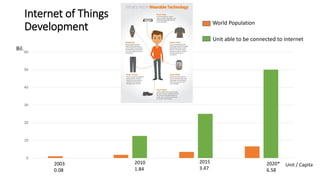
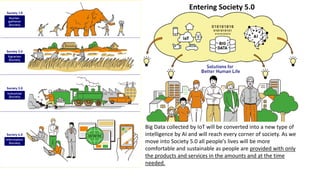
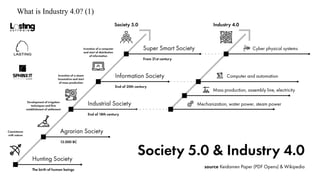
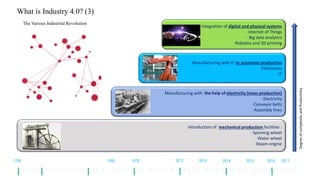
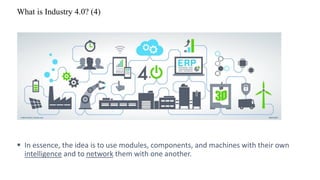
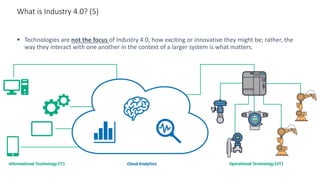
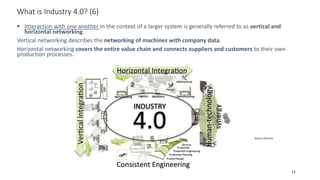
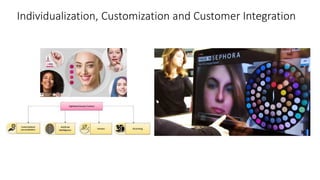
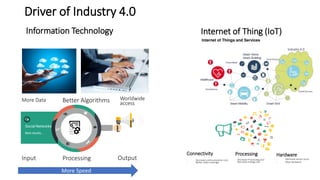
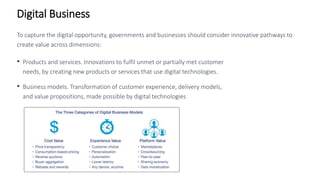
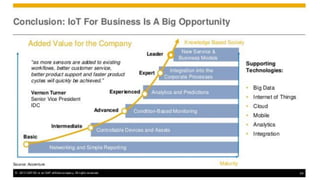
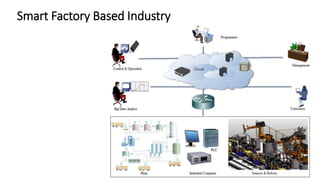
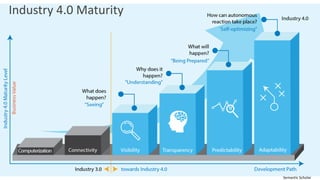
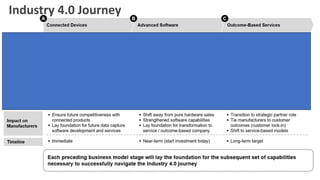
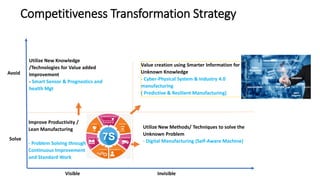
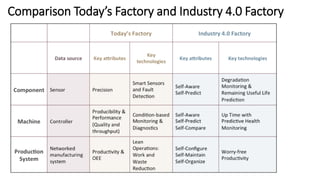
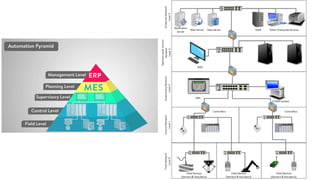
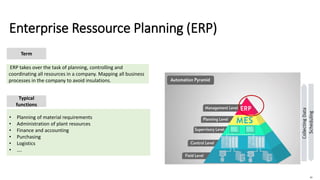
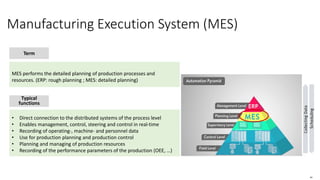
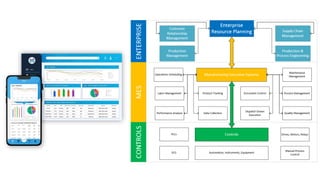
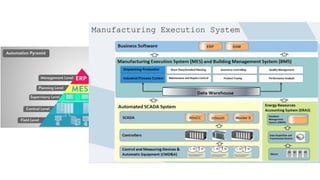
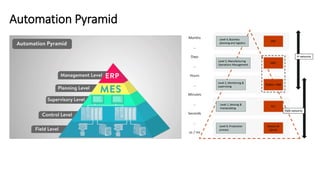
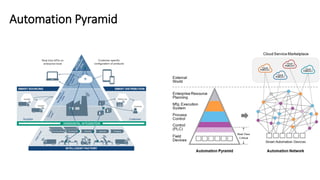
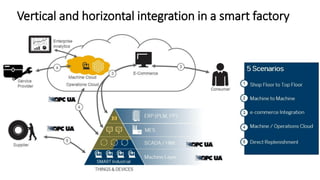
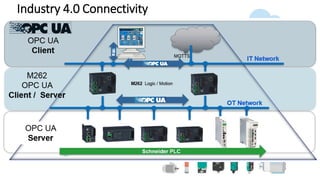
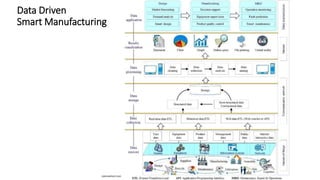
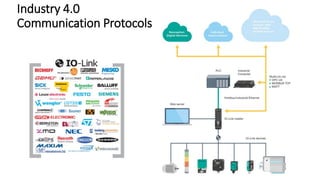
