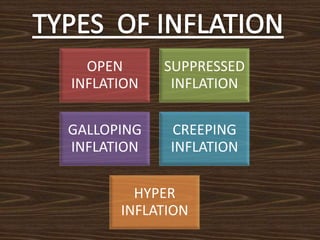
Inflation is defined as a sustained increase in the price level or fall in the value of money. It occurs when the level of currency exceeds production. The value of money depreciates with inflation. There are different types of inflation including open, suppressed, galloping, creeping, and hyper inflation. Factors that can cause inflation include an increase in money supply, disposable income, deficit financing, and changes to agricultural and industrial growth. Ways to control inflation include monetary policies like credit control and demonetization, fiscal policies like reducing spending and increasing taxes and savings, and other measures to increase production and implement price controls.