design. Methods discussed for agile UX include lean UX principles, rapid prototyping and testing, collaborative design, and representing users through personas and story mapping. The document emphasizes adapting UX to be integrated, iterative and focus on delivering working software over documentation.



![Agile manifesto [1]
• Individuals and Interactions over processes and
tools
Social and Collaborative – Goals & Motivation
Small Teams – Close Quarters
• Working software over comprehensive
documentation
Eliminates Waste
BUT – No big design up front](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agileuxbreakfastbriefingjun13-130627093954-phpapp02/75/Agile-UX-Breakfast-Briefing-Jun13-6-2048.jpg)
![Agile manifesto [2]
• Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Customer involved throughout
• Responding to change over following a plan
Adaptable
Identify and resolve issues ASAP
Lockheed Skunk Works and Extreme programming
(KANBAN/JIT) – Lean processes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agileuxbreakfastbriefingjun13-130627093954-phpapp02/75/Agile-UX-Breakfast-Briefing-Jun13-7-2048.jpg)
![The State of Agile (2012) – Highlights [1] n=4048
• More Companies practicing Agile
84%
• Practicing longer
36% 2-5 years (38% 1-2 years) practising Agile
• Being Applied on More Projects
76-100% projects – 37%
• Increasing number of teams and projects
2-5 teams (38%), 10+ teams (30%)
0-5 projects (59%), 10+ projects (30%)
• Methods - Scrum & Scrum variants (72%)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agileuxbreakfastbriefingjun13-130627093954-phpapp02/75/Agile-UX-Breakfast-Briefing-Jun13-8-2048.jpg)
![The State of Agile (2012) – Highlights [2] n=4048
• Failure
• Issues at organisational level
• Barriers to further adoption](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agileuxbreakfastbriefingjun13-130627093954-phpapp02/75/Agile-UX-Breakfast-Briefing-Jun13-9-2048.jpg)
![The State of Agile (2012) – Highlights [3] n=4048
• Concerns
• Reasons to adopt
• Benefits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agileuxbreakfastbriefingjun13-130627093954-phpapp02/75/Agile-UX-Breakfast-Briefing-Jun13-10-2048.jpg)

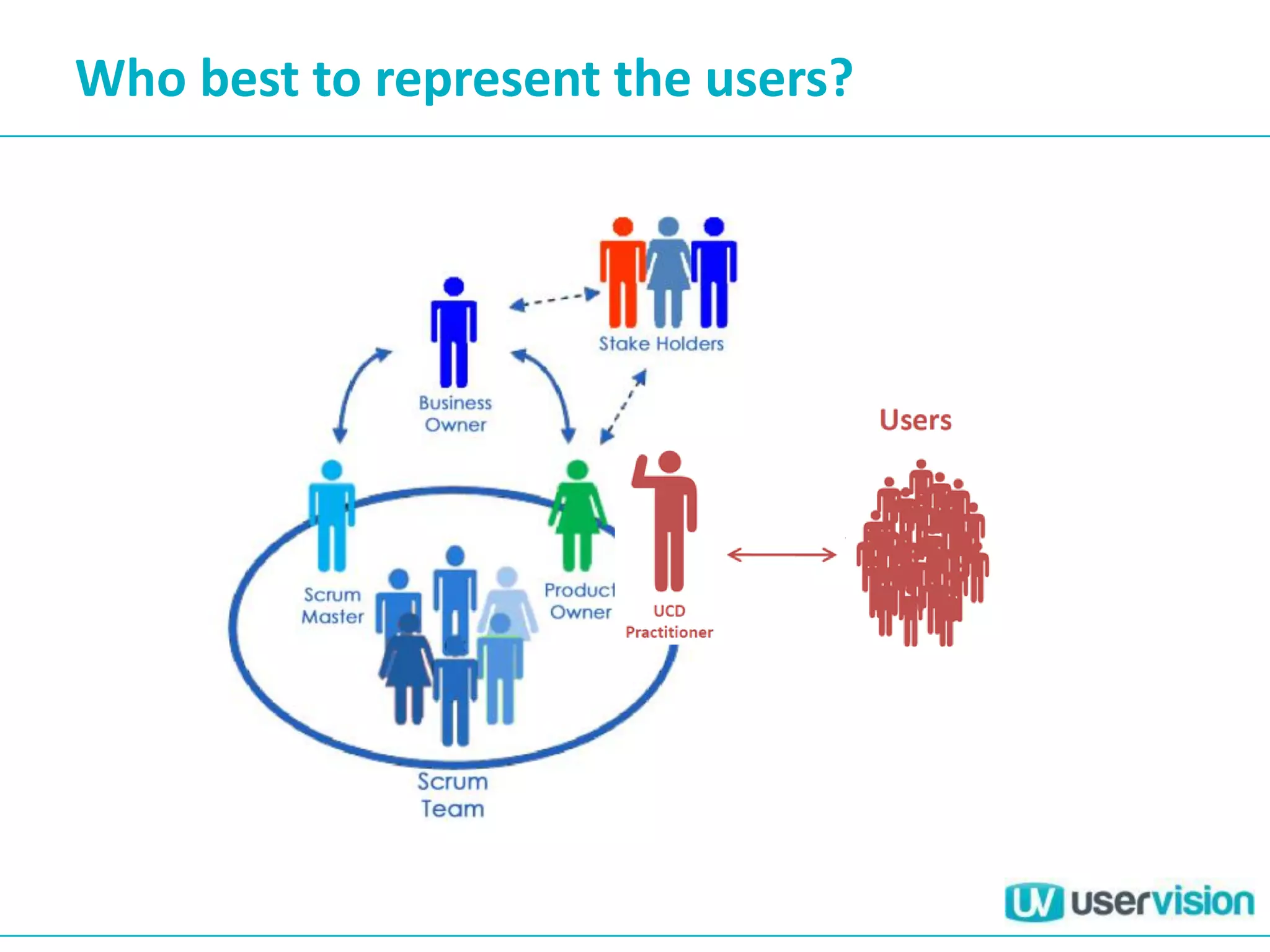














![Lean UX Principles [1]
• Cross-functional teams – High level of collaboration
• Small Dedicated Collocated – Communication, Focus and Cameraderie
• Progress = Outcomes not output…
• Problem-focused teams (c.f. features)
• Remove waste – If it doesn’t lead to the ultimate goal, remove from the
process
• Small batch size – create only what is needed at any given time
• Continuous Discovery – Engagement with customer and feedback
throughout
What is customer doing
Why are they doing it
Research done by the entire team](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agileuxbreakfastbriefingjun13-130627093954-phpapp02/75/Agile-UX-Breakfast-Briefing-Jun13-35-2048.jpg)
![Lean UX Principles [2]
• GOOB!
• Shared understanding – over time… Documents not needed
• No Rockstars, Gurus or Ninjas…team-based collaboration rules
• Get the work out there - Out of heads and onto the wall - immersion
• Making over analysis – Value in creating an idea, then taking it to
customers
• Learning over Growth – Figure out what to build before scaling it
• Permission to fail – Need to experiment with ideas and most will fail.
Culture needs to encourage this. Experimentation breeds creativity.
Risk taking > Big Ideas. Frequent failures > Mastery of skills.
• Lose the deliverable – focus on design process achieving outcomes not
artifacts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agileuxbreakfastbriefingjun13-130627093954-phpapp02/75/Agile-UX-Breakfast-Briefing-Jun13-36-2048.jpg)