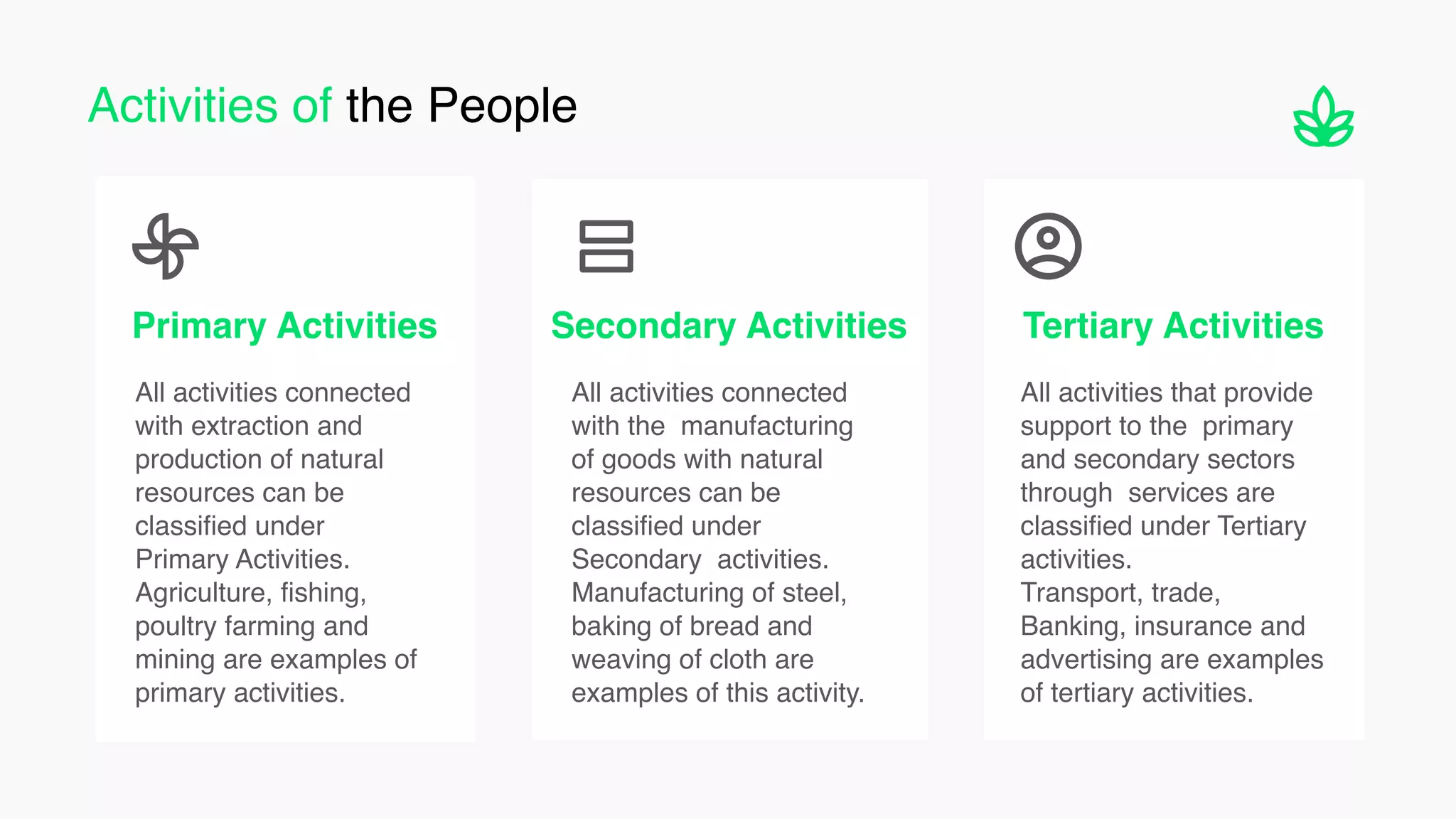
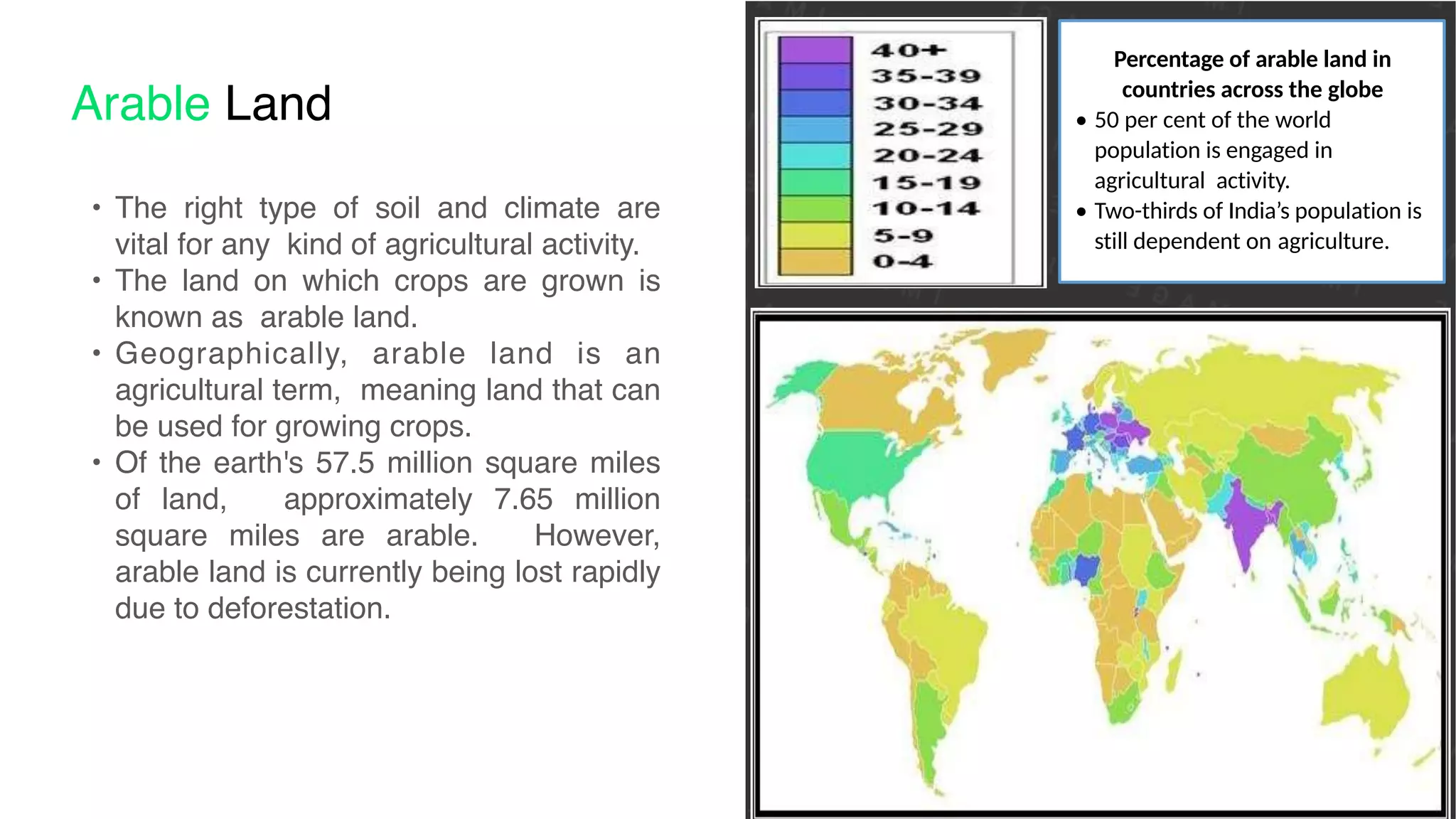
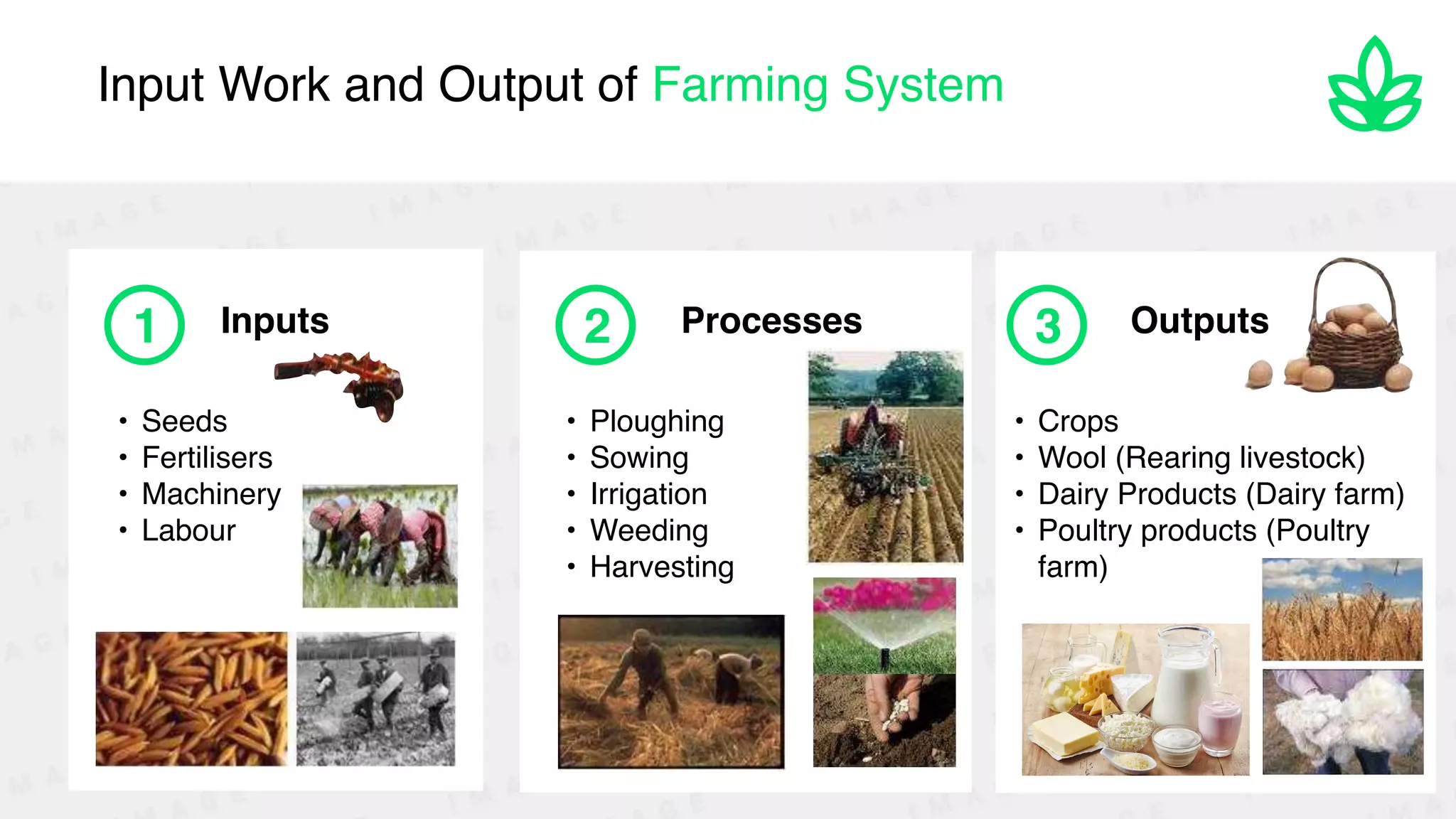
