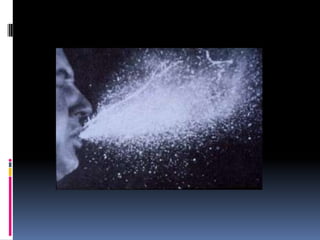
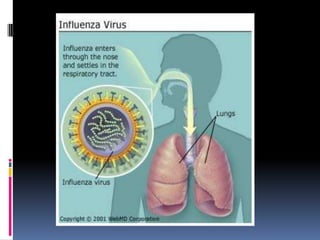
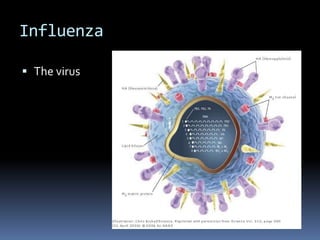
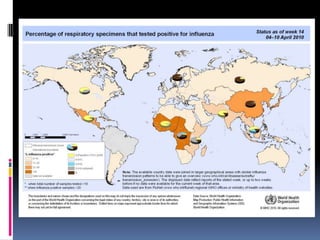
Infectious disease epidemiology describes influenza as an acute viral infection typically causing abrupt onset of fever and respiratory symptoms like cough and sore throat. Complications can include primary viral or secondary bacterial pneumonia. Influenza viruses are transmitted through respiratory secretions when people cough, sneeze or talk. There are annual epidemics in winter months in temperate regions that vary in severity each year. Pandemics occur less frequently and represent major antigenic shifts in influenza virus subtypes. Surveillance, vaccines, antiviral drugs, rest, and handwashing help prevent and treat influenza.