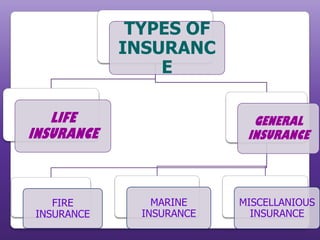
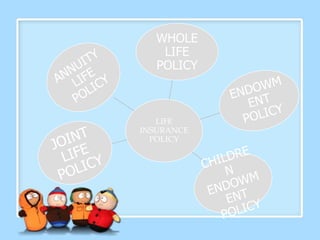
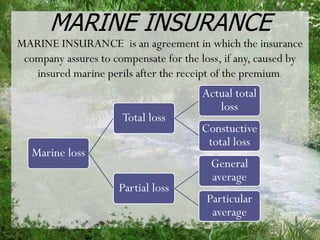
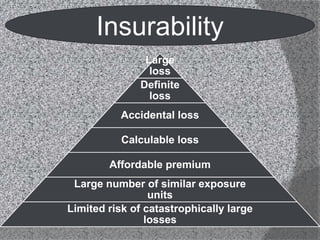
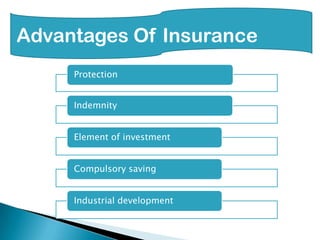
This document provides an overview of the insurance industry in India. It discusses key concepts like the insurer, insured, and policy. It outlines the history of insurance in India dating back to 1850 and the nationalization of insurance companies in 1956. It also describes the main types of insurance like life, fire, marine, and general insurance as well as principles of insurance such as insurable interest, indemnity, and mitigation. The advantages of insurance for protection, investment, and industrial development are highlighted.