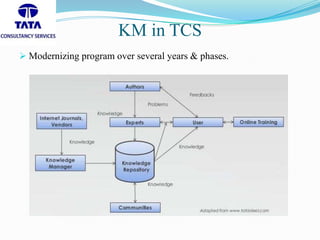
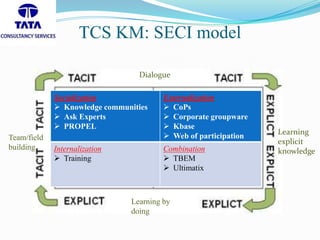
The document discusses knowledge management (KM) practices at Tata Consultancy Services (TCS). It notes that TCS was established in 1968 as a division of Tata Sons Ltd. and has since grown to operate in 46 countries with 199 branches. The document outlines TCS's use of the SECI model of knowledge management, which involves socialization, externalization, combination, and internalization. It also discusses some of TCS's key KM tools like communities of practice, corporate groupware, and knowledge bases. The document concludes that TCS uses a mixed approach of both codification and personalization strategies to balance capturing both explicit and tacit knowledge.