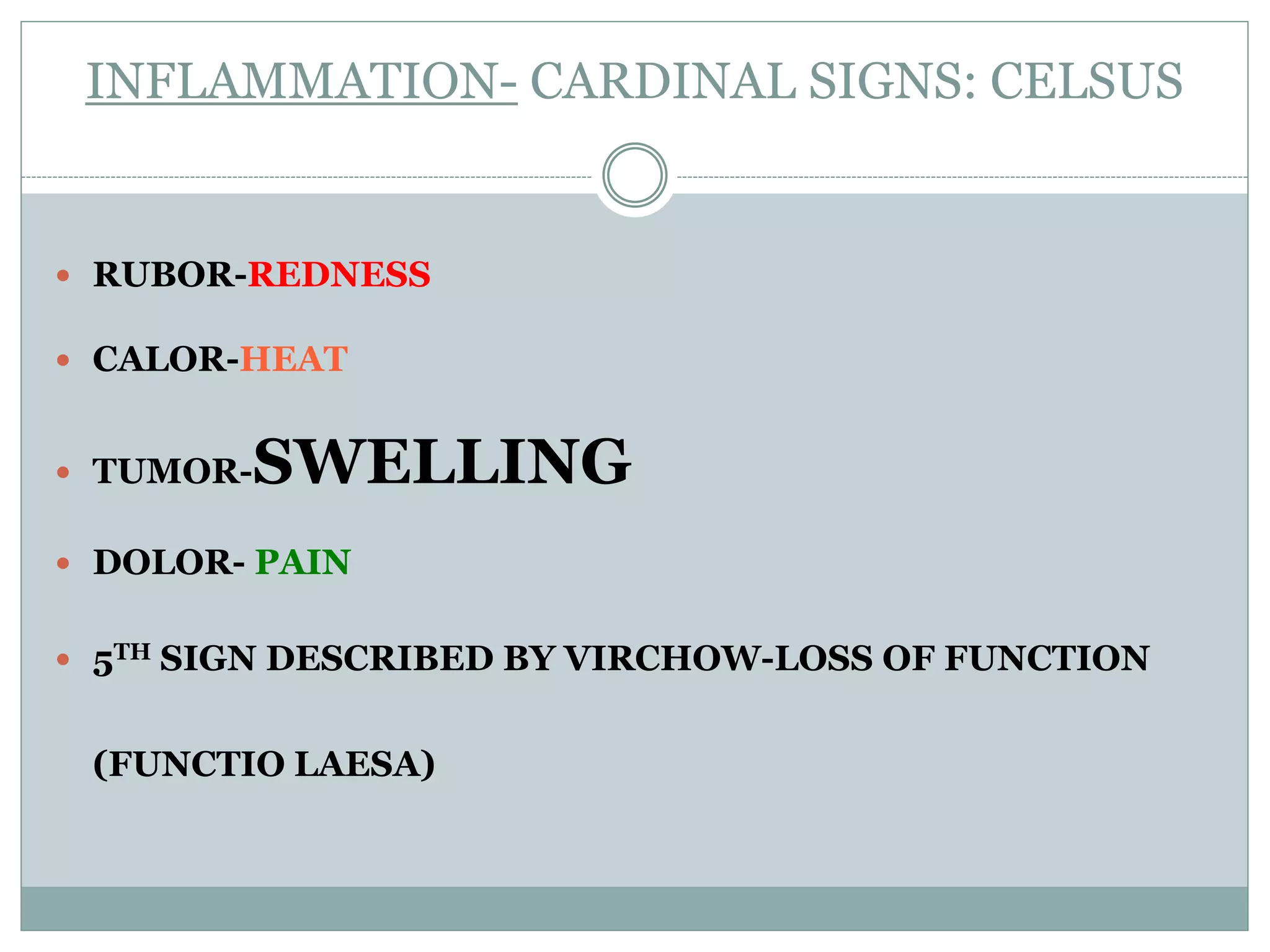
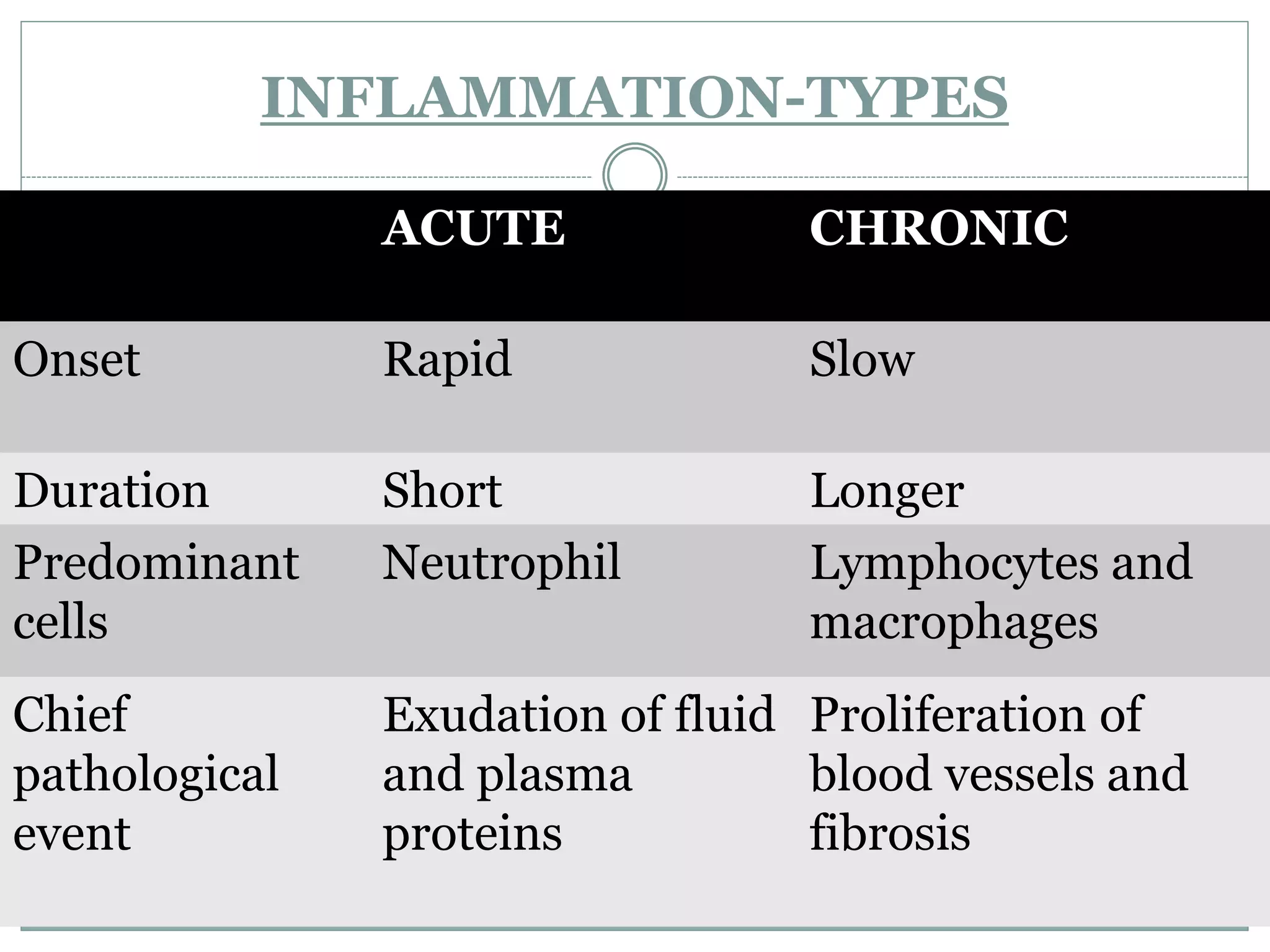
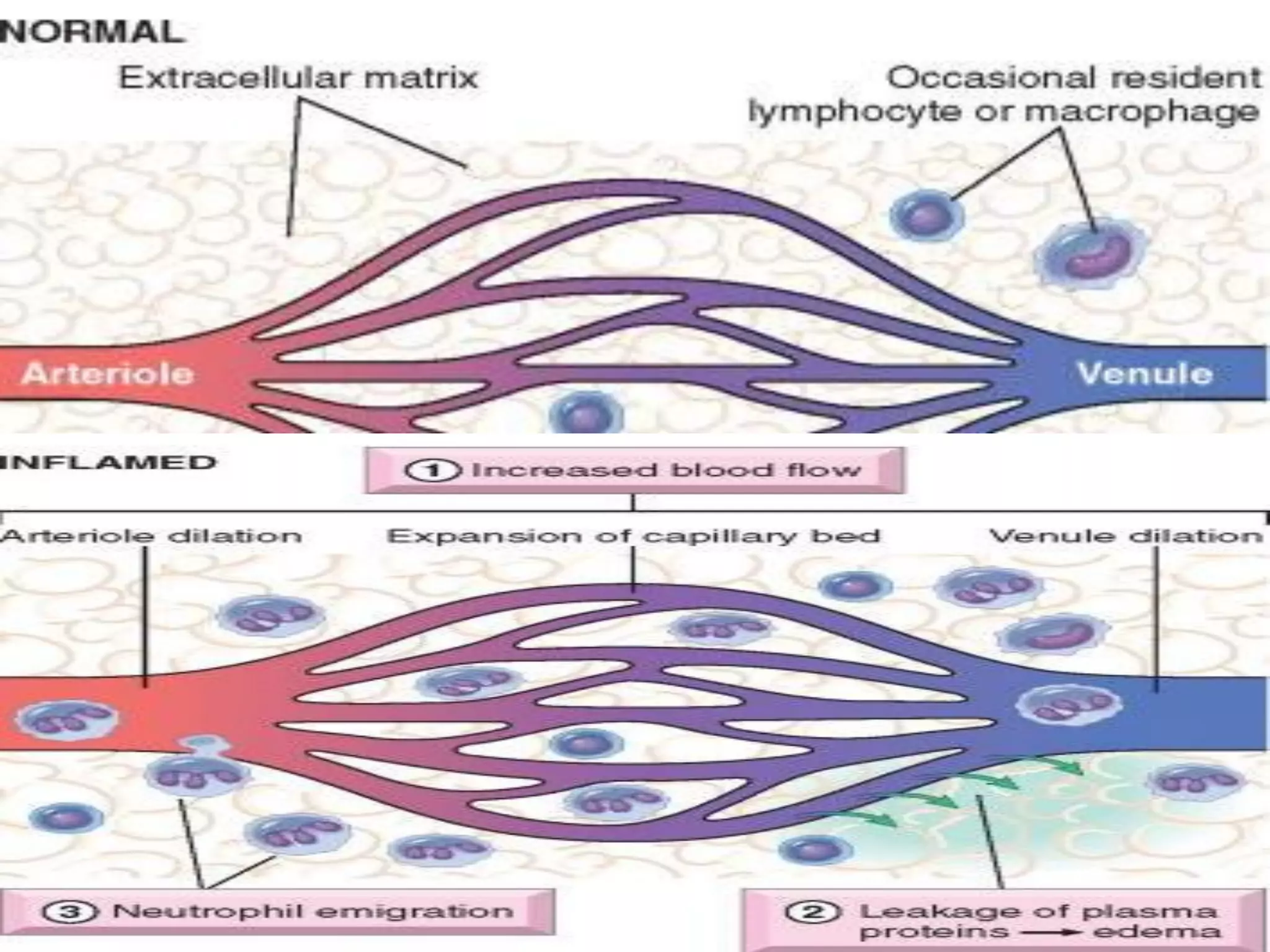
