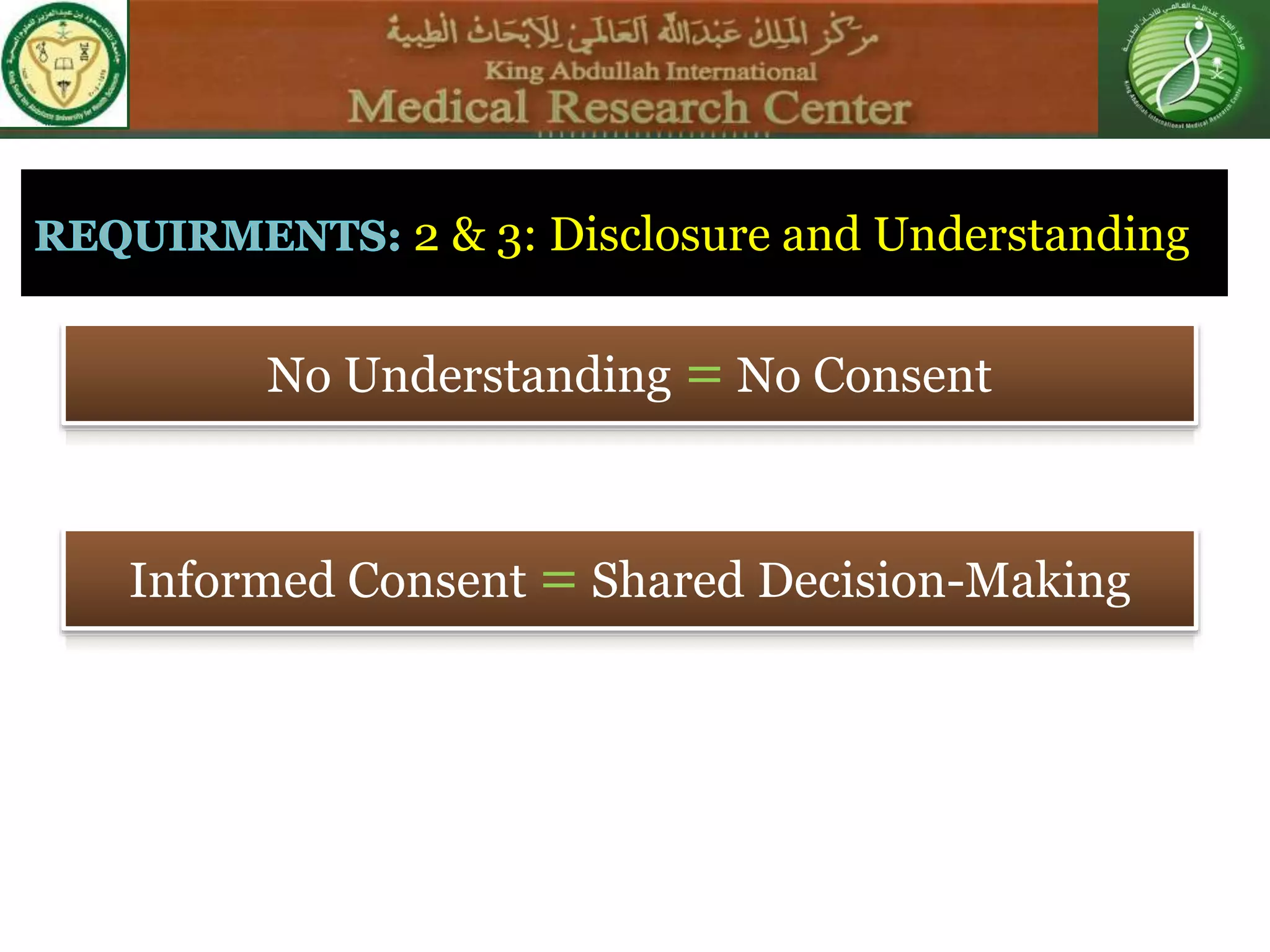
1) Informed consent requires disclosure, understanding, competence, and voluntariness. Patients must understand the nature of the procedure, risks, benefits, and alternatives in order to make an informed decision.
2) There are basic elements that must be included in an informed consent form such as purpose, procedures, risks, benefits, and confirmation that participation is voluntary. Additional elements may also be required depending on the level of risk.
3) Obtaining consent from children requires consideration of their developmental level. For children under age 7, consent is implied. Children ages 7-11 must provide verbal assent. Those 12-17 can provide written assent with parental consent.