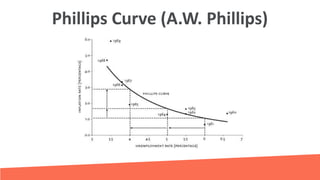
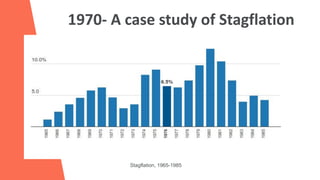
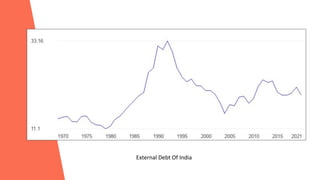
Inflation refers to a sustained increase in price levels over time that reduces purchasing power. It is measured using indices like CPI and PPI which track the cost of common goods. Inflation can be caused by factors like increased demand, rising production costs, or wage-price spirals. It can lead to issues like uncertainty, reduced savings, and wealth redistribution. India and other nations experienced stagflation in the 1970s due to oil crises and other economic issues. The 1991 Indian crisis demonstrated the need for reforms like currency devaluation and trade liberalization.