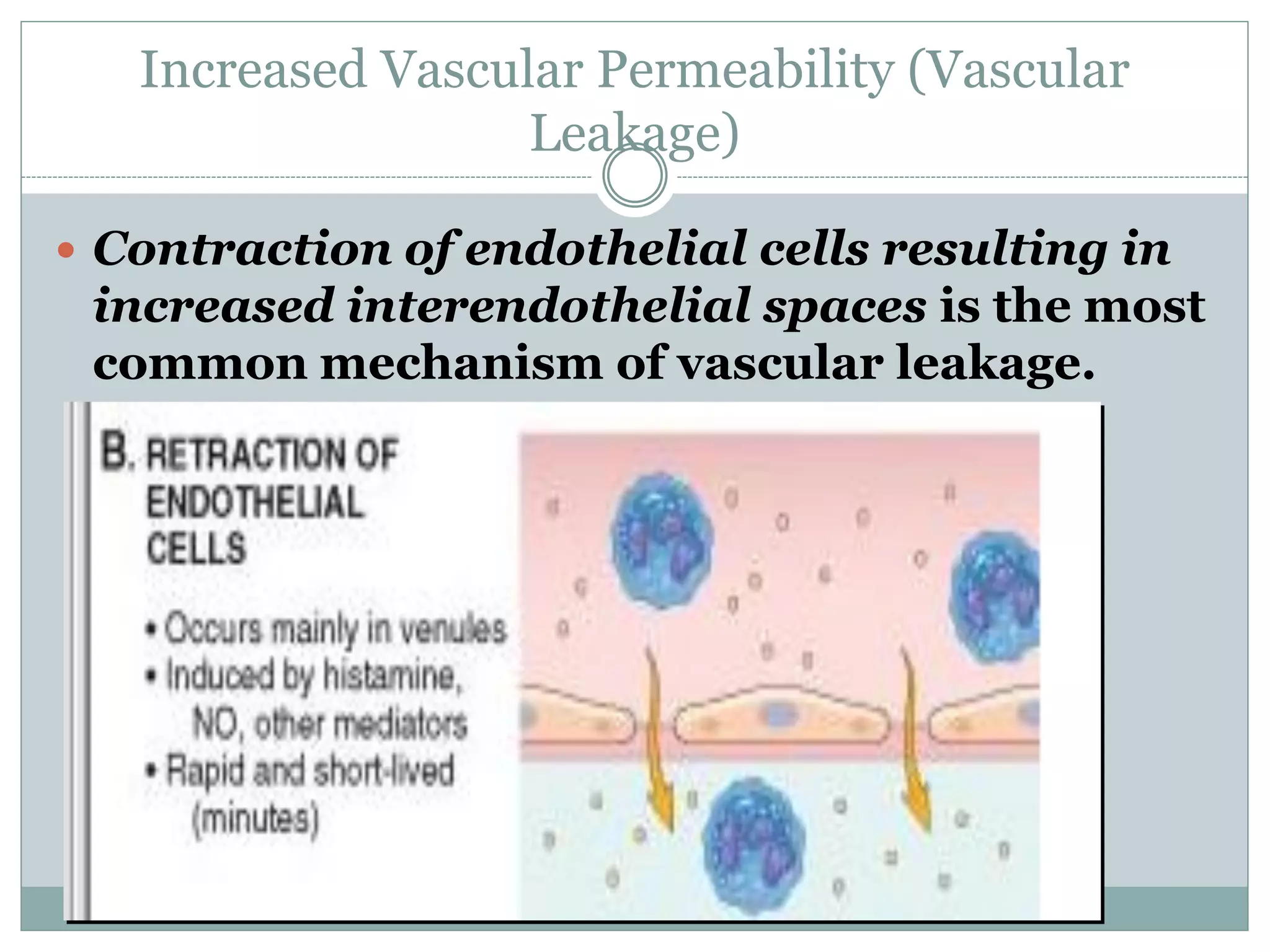
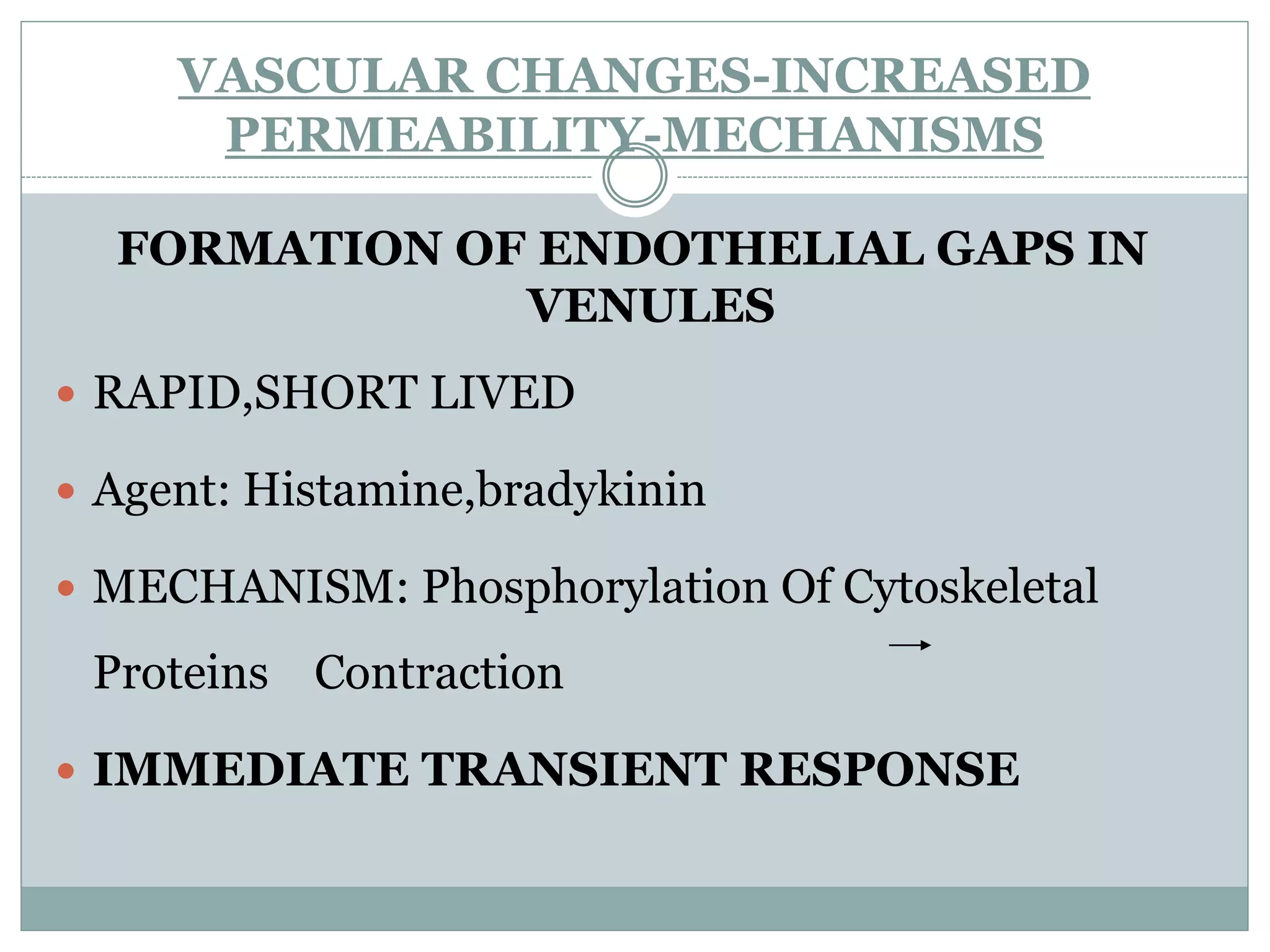
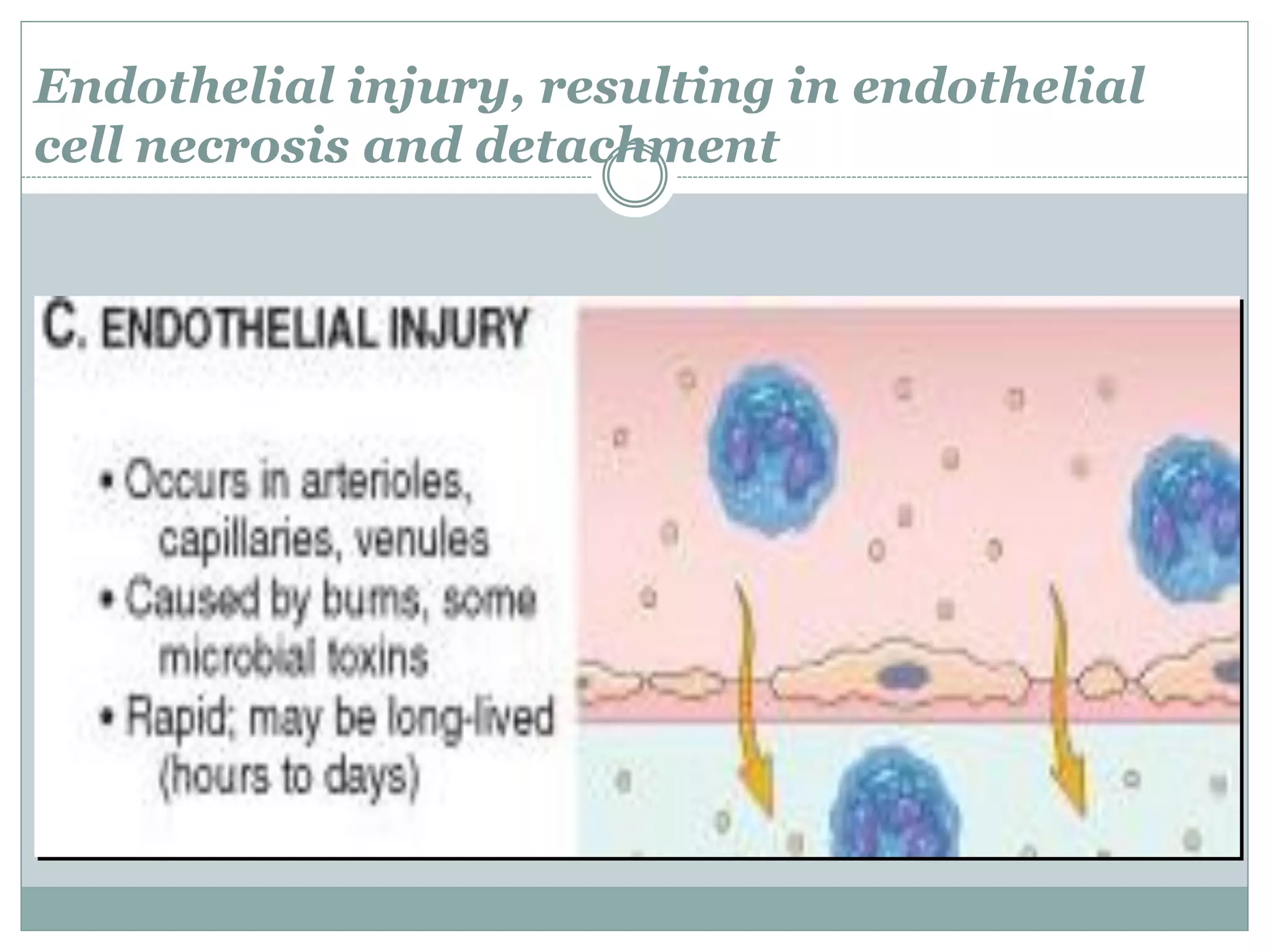
