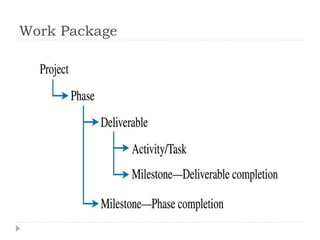
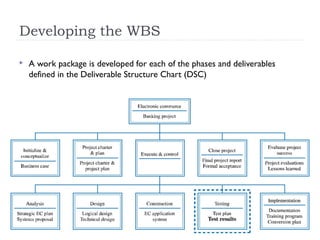
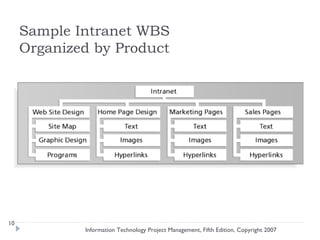
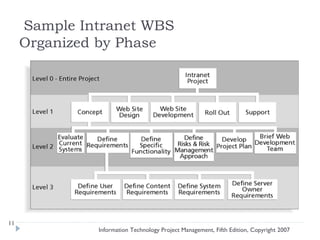
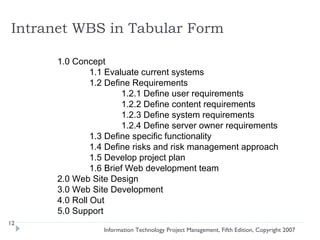
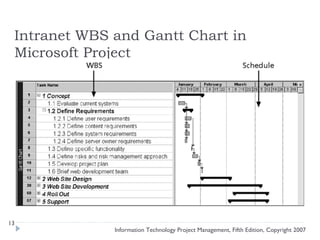
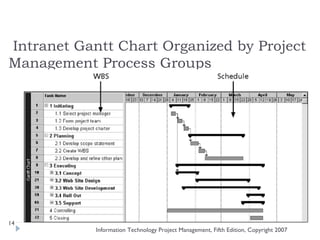
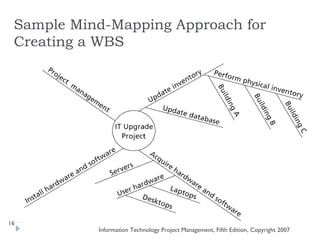
The document discusses various techniques for developing work breakdown structures (WBS), estimating activity durations, and improving estimates for projects. It describes defining and sequencing activities, estimating resources and durations, and developing schedules. Methods covered include top-down, bottom-up, analogy, and parametric modeling approaches. Factors that can impact estimates and ways to enhance estimating accuracy are also outlined.