This document discusses various concepts related to inflation including:
- Inflation is defined as a persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services. It is measured using price indexes like the CPI and WPI.
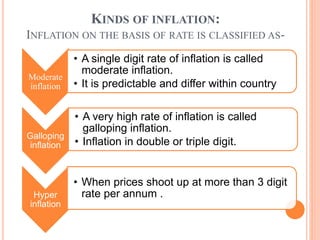
- There are different types of inflation based on rates like moderate, galloping, and hyperinflation. Additionally, inflation can be open or repressed based on government reaction.
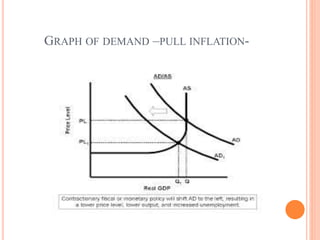
- Inflation has causes like excess money supply, deficit financing, population growth, and high import prices. It can be demand-pull or cost-push.
Related concepts discussed include deflation, disinflation, reflation, stagflation, and recession.