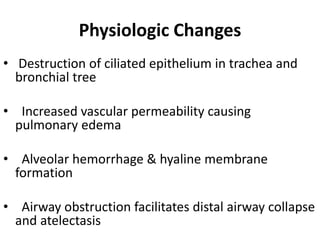
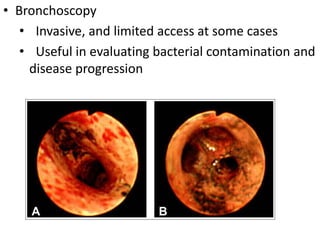
Smoke inhalation can cause serious respiratory complications through three main mechanisms: thermal injury from heat, hypoxic gases like carbon monoxide that displace oxygen, and particulate matter in smoke. Thermal injury can damage the upper airways and cause swelling, while hypoxic gases like carbon monoxide can be fatal. Particulate matter triggers inflammation in the small airways leading to problems like atelectasis. Diagnosis involves assessing signs of inhalation like stridor or soot in the mouth along with chest x-rays, blood gases, and bronchoscopy. Treatment focuses on humidified oxygen, bronchodilators, ventilation if needed, antibiotics, IV fluids, and managing complications.