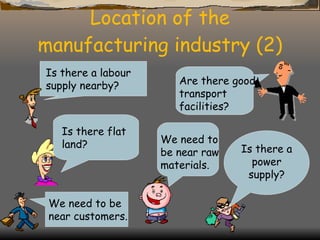
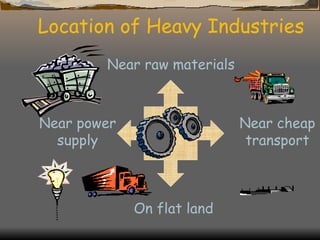
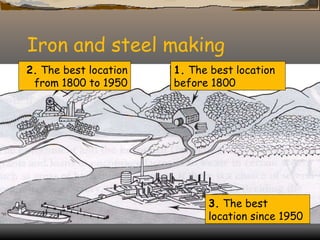
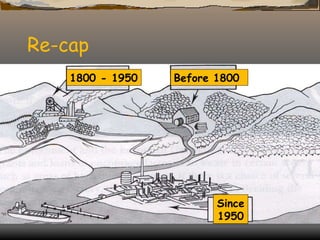
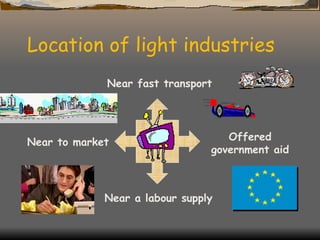
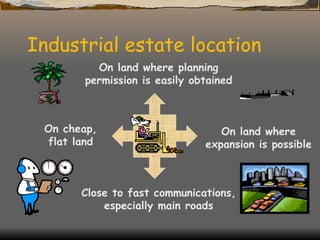
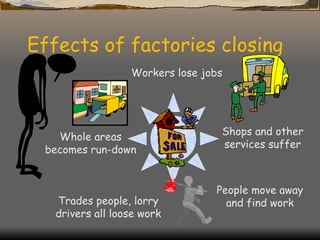
The document defines and classifies different types of industries. It discusses the location factors that influence where each type of industry tends to be found. Primary industries are usually located near raw materials, while service and quaternary industries are commonly found in urban areas. Manufacturing industries consider various location factors, including access to materials, labor, transportation, and markets. Heavy industries tend to locate near materials and transportation, while light industries prioritize transportation and markets. The document also examines how the optimal location of iron and steel making has changed over time based on shifting fuel and transportation conditions.