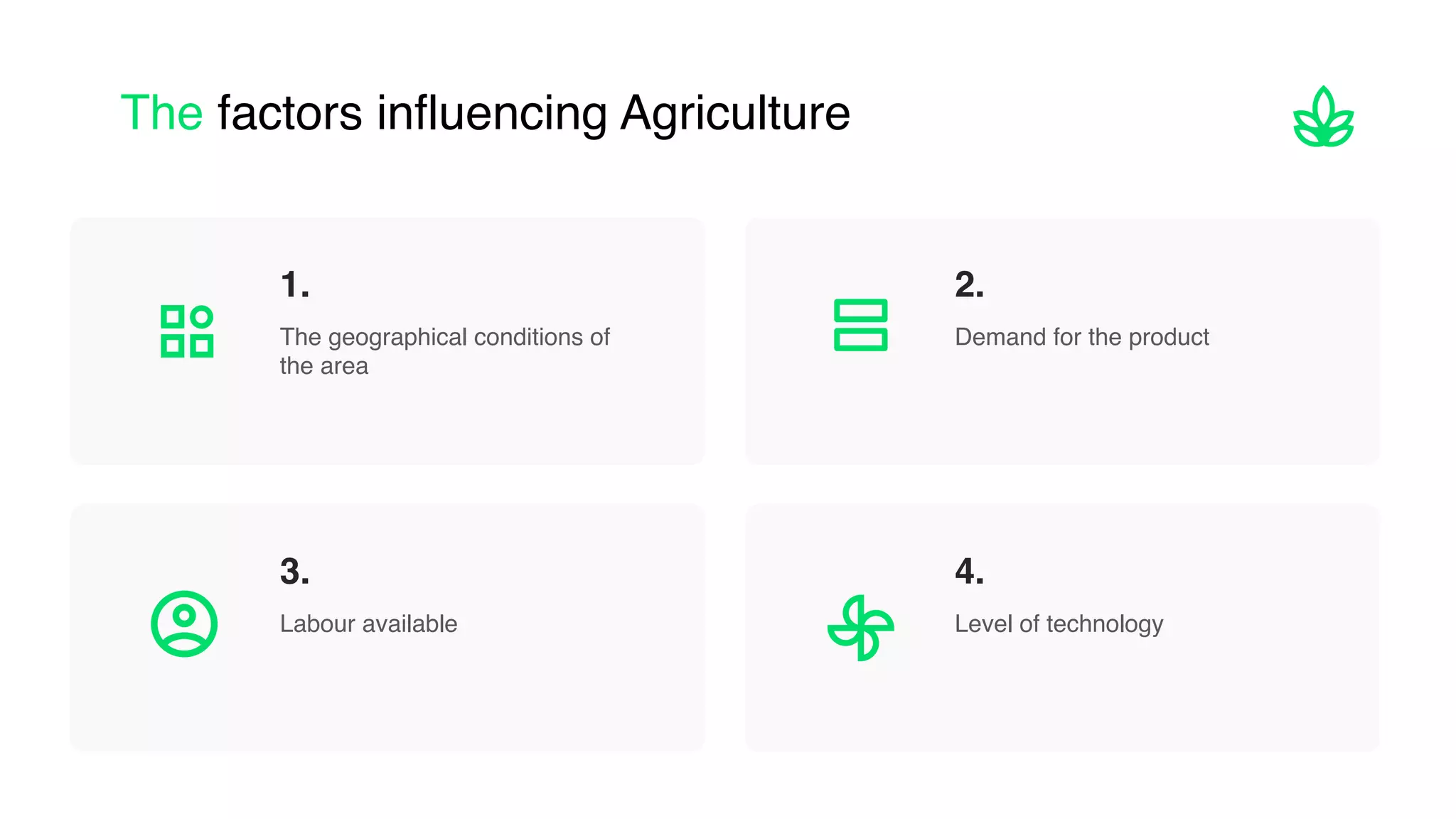
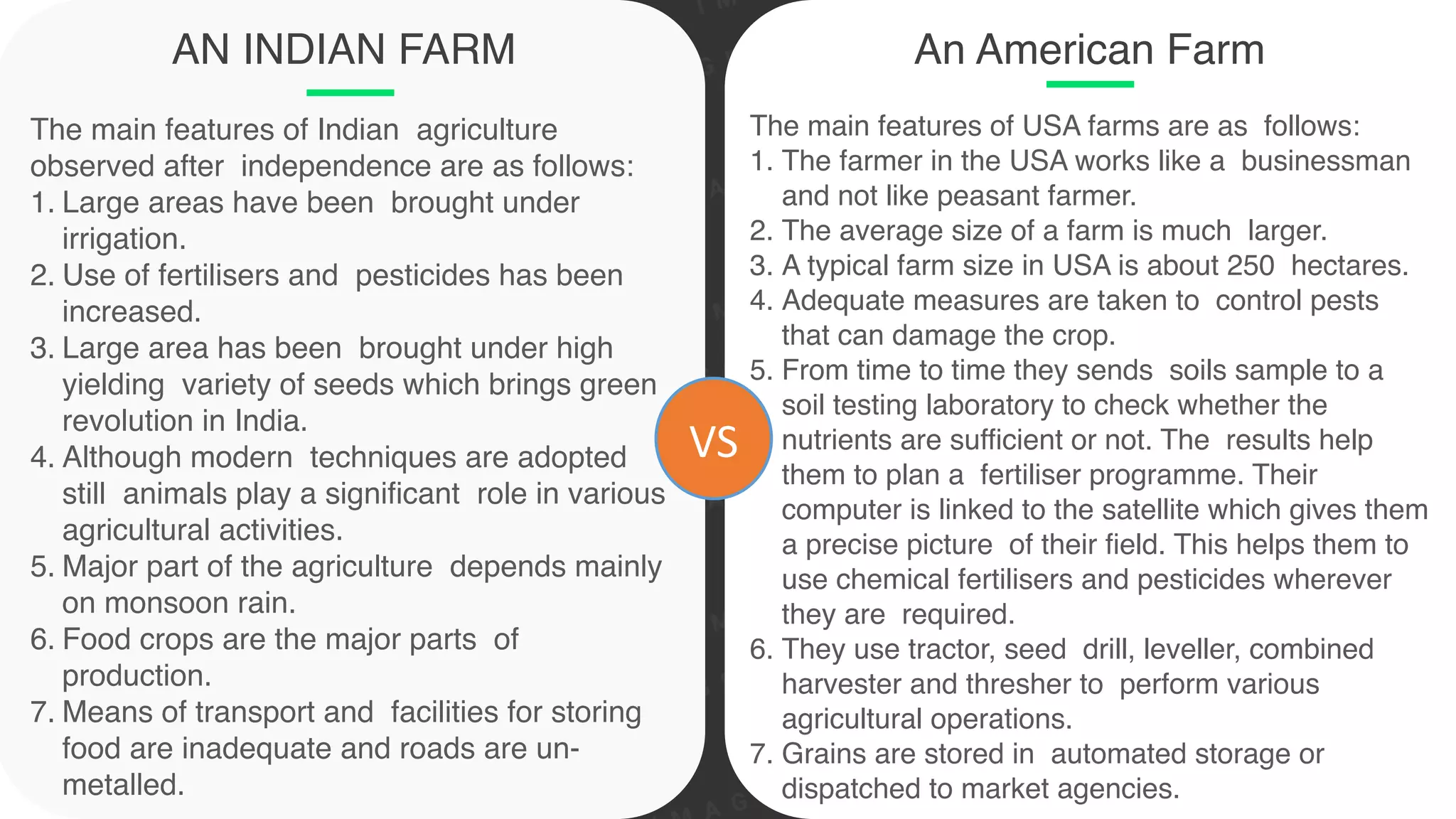
The document discusses the classification and significance of primary, secondary, and tertiary activities, with a primary focus on agriculture as a key economic activity. It outlines various types of farming, including subsistence and commercial farming, their characteristics, and the factors influencing agricultural practices globally. Additionally, it compares agricultural practices in India and the USA, highlighting technological advancements and production methods in both countries.