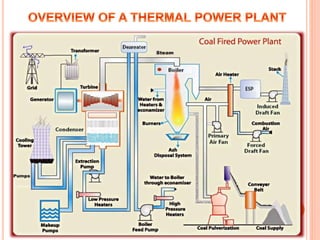
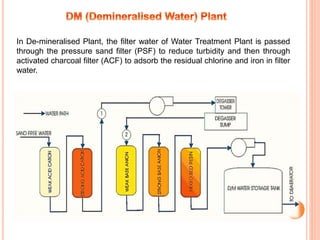
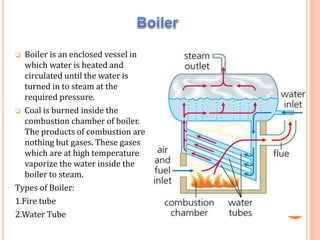
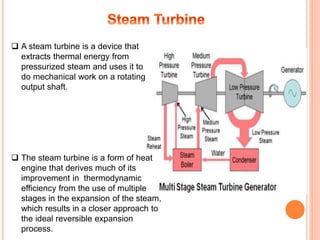
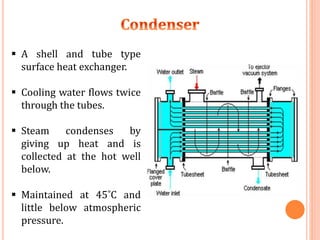
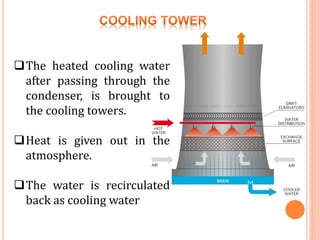
A thermal power plant operates by burning coal to create steam, which spins turbines that drive generators to produce electricity. The thermal power plant uses various processes: coal is pulverized and blown into a boiler to create steam, which expands in a turbine to spin a generator. The steam is then condensed in a condenser and recycled to the boiler. Ash produced during combustion is collected by an electrostatic precipitator and disposed of properly. The plant's operations are controlled and monitored in a central control room.