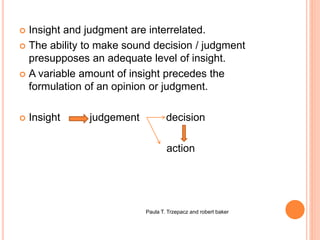
This document discusses insight and judgment in psychiatry. It defines insight as conscious awareness and understanding of one's own mental condition and symptoms, while judgment involves evaluating choices within a set of values to choose an action. Insight and judgment are interrelated, as good judgment requires adequate insight. The document describes factors that influence insight like culture, intelligence, and symptoms. It also discusses assessing levels of insight from complete denial to true emotional insight. Judgment is assessed through social situations and test questions. Various psychiatric disorders can impair insight and judgment.