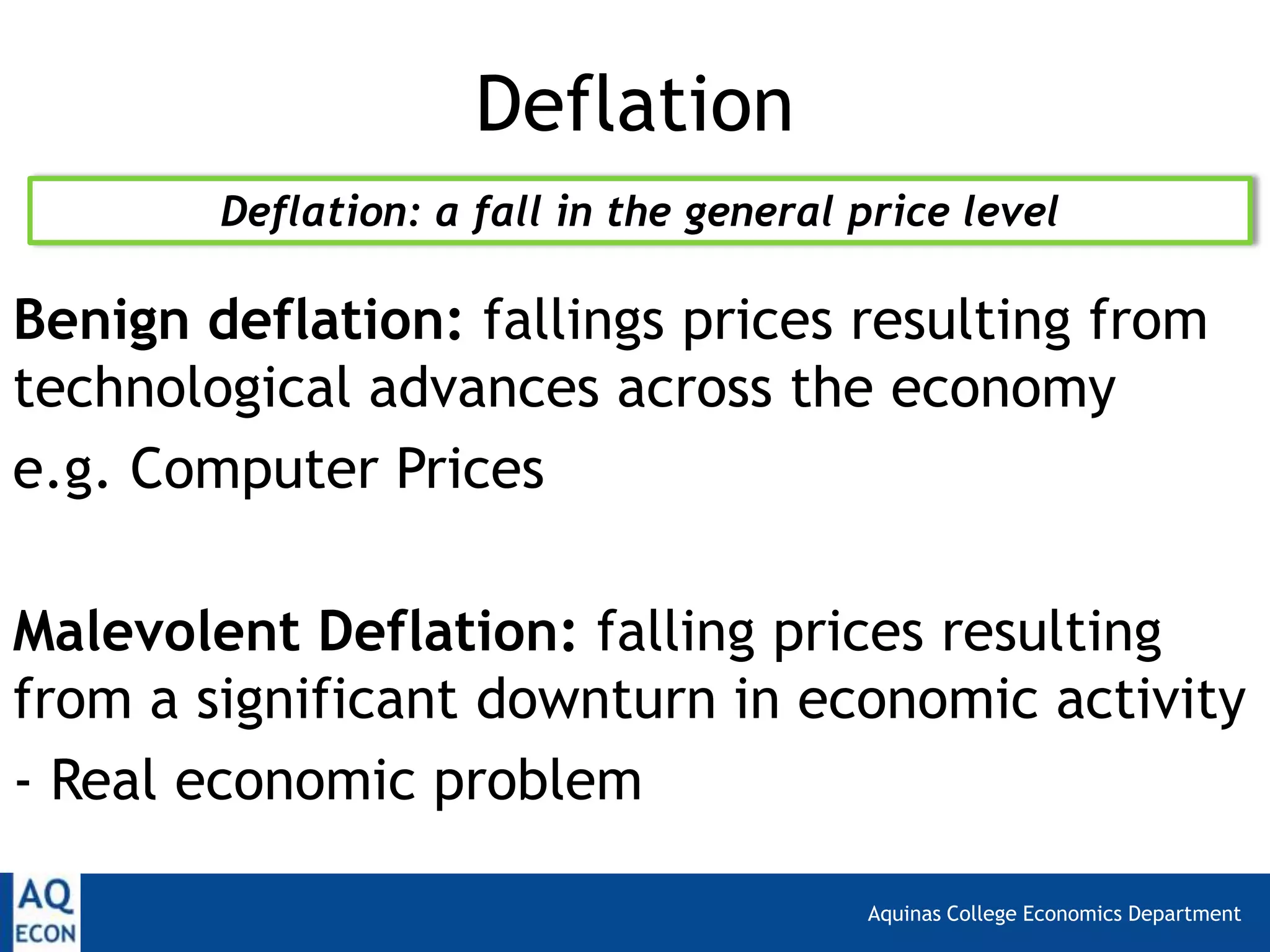
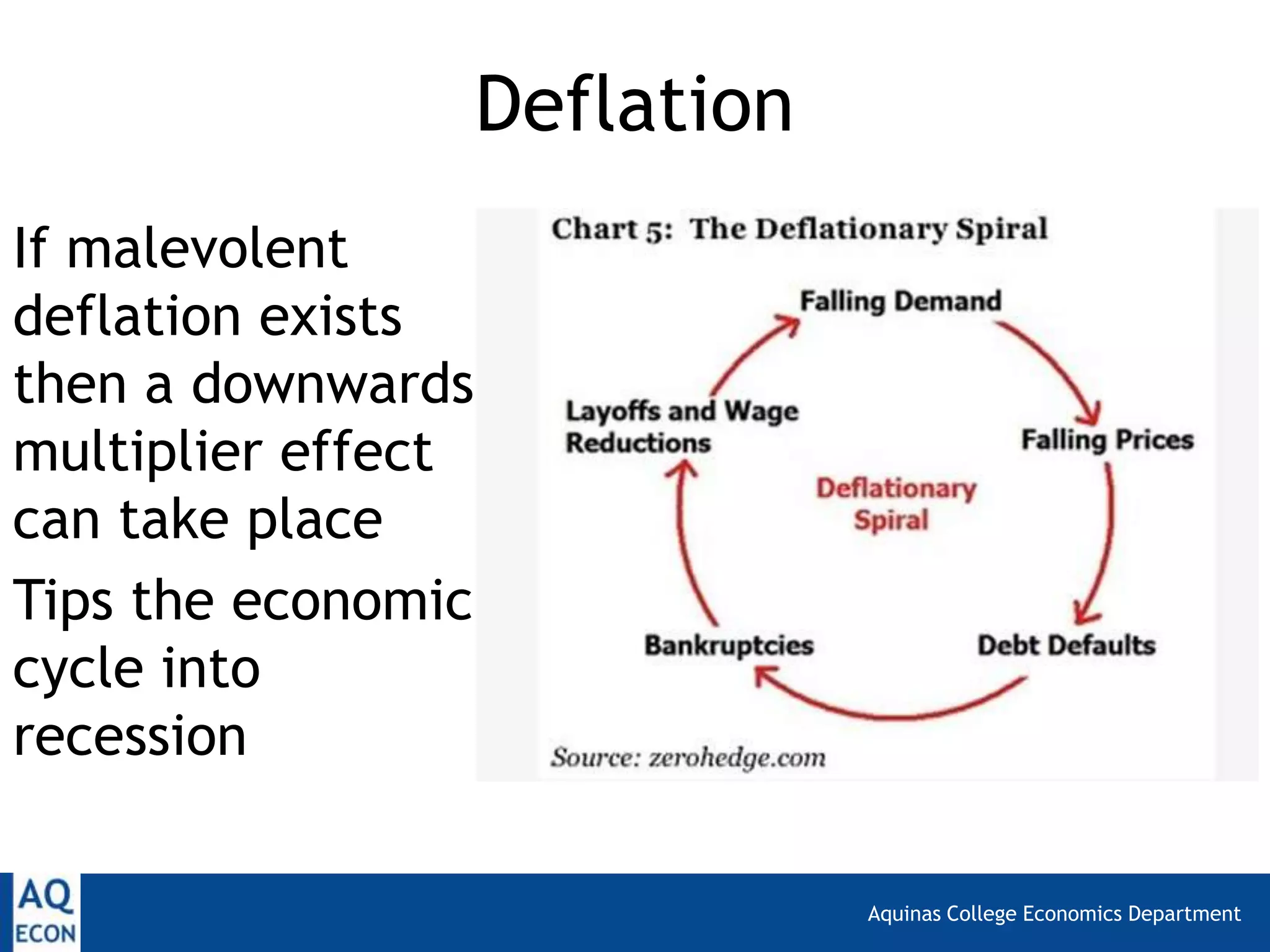
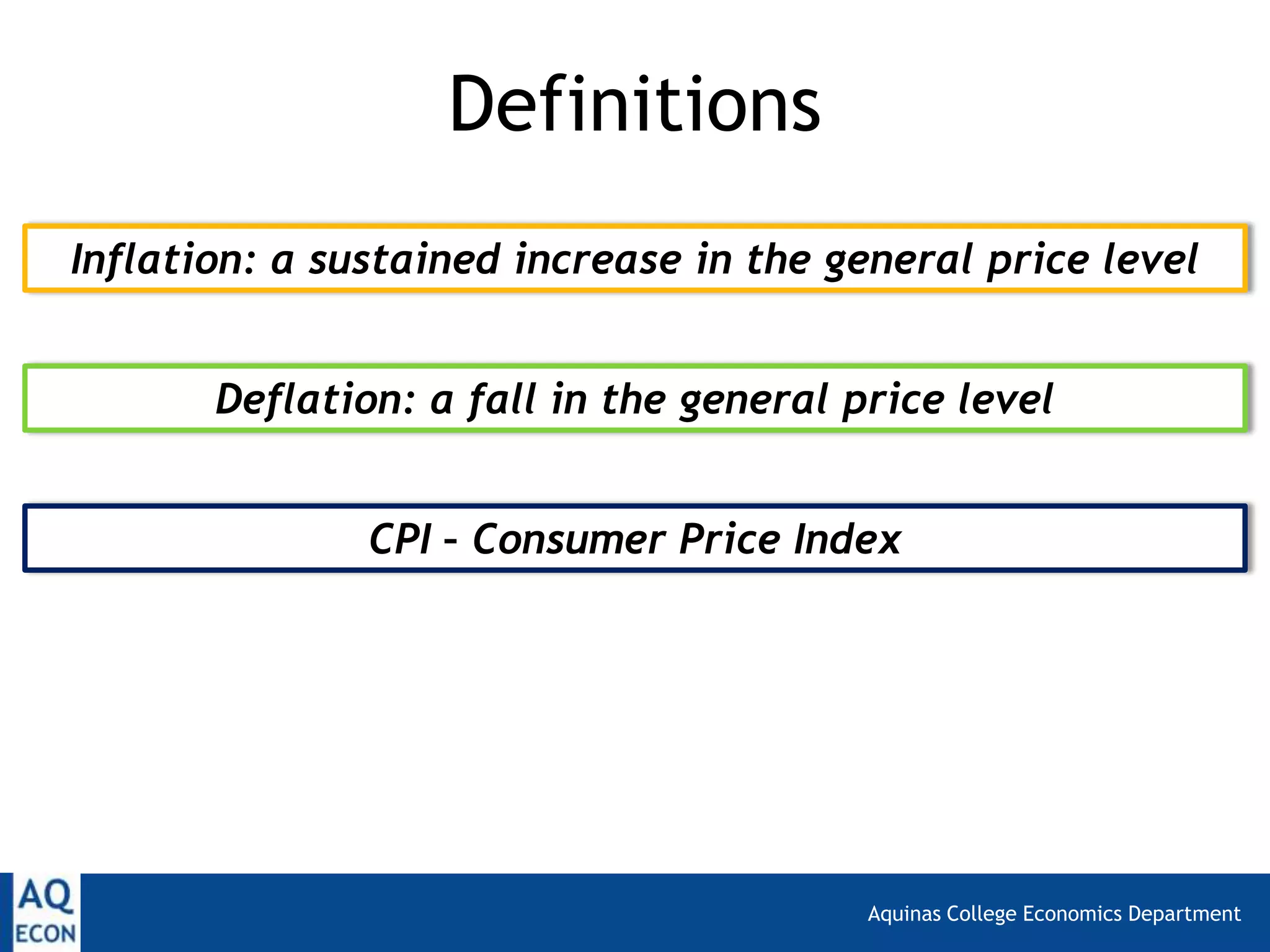
The document provides an overview of inflation and deflation, including their definitions, calculation methods, causes, and consequences. It explains the Consumer Price Index (CPI) as a measure of inflation in the UK and discusses limitations of CPI. Additionally, it distinguishes between benign and malevolent deflation and highlights the economic implications of both inflationary and deflationary trends.







![Aquinas College Economics Department
Consequences of Inflation
Consequence Explanation
Global Competitiveness Makes UK Goods more expensive on foreign
markets [BoP issues]
Investment As inflation creates uncertainty investment
levels fall
‘Menu Costs’ Admin costs to business when changing prices
‘Shoe-Leather Costs’ Cost to consumers who shop around
Distribution of Income Savers lose out with a real interest rate
Employer-Employee Relationship Workers demand higher pay, resulting in a
wage-spiral
Fiscal Drag When tax exempt amounts are not increased in
line with inflation meaning tax payers may be
dragged into the next tax band
Hyperinflation Currency is effectively worthless and a barter
economy appears](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflationanddeflation-130610064425-phpapp02/75/Inflation-and-Deflation-14-2048.jpg)