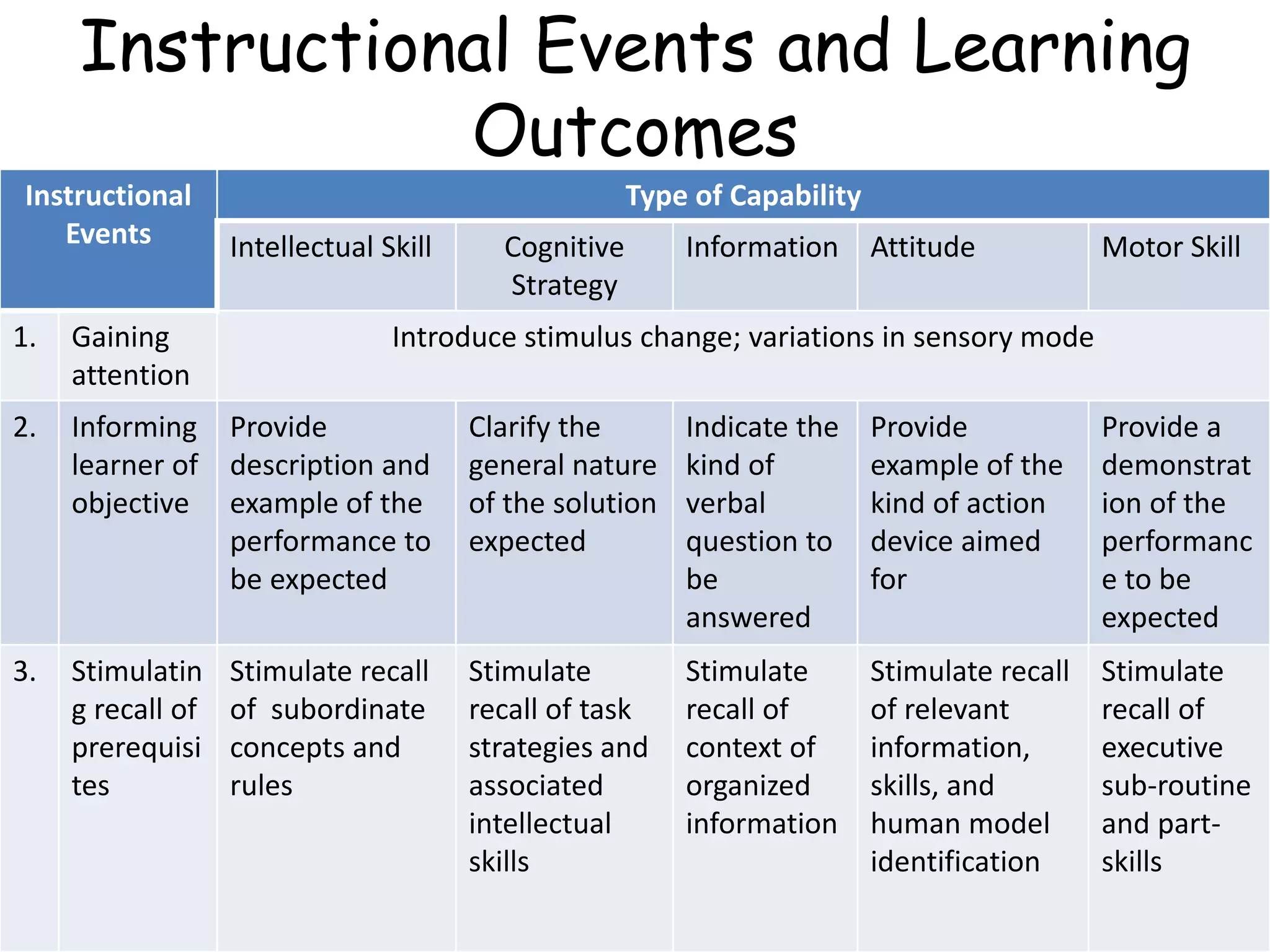
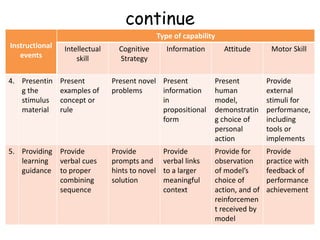
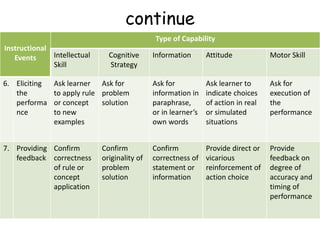
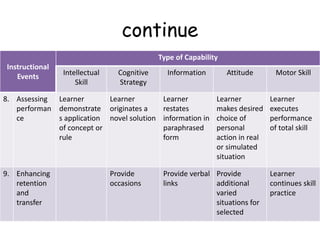
This document outlines 9 instructional events that can be used to develop different types of learning capabilities in students. It provides examples of each event, from gaining a student's attention to enhancing retention and transfer of knowledge. For example, in a first grade science lesson on measuring length, the teacher placed a large box in the classroom to gain attention, then had students use different length measuring sticks to measure the box and other objects. Throughout the lesson, the teacher elicited performance from students, provided feedback, and helped assess their understanding of linear measurement. The document contrasts this with how instructional events may be more controlled by materials or students themselves for older, more motivated learners.