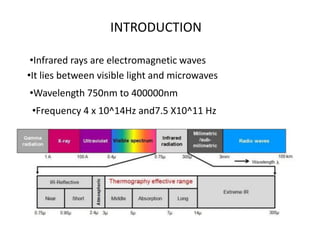
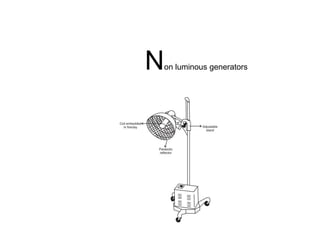
Infrared radiation lies between visible light and microwaves in the electromagnetic spectrum. It can be subdivided based on wavelength. There are two main types of infrared generators used in physiotherapy - luminous generators which emit infrared, visible light, and ultraviolet rays, and non-luminous generators which only emit infrared rays. Luminous generators penetrate less deeply but are used for more chronic conditions while non-luminous generators penetrate more deeply and are used for acute conditions. Infrared radiation has physiological effects like increasing metabolic rate and cutaneous blood flow, and therapeutic effects like reducing pain and increasing joint mobility. New infrared therapies have emerged but proper technique and safety precautions must still be followed to avoid potential dangers like burns.






![NO
Luminous
generators
Non luminous
generators
1 Sources Electrically heated filament Electrically heated resistance wire coiled
2 Gives IR + visible rays Only IR rays
3 Produce Short IR Long IR
4 Wavelength 350 – 4000 nm [ max .= 1000 nm ] 1500 – 12000 nm [ max. 4000 nm ]
5 Emission
70 % near IRR
24 % far
5 % visible light
1 % UV
90 % far IRR
10 % near IRR
6 Penetration
Epidermis , dermis &
Subcutaneous tissue [ 5-10 mm ]
Epidermis & superficial dermis [ 2 mm ]
7 Heating Deeply Superficial
8 Uses Chronic inflammation Acute inflammation
9
Physiological
effect
Pain reduction via
counter – irritant effect
Pain reduction via
sedative effect
10
Therapeutic
effect
Heating Sensory heating
11 Treatment time 15 -20 minute 20 -30 minutes
12 Distance 40 – 60 cm form treated area 75 -90 form treated area
Difference between luminous and non luminous generators :
Difference between luminous and non luminous generators](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infraredradiationppt1new-230112140612-6c89bfd2/85/INFRARED-RADIATION-ppt-1-new-pdf-9-320.jpg)