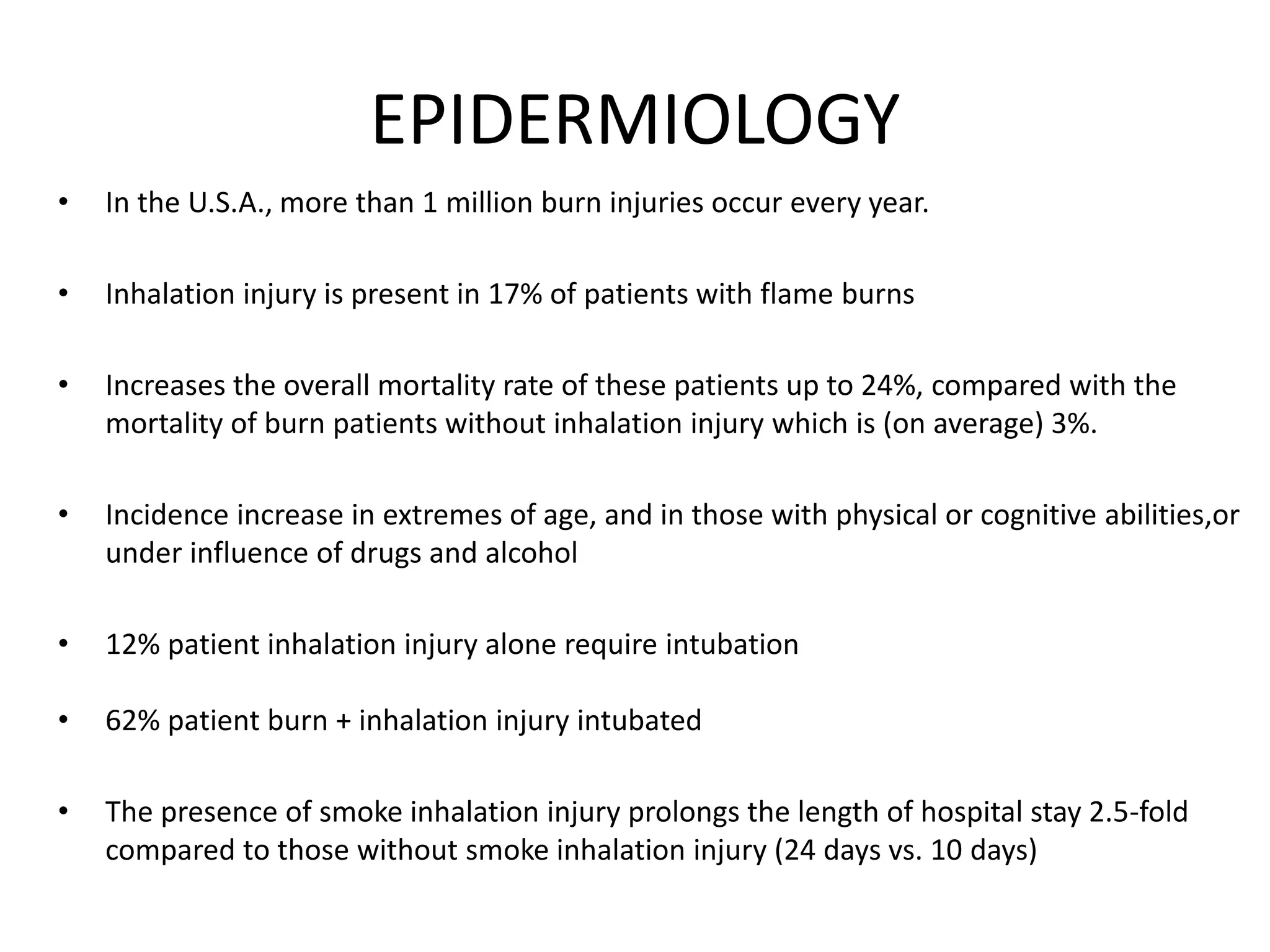
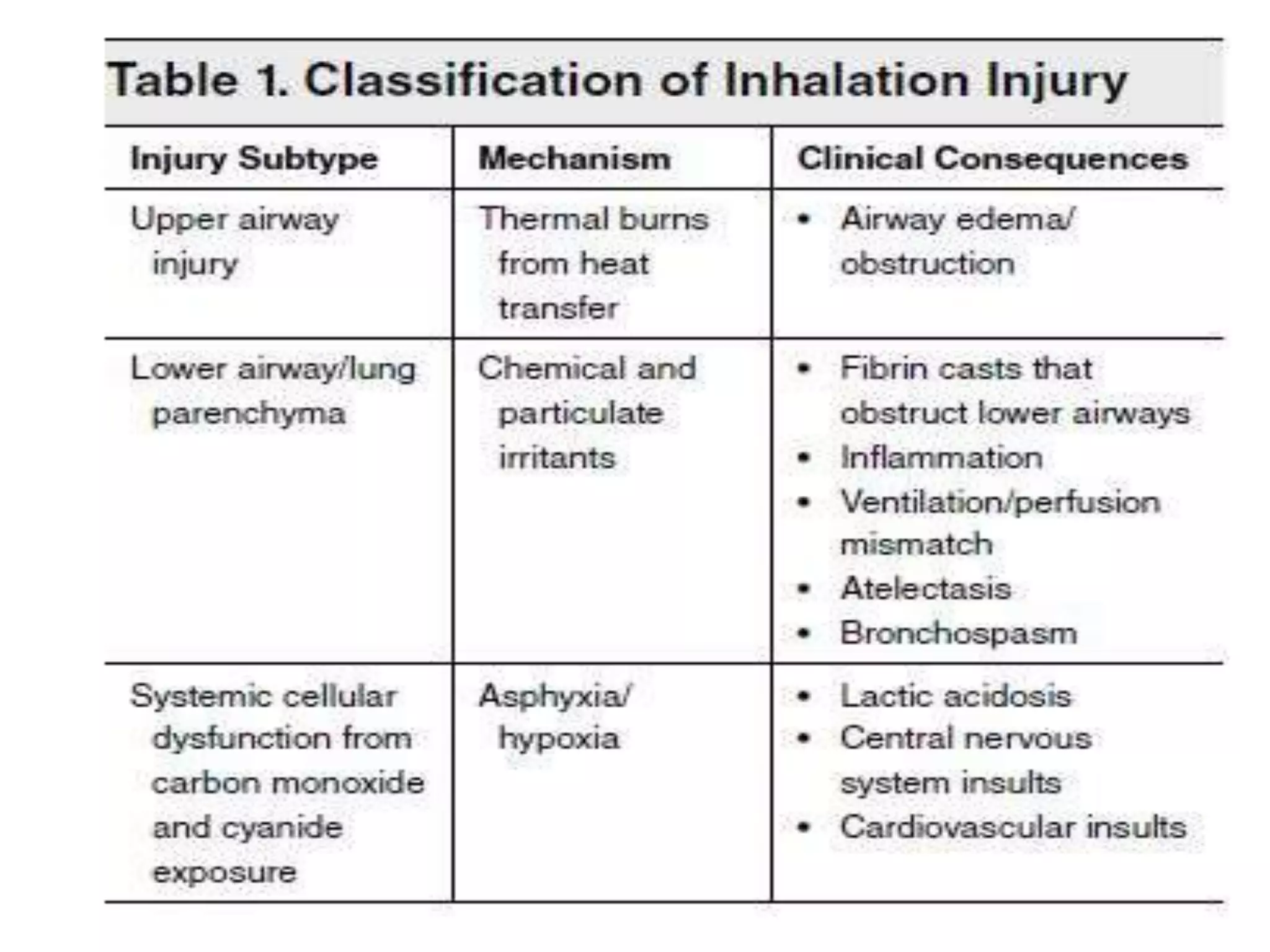
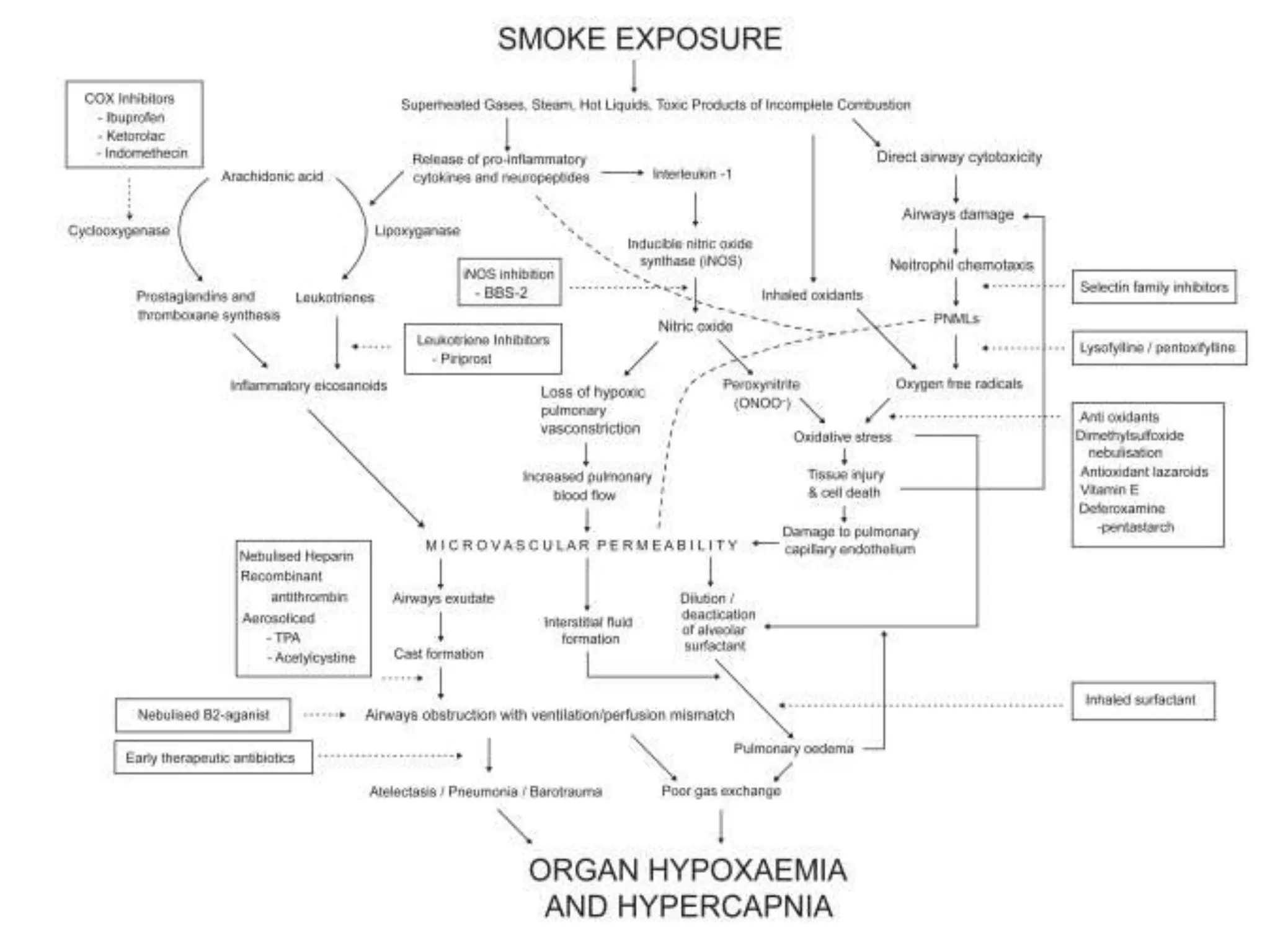
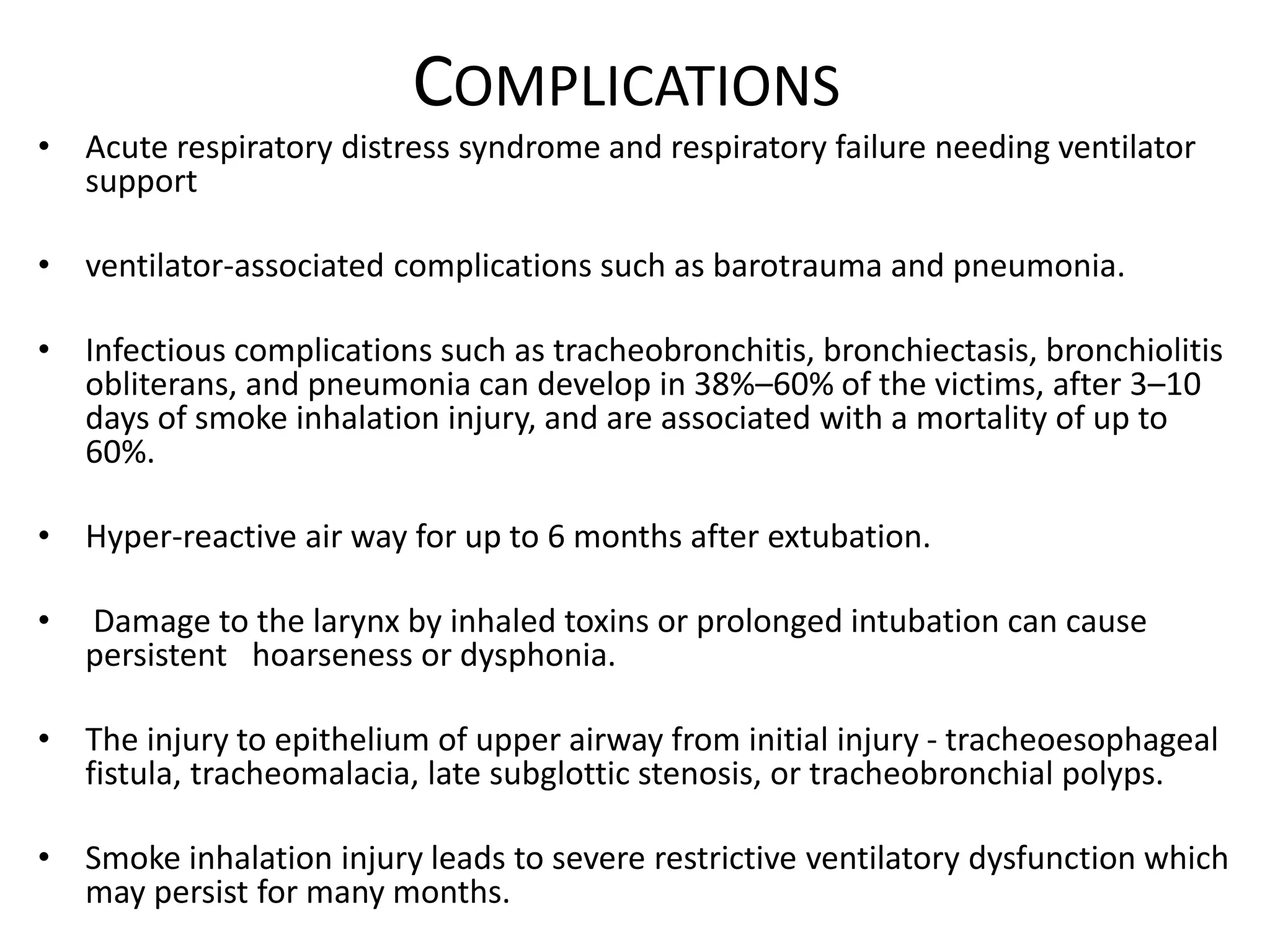
Smoke inhalation injury causes damage to the lungs and systemic toxicity. It occurs in 17% of burn patients and increases mortality up to 24%. Diagnosis is clinical with bronchoscopy and other tests. Treatment involves airway management, cardiovascular support, antibiotics, steroids, and treatments for carbon monoxide and cyanide poisoning. Complications include respiratory failure, infections, and long term lung damage. Prognosis depends on factors like burn severity and lung injury score. Close monitoring is needed due to the progressive nature of inhalation injury.