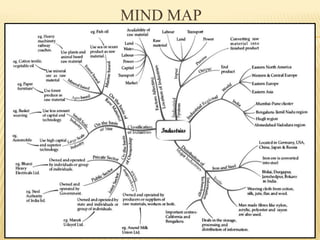
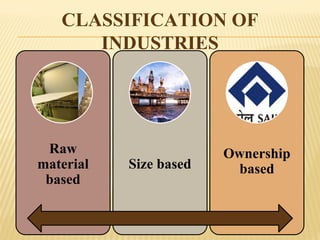
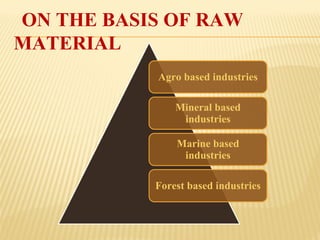
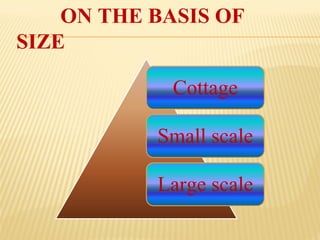
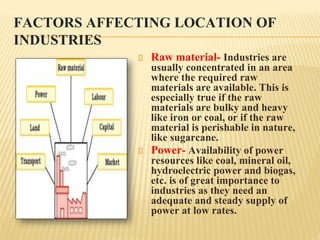
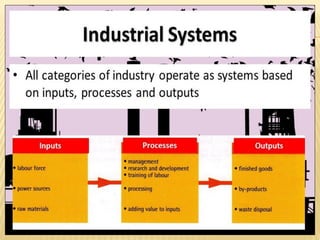
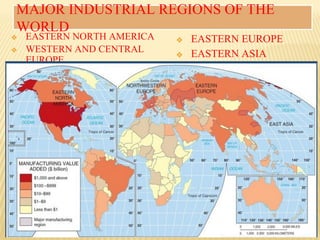
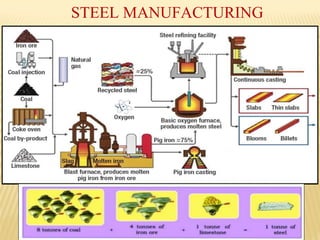
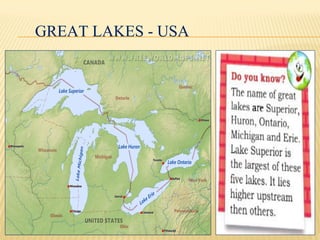
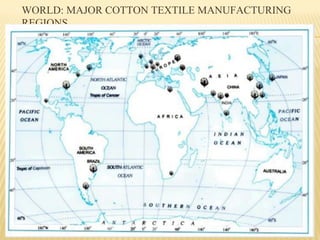
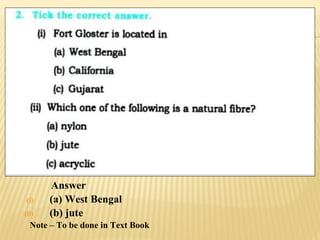
This document provides an overview of industries in India. It begins with defining industry and manufacturing. It then discusses the importance of industries and classifications of industries based on raw materials, size, and ownership. Key factors affecting the location of industries like raw materials, power, labor, capital, transport, markets, and government policies are outlined. Industrial systems and regions in India and worldwide are described. Specific industries discussed in more detail include iron and steel, with focuses on Tata Steel in Jamshedpur, India and the steel industry in Pittsburgh, USA. The cotton textile industry is also examined through the examples of Ahmedabad, India and Osaka, Japan.