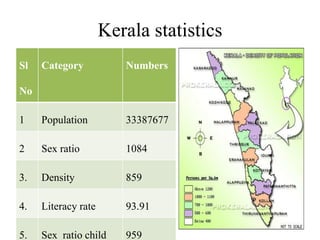
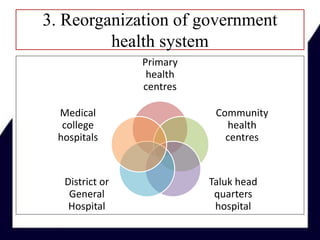
This document outlines Kerala's state health policy from 2013. It discusses 6 components of the health system and provides statistics on Kerala's demographics and health infrastructure. It describes the current scenarios around social determinants of health, emerging diseases, non-communicable diseases, and vulnerable populations. The plan of action focuses on improving determinants of health like water, sanitation, and poverty reduction. It also details reorganizing the public health system from primary to tertiary levels and strengthening specialized services like communicable disease control and mental health.