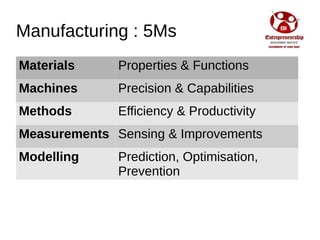
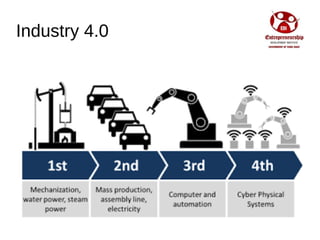
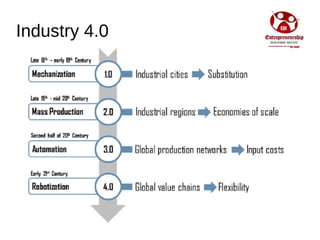
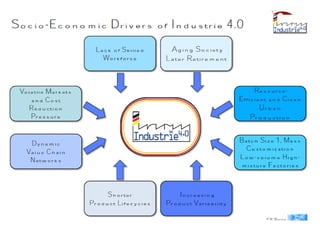
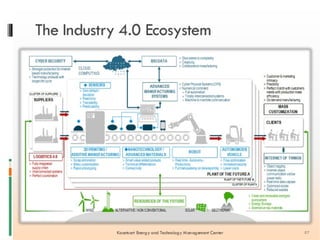
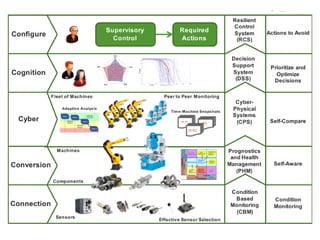
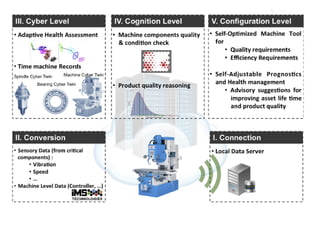
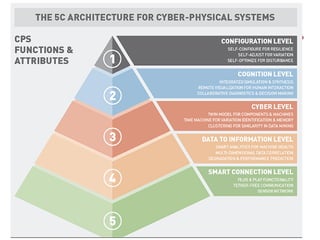
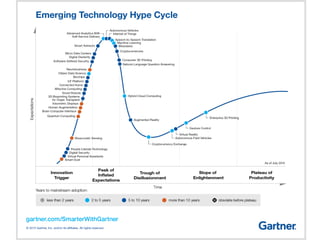
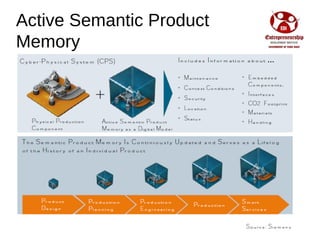
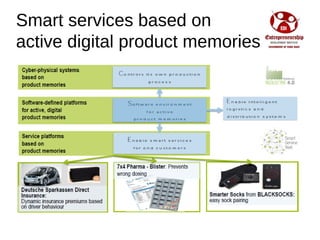
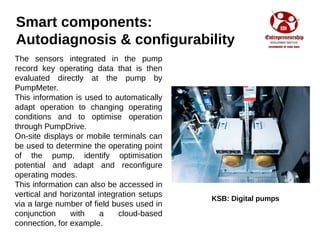
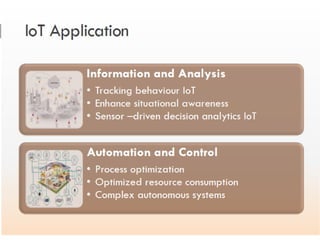
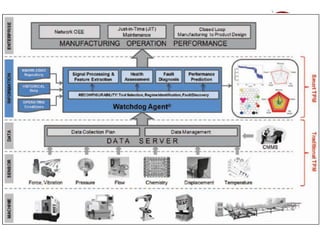
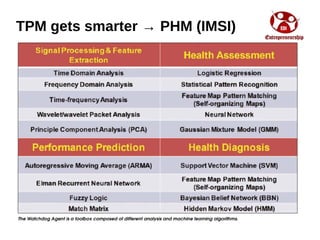
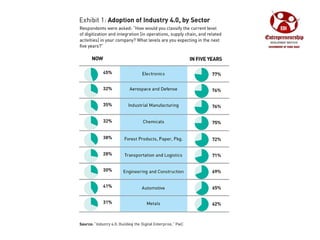
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution driven by four disruptions: exponentially growing data and computing power, new analytics capabilities, advanced human-machine interaction, and improvements in transferring digital instructions to the physical world. Key aspects of Industry 4.0 include smart manufacturing platforms that enable data and resource sharing, advanced customization enabled by digital technologies like 3D printing, pay-per-use business models, smart connected products and machines, predictive maintenance using sensors and analytics, and new digital business models focused on services rather than products. While the impacts will be significant, changing industrial operations will likely take time as factories have long investment cycles.