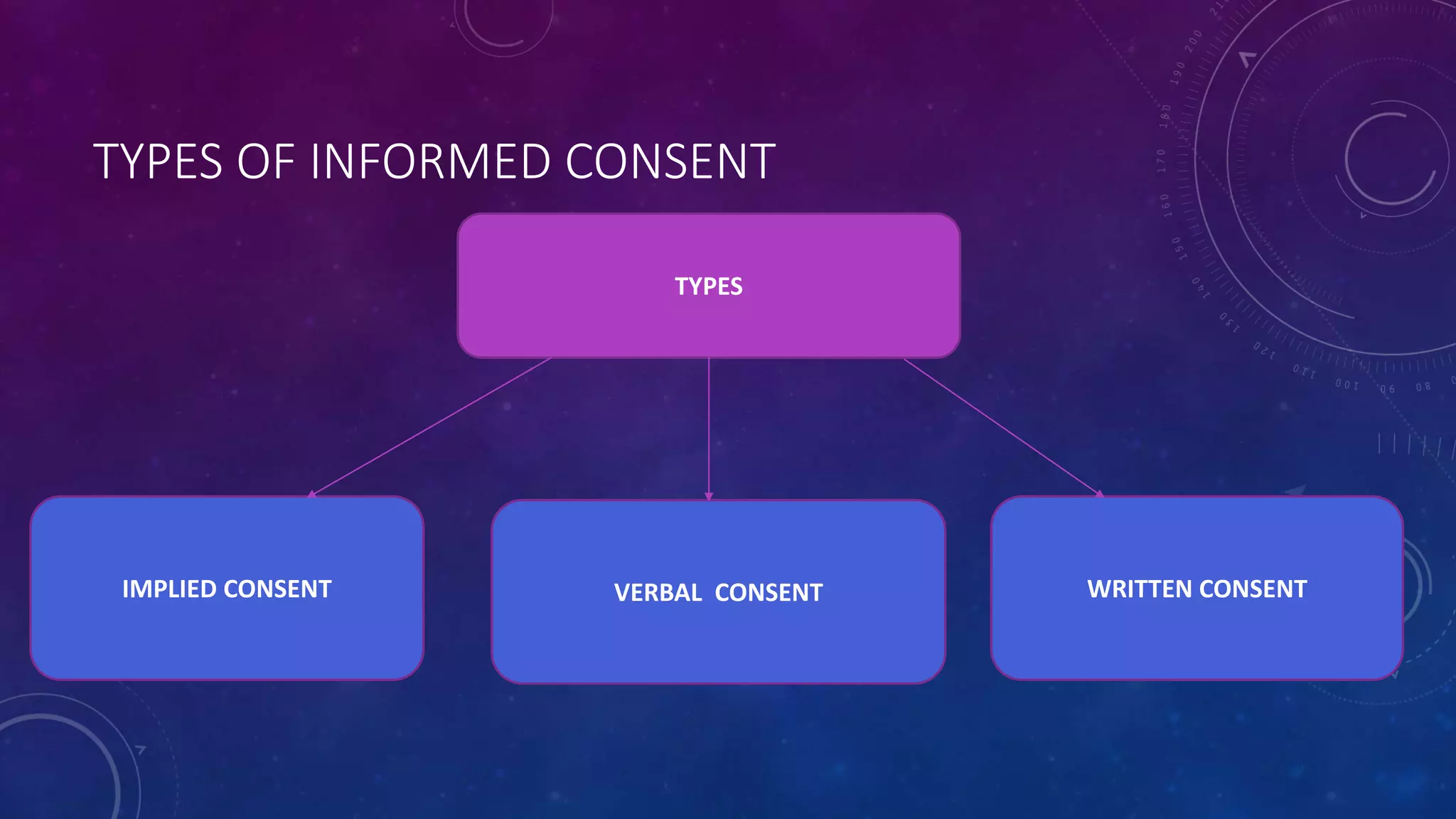
Informed consent is required before any medical treatment and involves explaining the risks and benefits to help patients understand their treatment options. There are three main types of consent - implied, verbal, and written. Informed consent includes describing the clinical issue, proposed treatment and alternatives, discussing risks and benefits, assessing patient understanding, and obtaining their preference. Key principles are that consent must be given voluntarily without pressure, the patient must have capacity, and consent is ongoing. Informed consent is important for trust between doctors and patients and protects patient autonomy and rights. It is generally required for medical procedures but not in emergencies when immediate treatment is necessary.