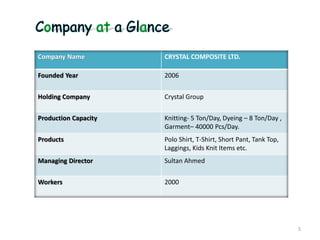
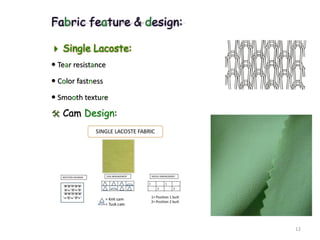
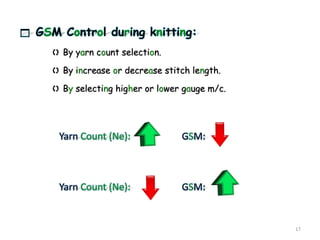
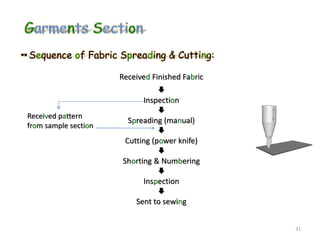
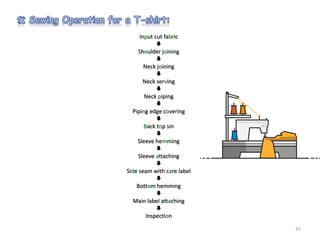
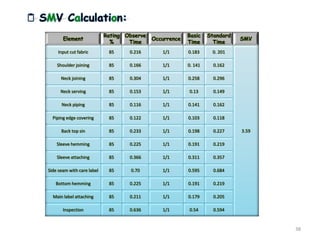
This document summarizes Noorul Islam Saiful's internship experience at Crystal Composite Ltd. It provides details about the company, his activities and responsibilities in different departments, including knitting, dyeing, sewing, and finishing. It also discusses fabric and garment defects, quality control measures, and standard minute values for sewing operations. Overall, the internship helped him gain work experience and professional skills.