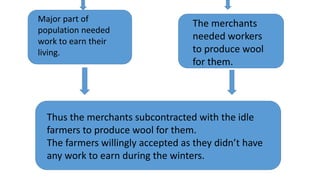
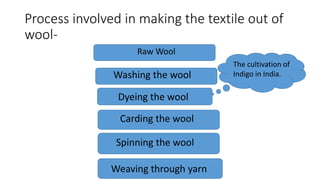
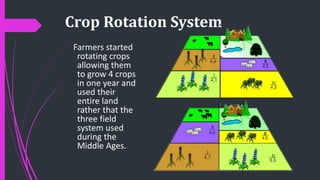
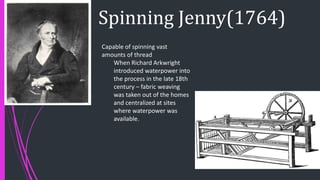
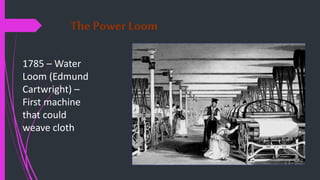
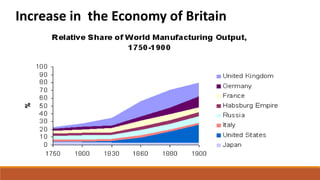
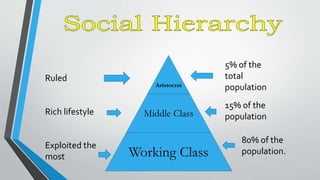
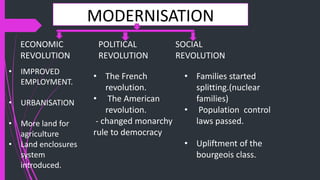
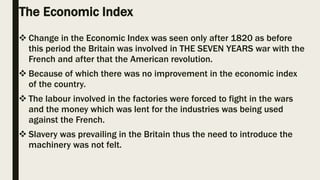
The document outlines the historical transition from agrarian economies to industrialization, detailing how wool production involved subcontracting from idle farmers and evolved into cotton production due to market demand. It highlights significant inventions during the Industrial Revolution that transformed textile processing and increased productivity, resulting in profound social and economic changes, including urbanization and the emergence of new social classes. Furthermore, it discusses the uneven spread of industrialization and the varying impacts across different countries, while critically examining whether this process can truly be characterized as a 'revolution.'