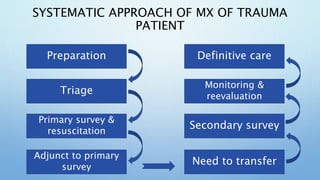
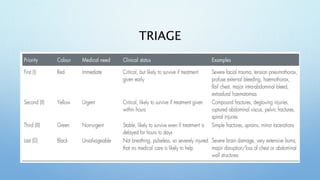
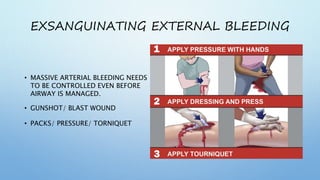
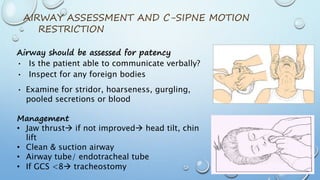
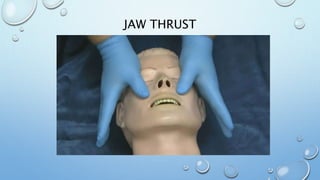
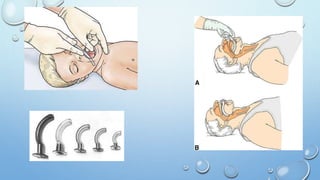
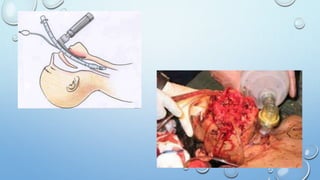
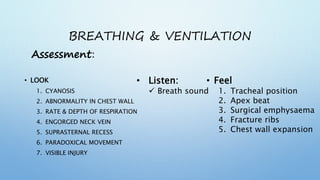
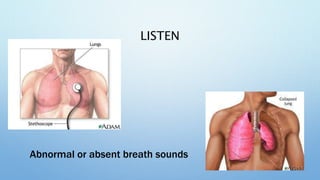
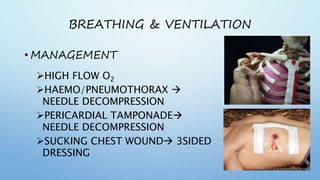
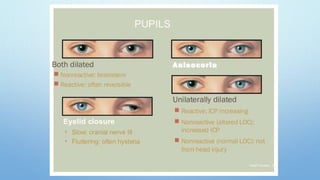
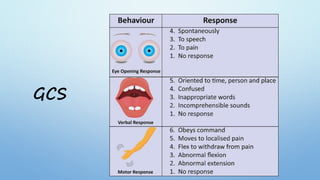
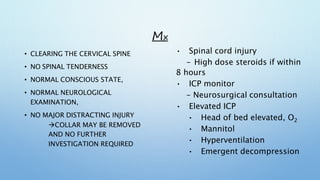
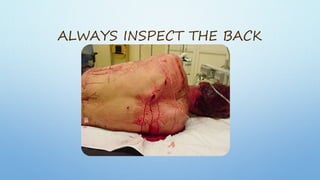
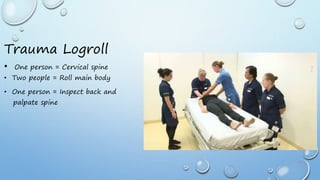
The document outlines the initial management of trauma patients according to ATLS protocols. It discusses the systematic approach including preparation, triage, primary and secondary surveys, monitoring and definitive care. The primary survey focuses on the ABCDE approach - controlling hemorrhage, establishing airway and breathing, assessing circulation, neurological status and conducting full body exposure. Adjunct tests and special considerations for different patient groups are also reviewed.