Embed presentation
Downloaded 23 times


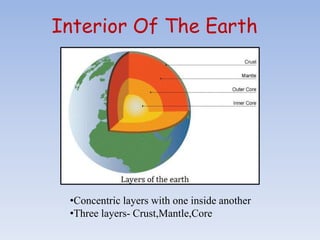


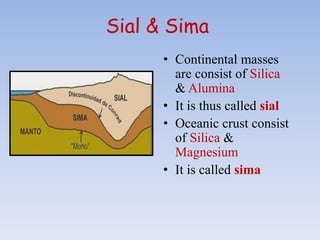




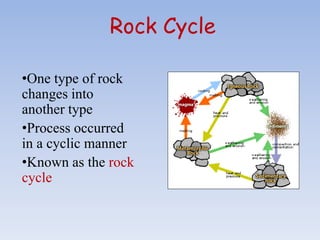

The Earth is made up of concentric layers, with the crust being the outermost layer. Below the crust lies the mantle, which extends almost 3000 km deep. The innermost layer is the core, with a radius of 3500 km. The crust varies in thickness depending on whether it is over continental masses or ocean floors. Continental crust consists of silica and alumina, called sial, while oceanic crust contains silica and magnesium, called sima. The Earth's crust contains various types of rocks that form through igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic processes and undergo continuous changes through the rock cycle.











