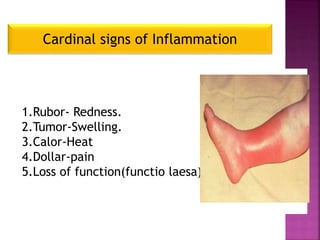
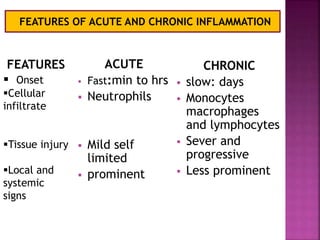
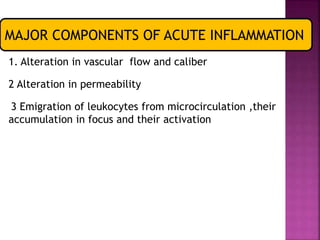
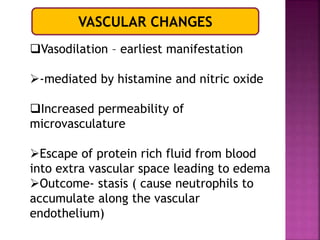
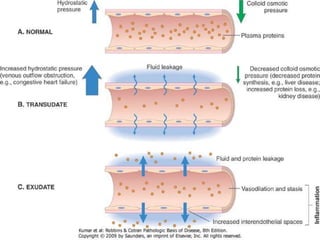
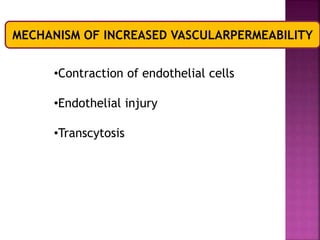
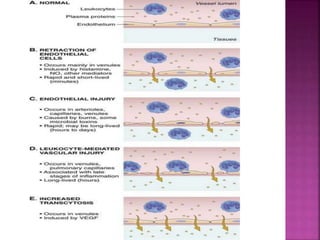
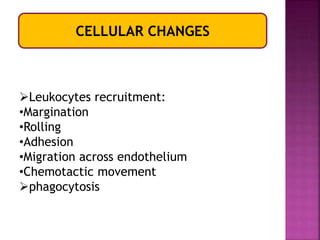
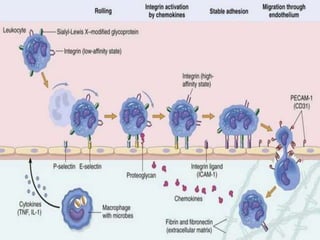
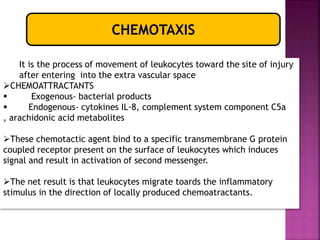
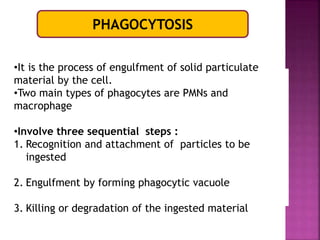
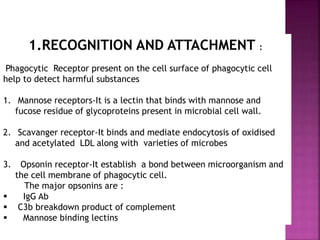
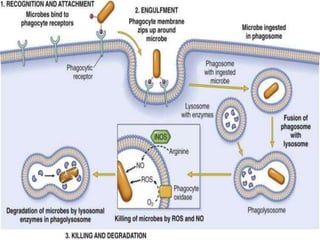
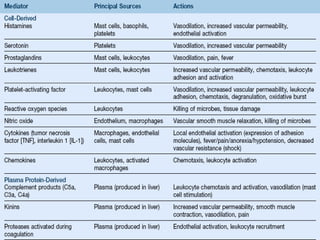
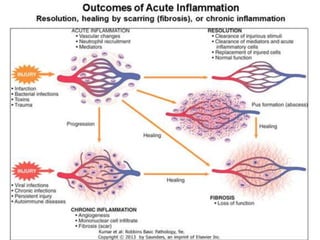
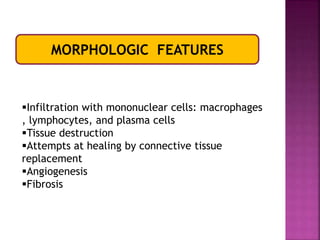
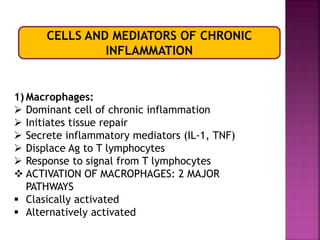
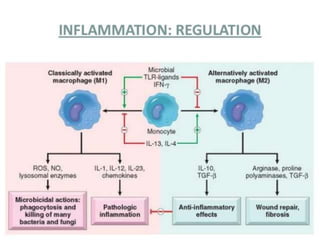
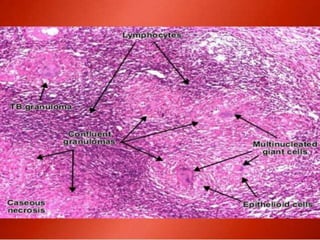
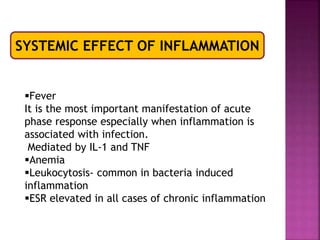
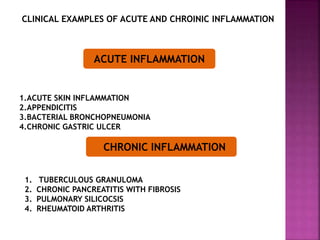
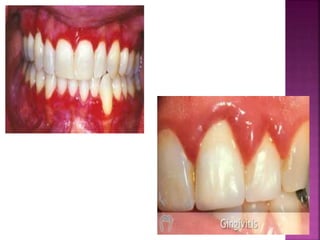
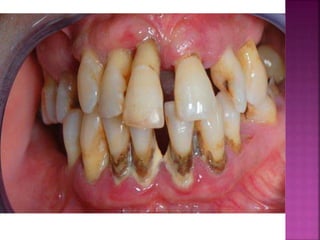
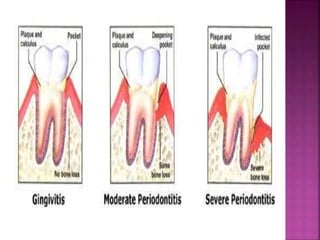
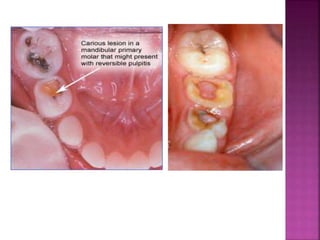
This document provides an overview of inflammation. It defines inflammation as the body's response to infection or damaged tissue where immune cells are recruited to sites of injury. The goals of inflammation are to eliminate the cause of injury and initiate repair. Common causes include infection, necrosis, and foreign bodies. Cardinal signs are redness, swelling, heat, pain, and loss of function. Acute inflammation resolves quickly while chronic inflammation persists long-term. Mediators such as histamine and cytokines regulate the inflammatory response, which involves vascular changes, cellular recruitment, and phagocytosis. Chronic inflammation can lead to fibrosis and tissue destruction. Clinical examples provided are gingivitis, periodontitis, and pulpitis.