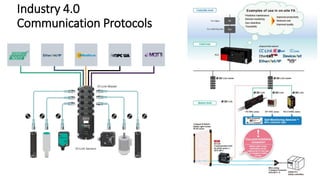
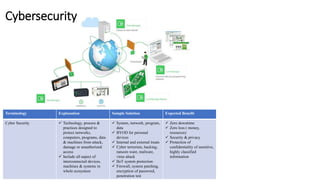
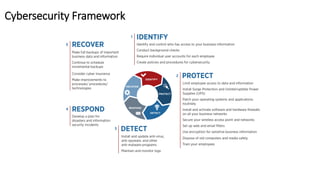
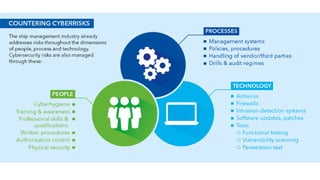
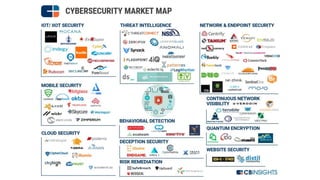
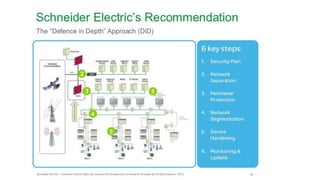
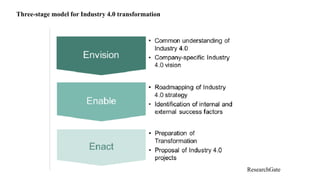
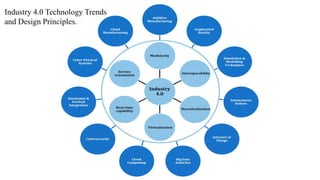
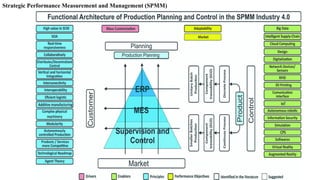
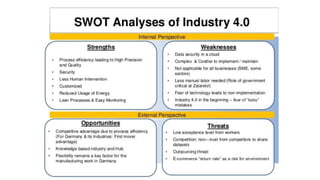
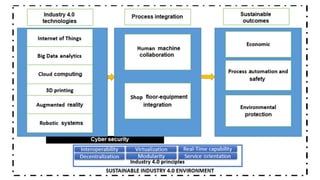
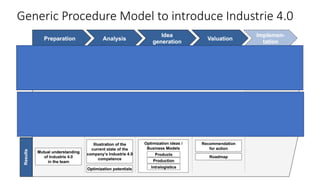
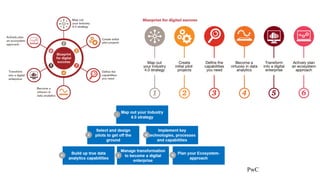
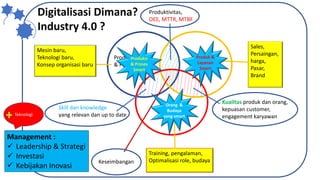
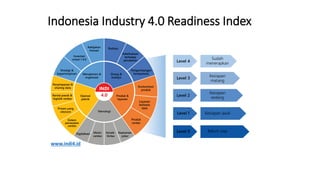
The document discusses Industry 4.0, highlighting its key components such as digital transformation, the Internet of Things (IoT), and smart manufacturing. It addresses the evolution from previous industrial revolutions, emphasizing the importance of interconnected and intelligent systems in manufacturing processes. Additionally, it outlines the design principles of Industry 4.0, the role of digital technologies in optimizing business models, and the potential impact on productivity and competitiveness in the industry.