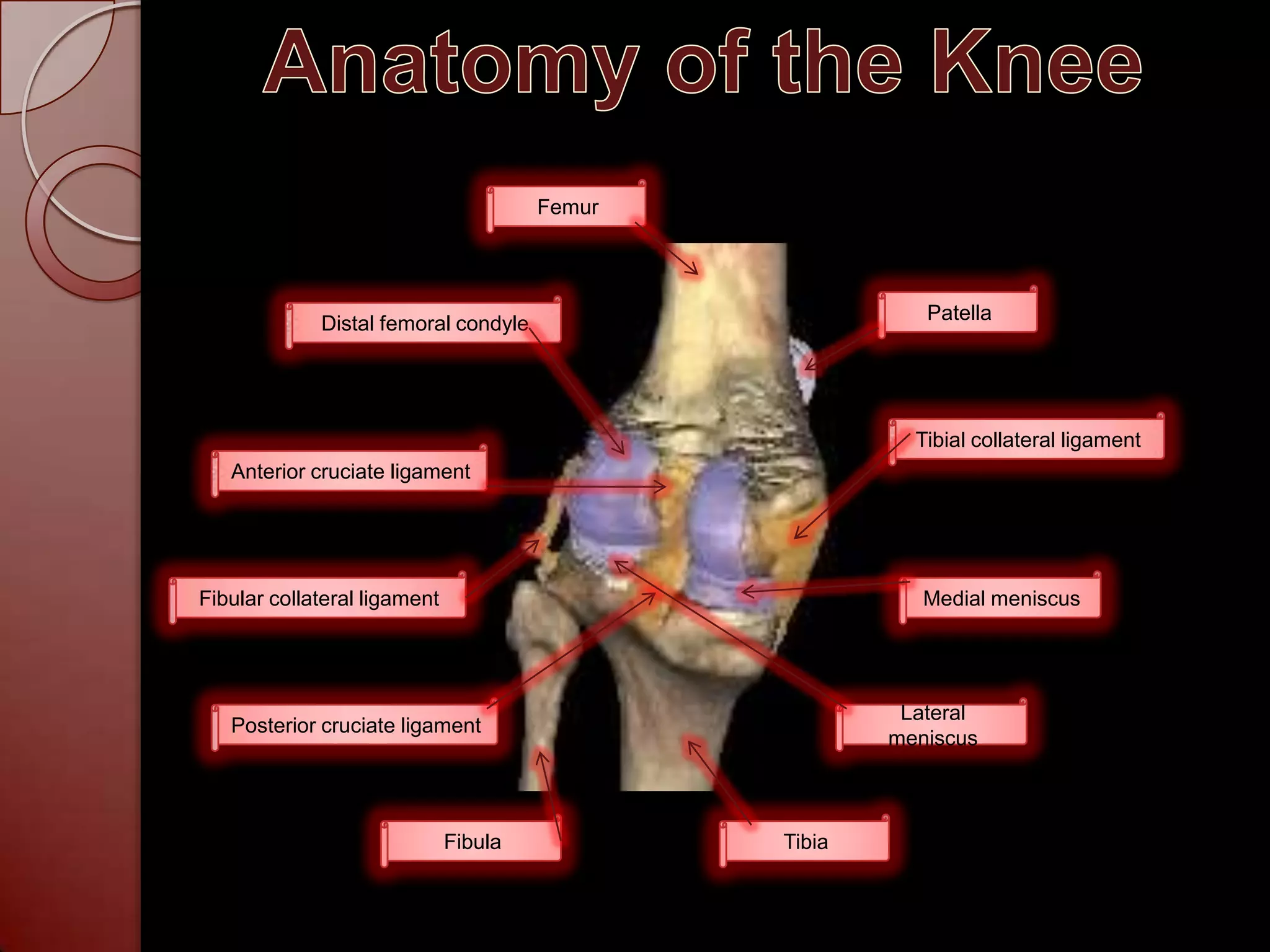
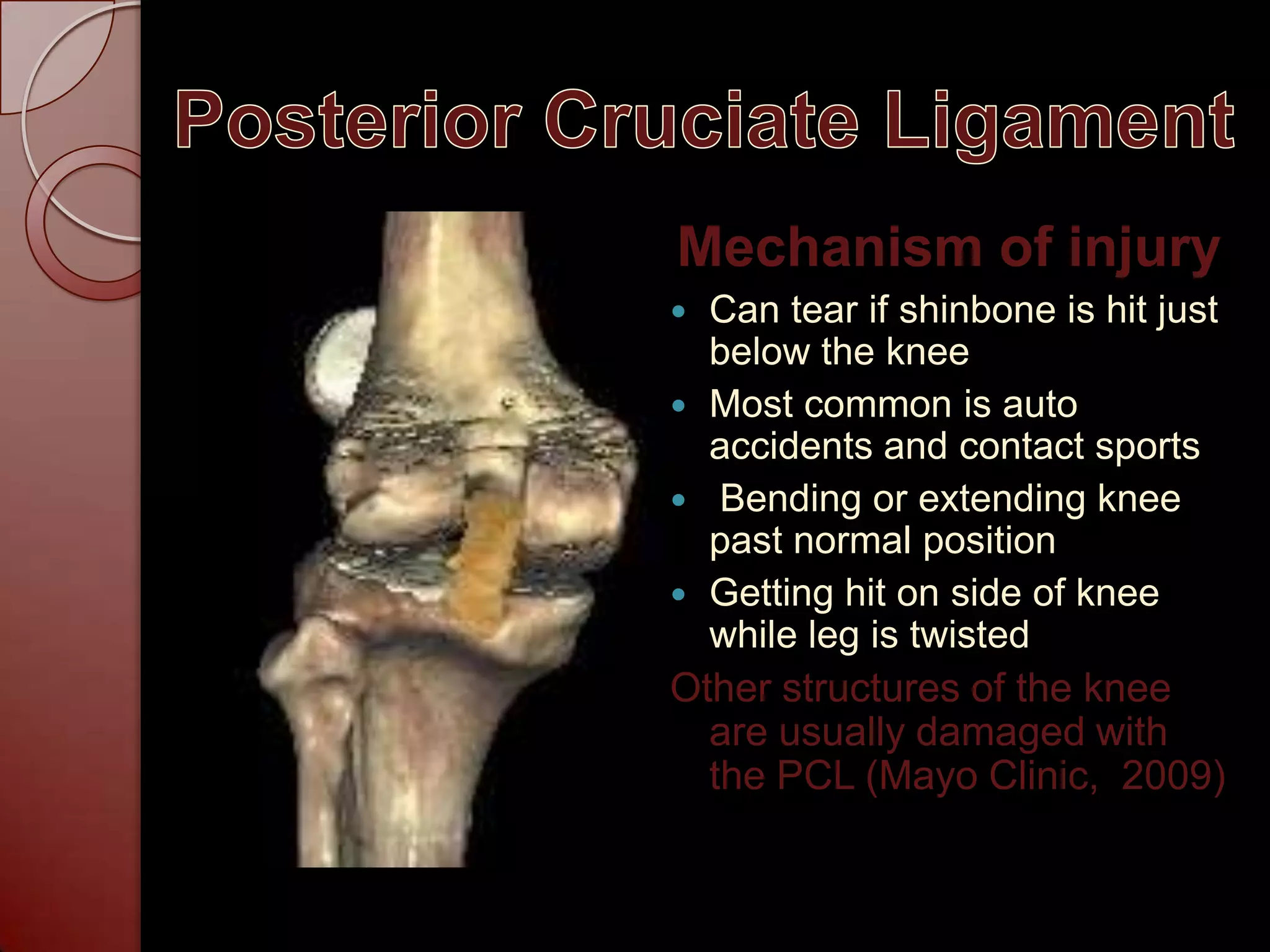
The document discusses injuries and treatments to the ACL, PCL, and MCL ligaments in the knee. It describes the anatomy of the knee and mechanisms of injury for each ligament, including being hit on the side of the knee or twisting motions. Treatment options are outlined depending on the severity of each ligament tear, ranging from RICE therapy for mild injuries to surgery and bracing for complete tears. The rehabilitation process after ACL surgery is also summarized, focusing on regaining strength and mobility over several months.