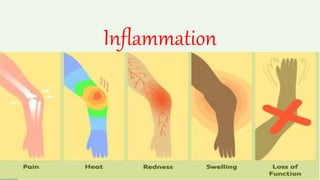
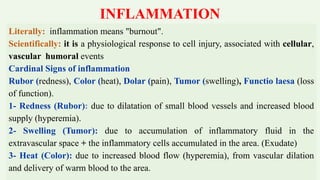
Inflammation is the body's physiological response to cell injury and is characterized by redness, swelling, heat, pain, and loss of function. The purposes of inflammation are to localize the injury, remove the cause, and repair damaged tissue. Inflammation can have both beneficial effects, like fighting infections, and harmful effects, such as organ obstruction or loss of function. Acute inflammation occurs over days or weeks and involves neutrophils, while chronic inflammation lasts months or years and is associated with lymphocytes and fibrosis.