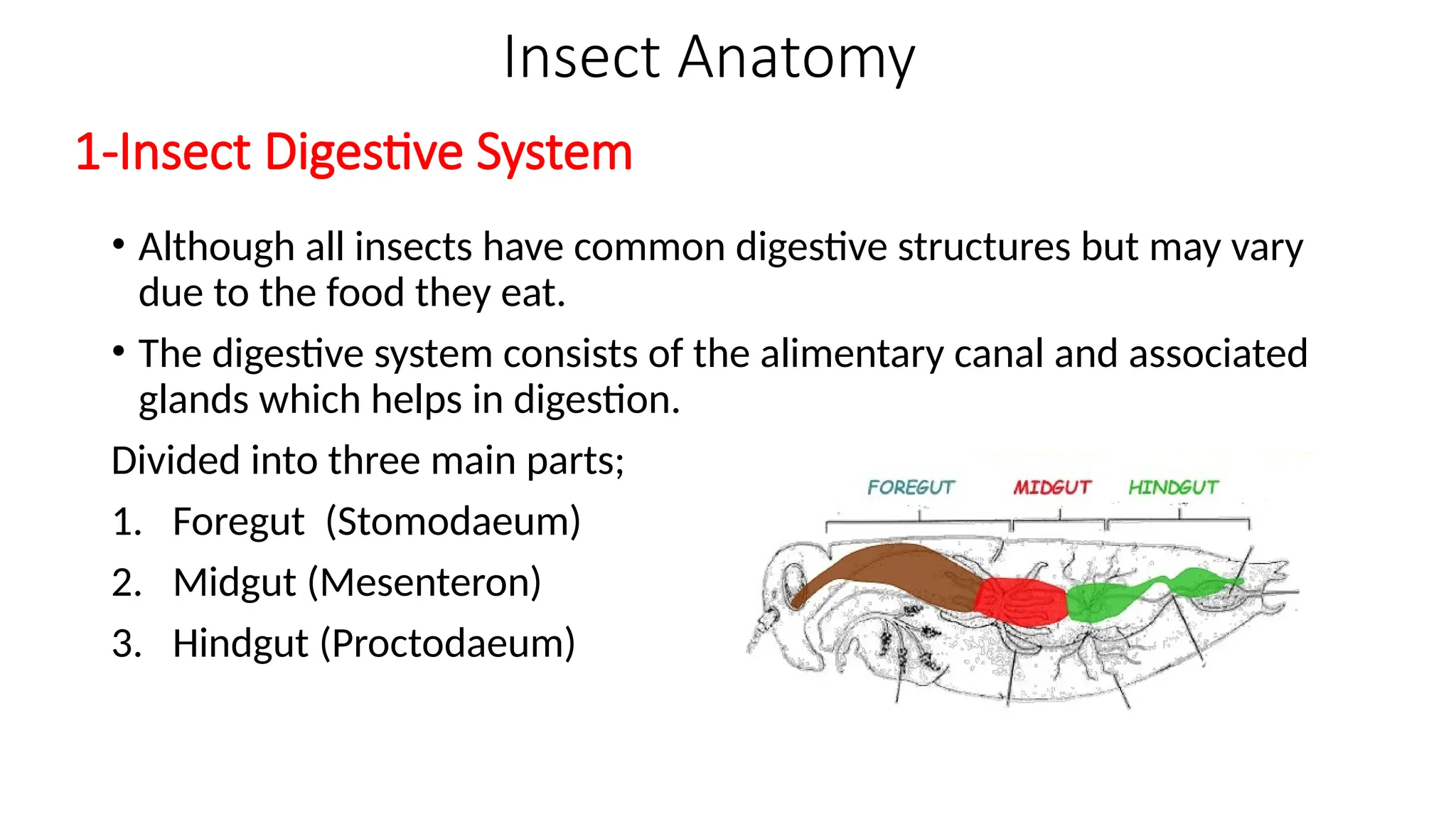
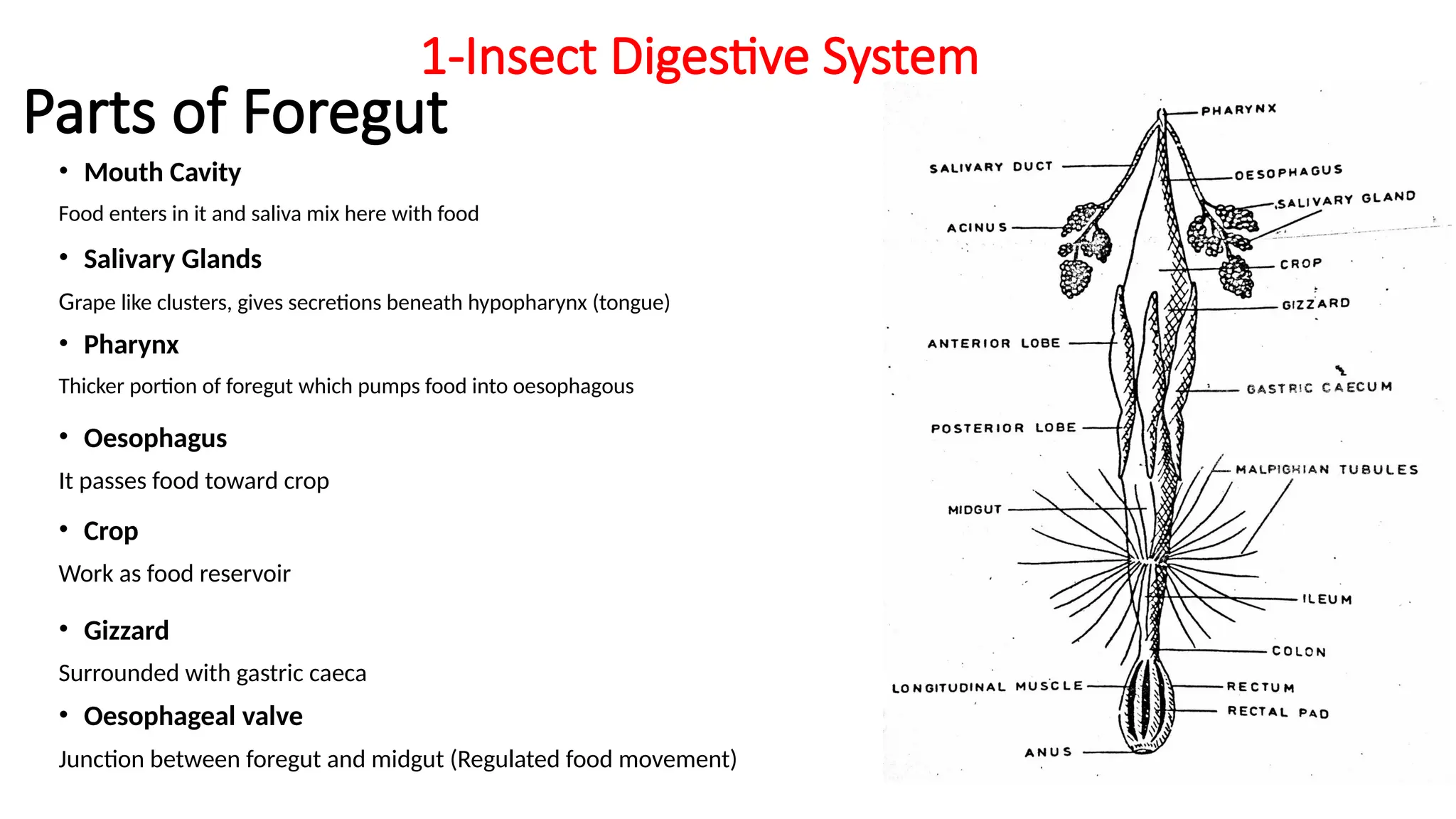
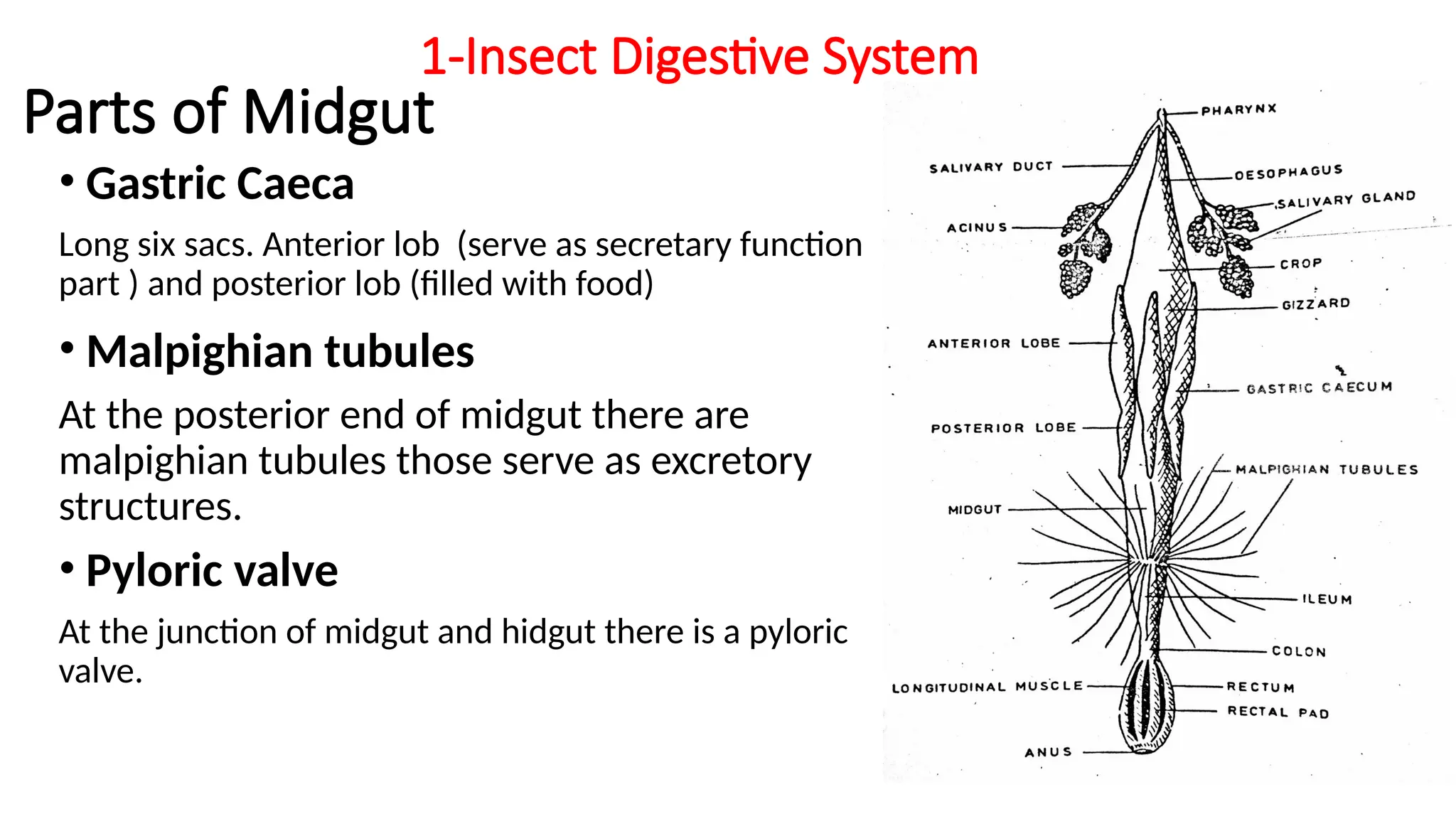
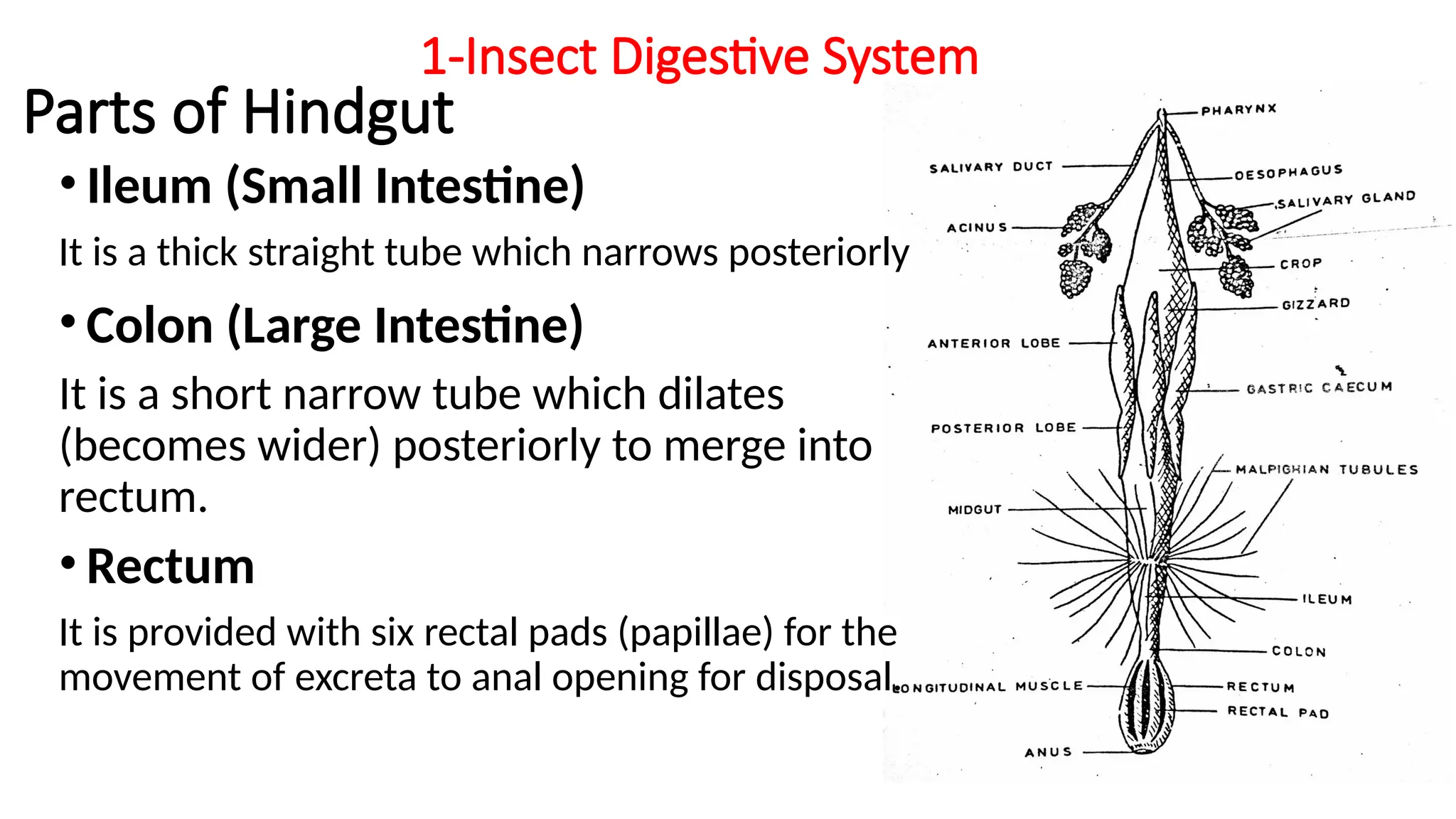
The document outlines the digestive and excretory systems of insects, emphasizing their common structures while noting variations based on food consumption. The digestive system is divided into three parts: foregut, midgut, and hindgut, each with specific roles in processing food. The excretory system primarily consists of malpighian tubules and fat-bodies, which manage waste and store nutrients, respectively.