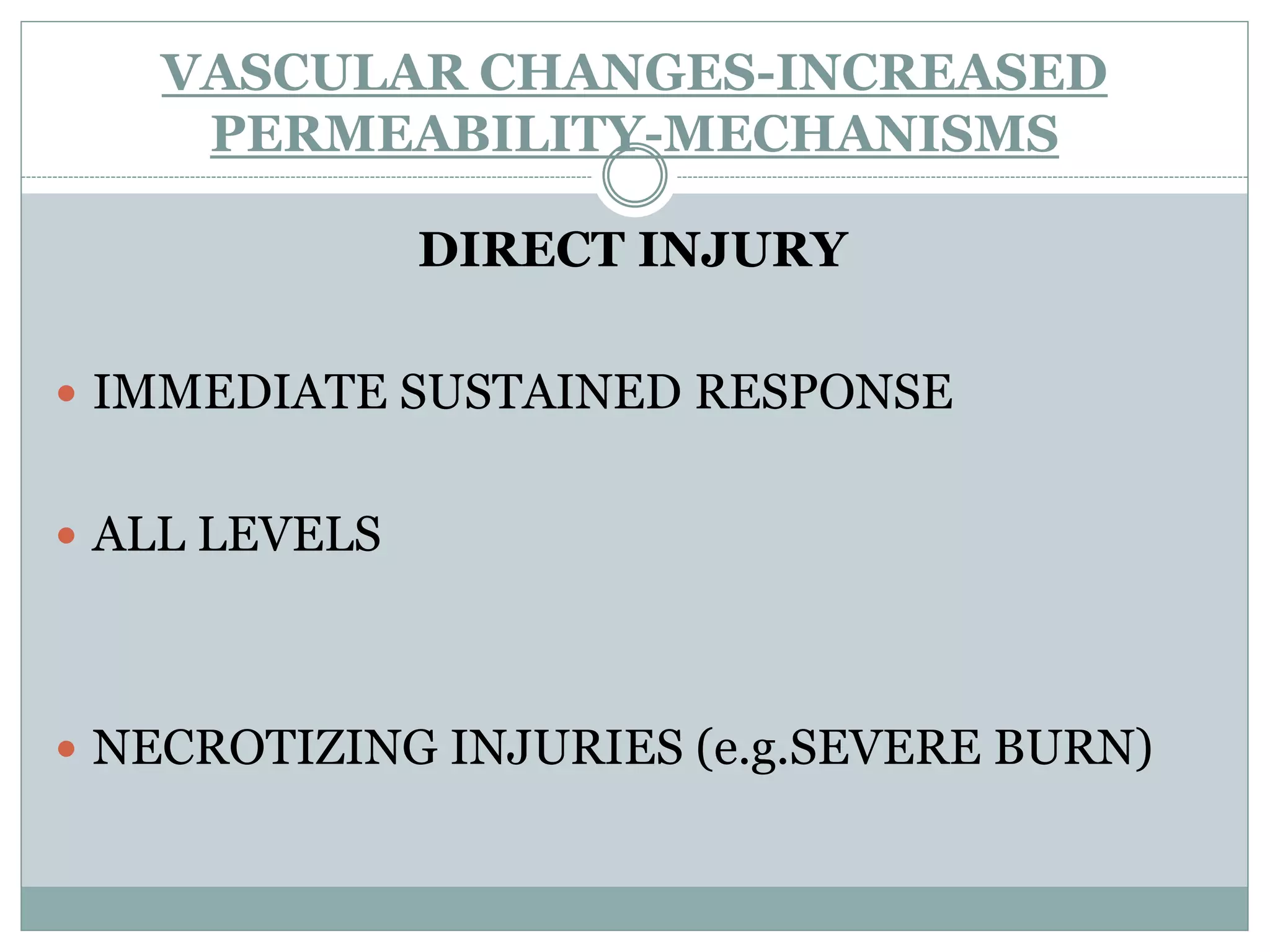
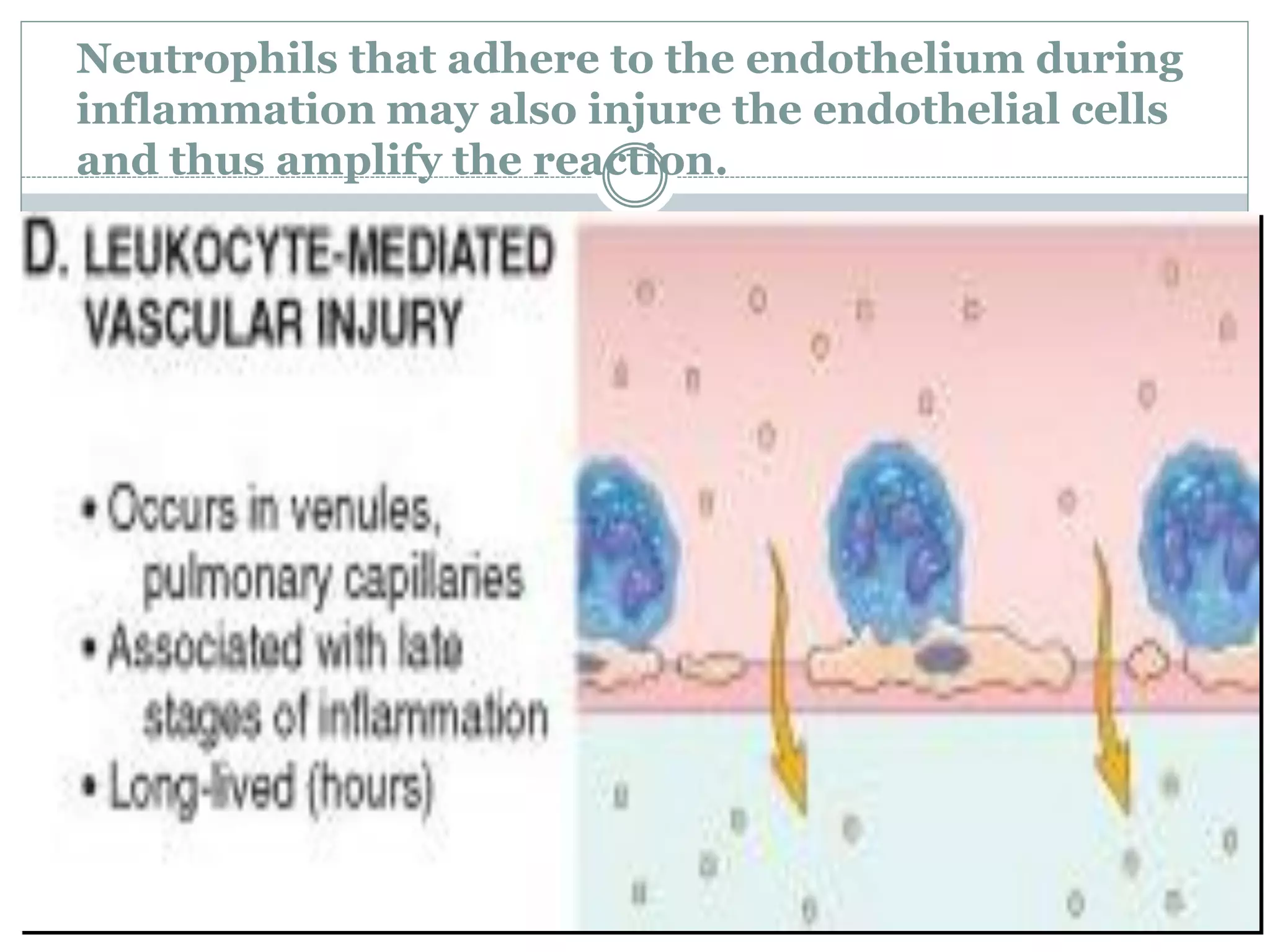
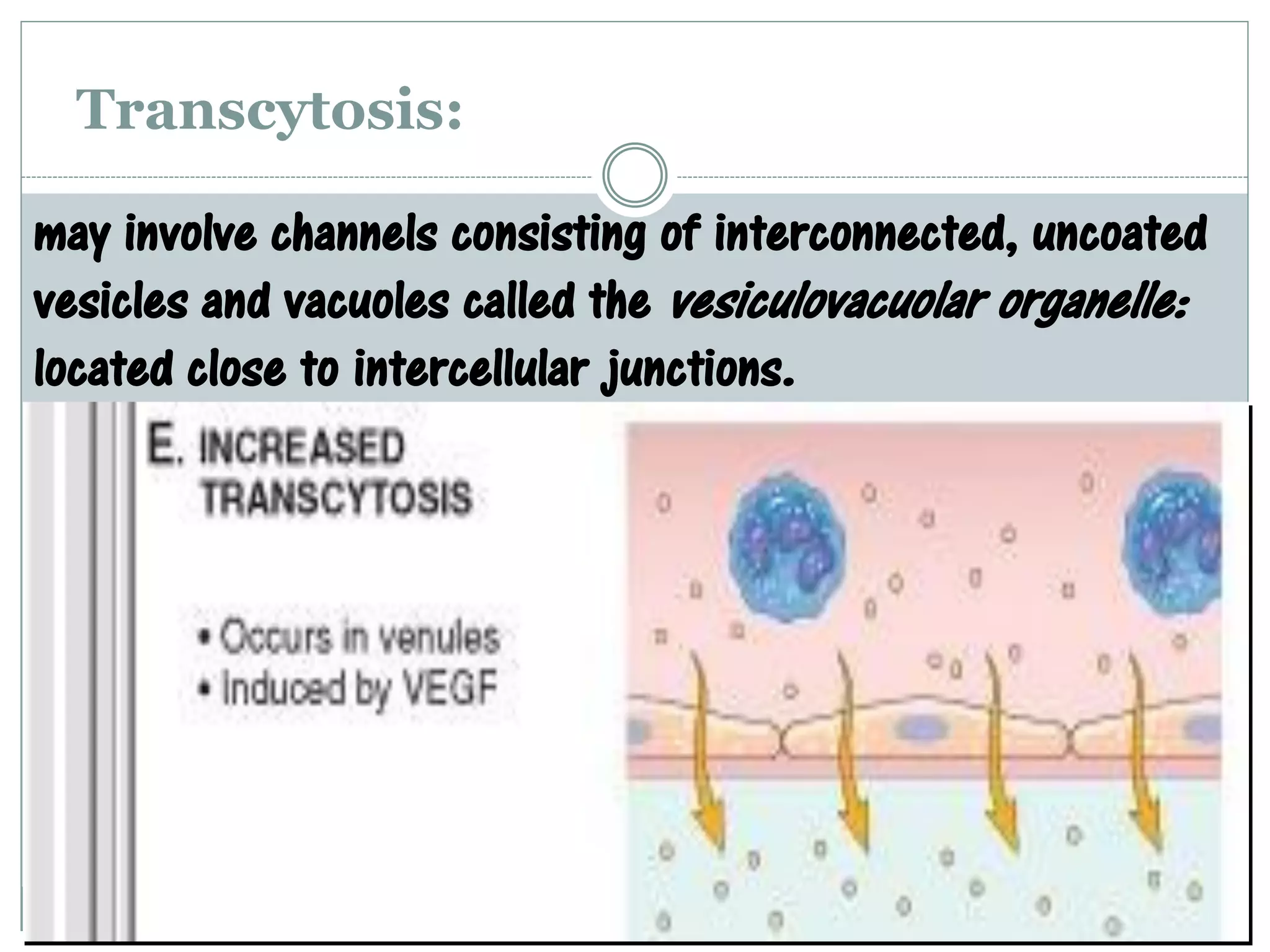
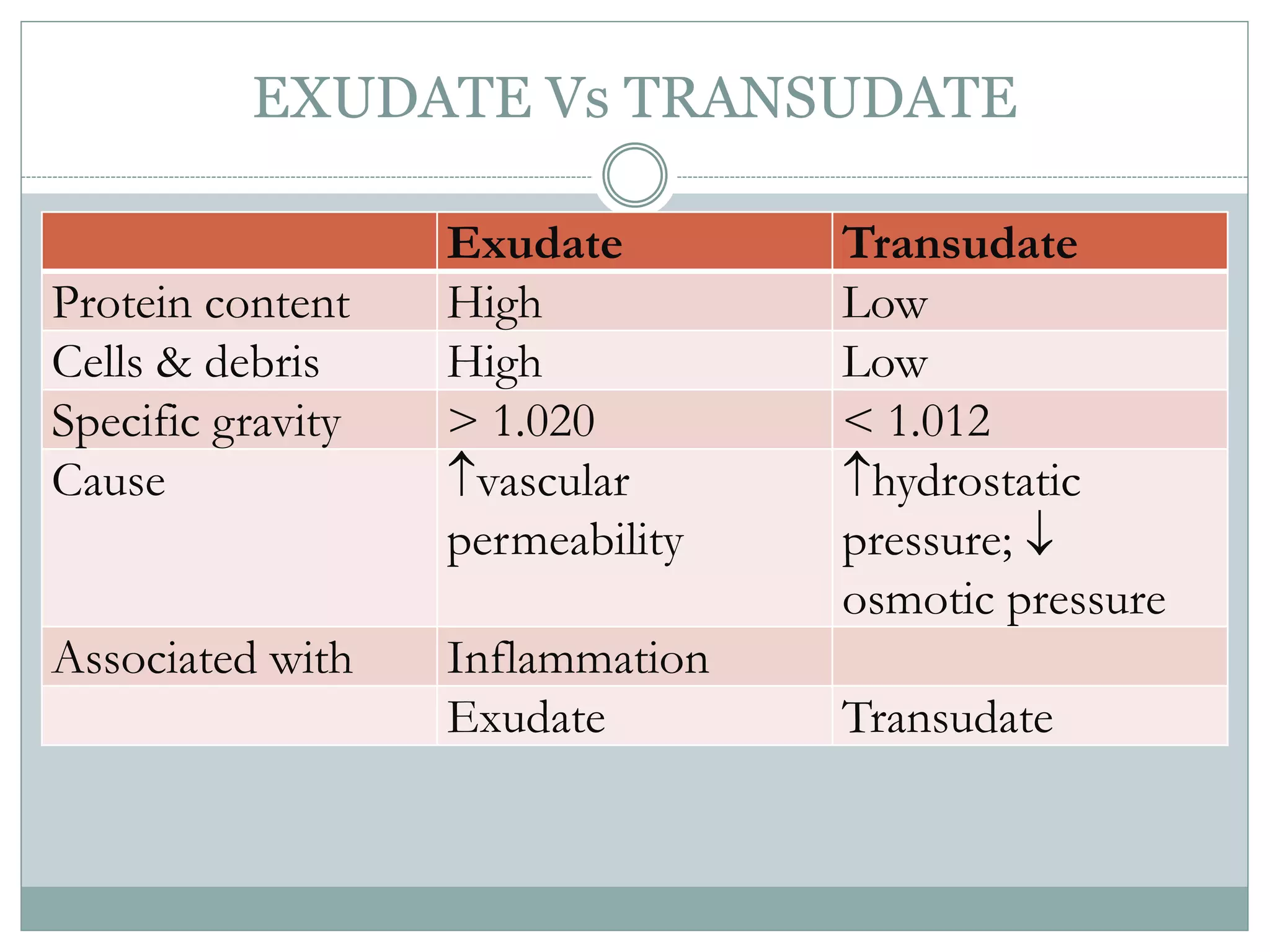
