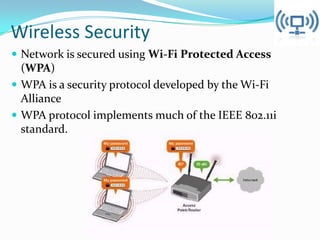
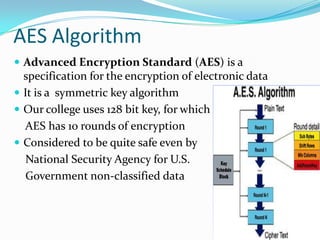
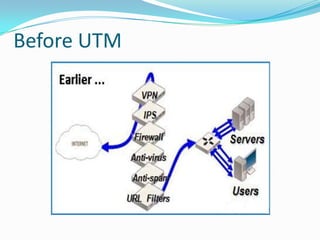
The document discusses the IT security architecture at IIM Rohtak, including wireless security, the AES encryption algorithm, the IIM Rohtak network configuration, unified threat management (UTM), firewalls, and Windows Active Directory services. The network uses WPA and AES encryption for wireless security. The college network has dual security with Wifi and firewall-based user logins, and can enable/disable users. UTM provides a single security solution for threats while Active Directory provides authentication, authorization, and backup of centralized user data.