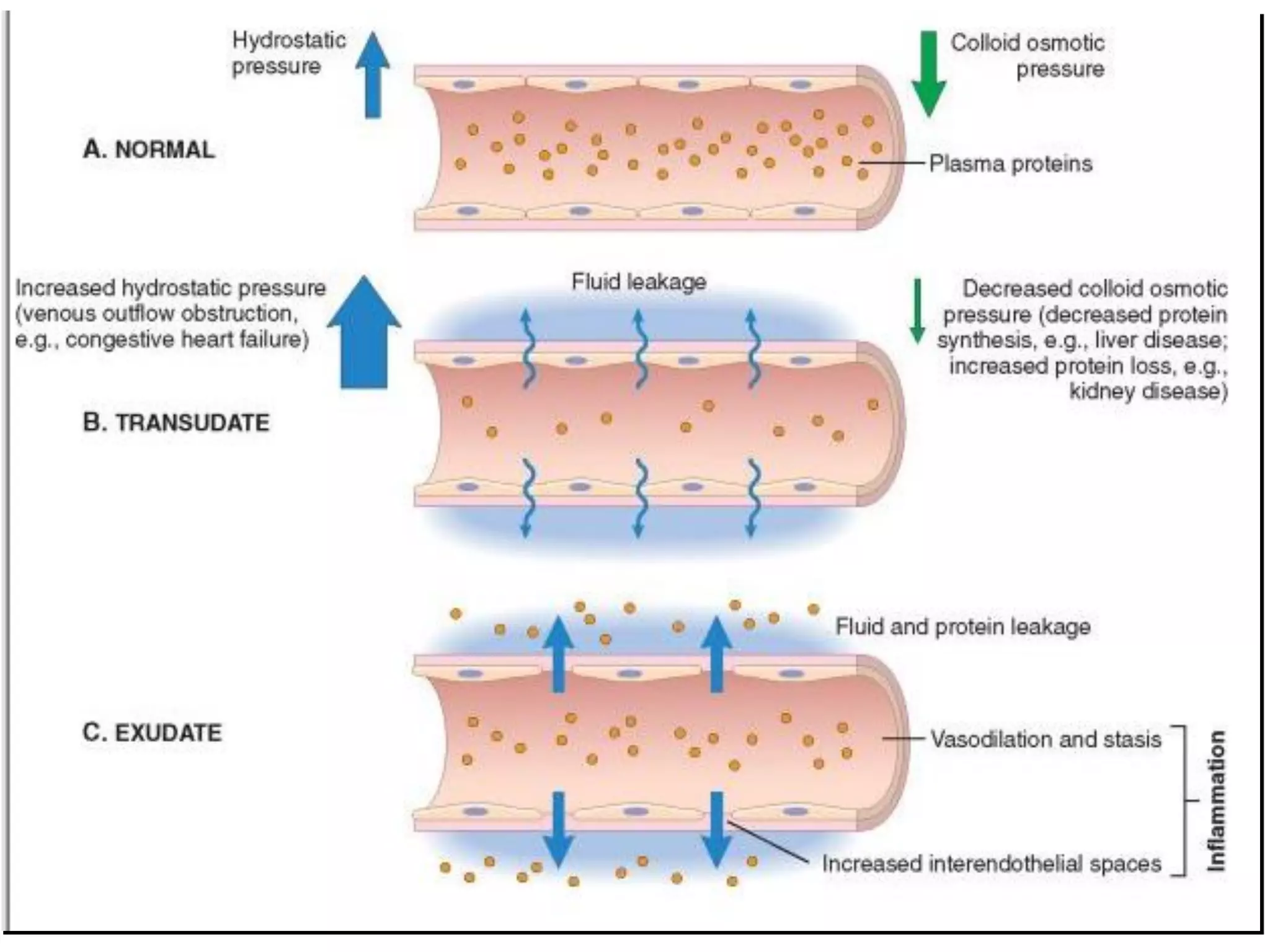
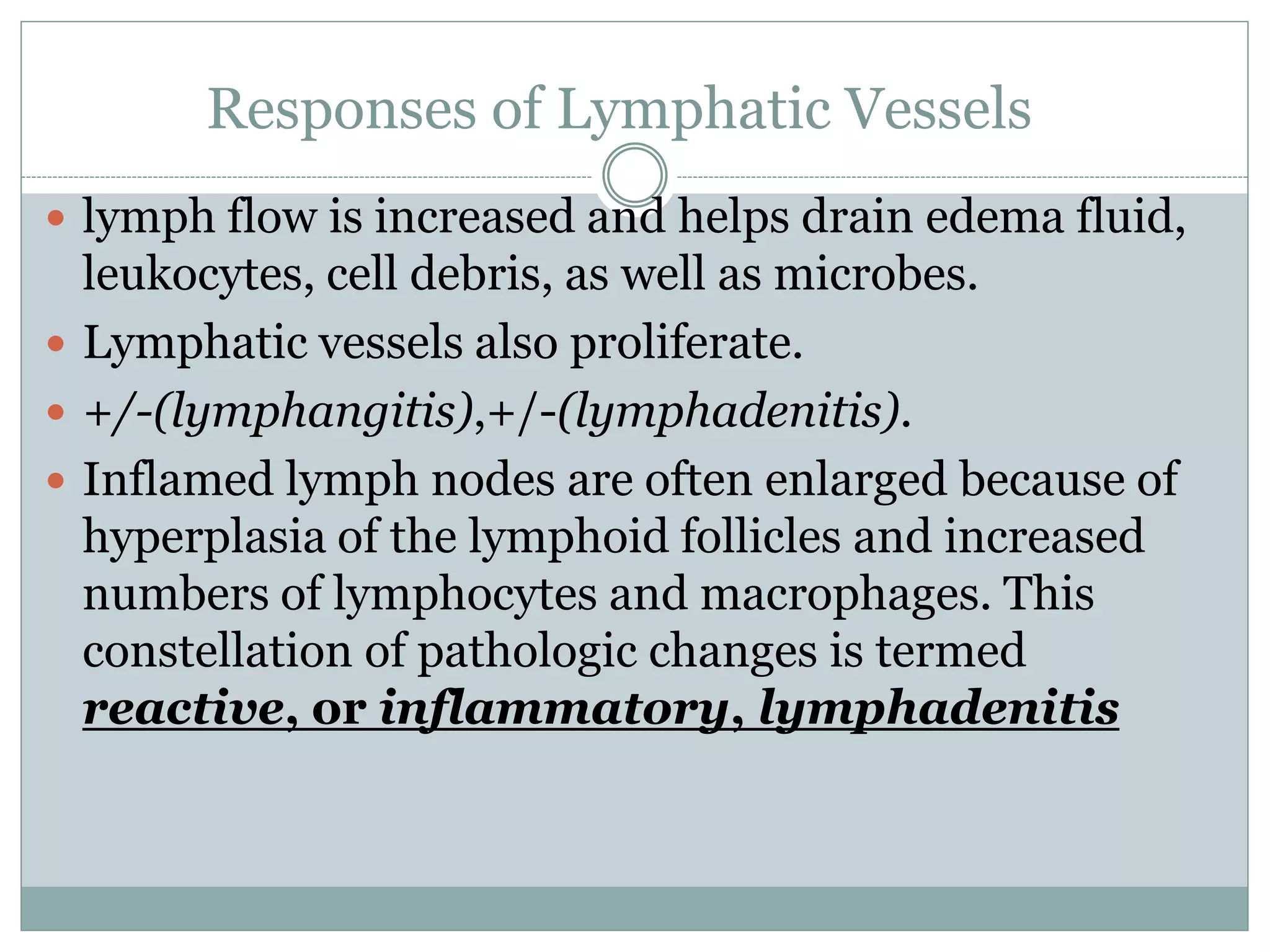
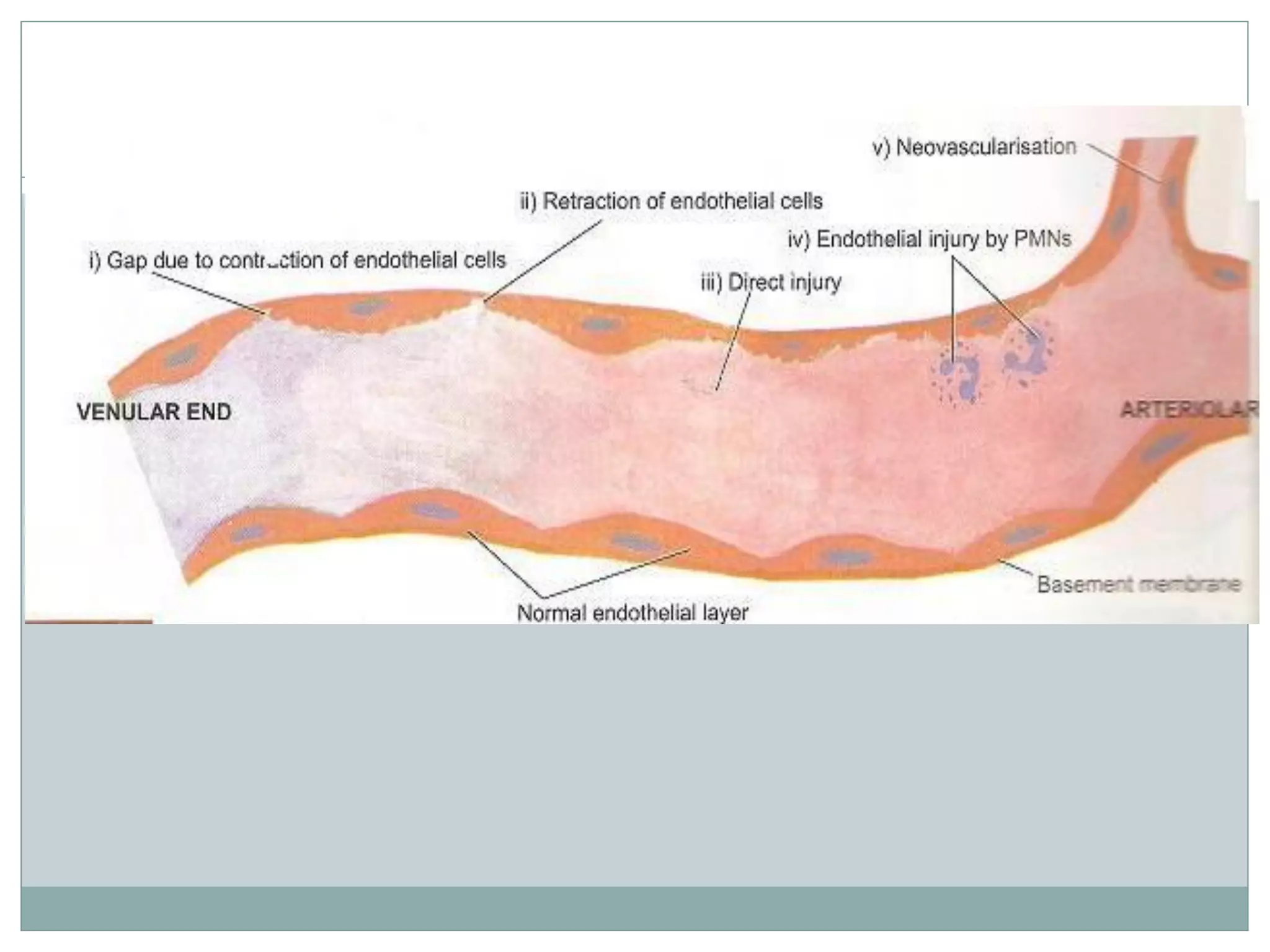
Inflammation is the body's response to injury and involves cardinal signs like redness, heat, swelling, and pain. Acute inflammation is rapid in onset and short in duration, involving increased blood flow, vascular permeability, and neutrophil infiltration. The vascular changes that occur during acute inflammation include vasodilation, increased permeability through mechanisms like endothelial cell contraction and injury, and transcytosis, which together allow fluid, proteins, and cells to exit into tissues as an exudate.