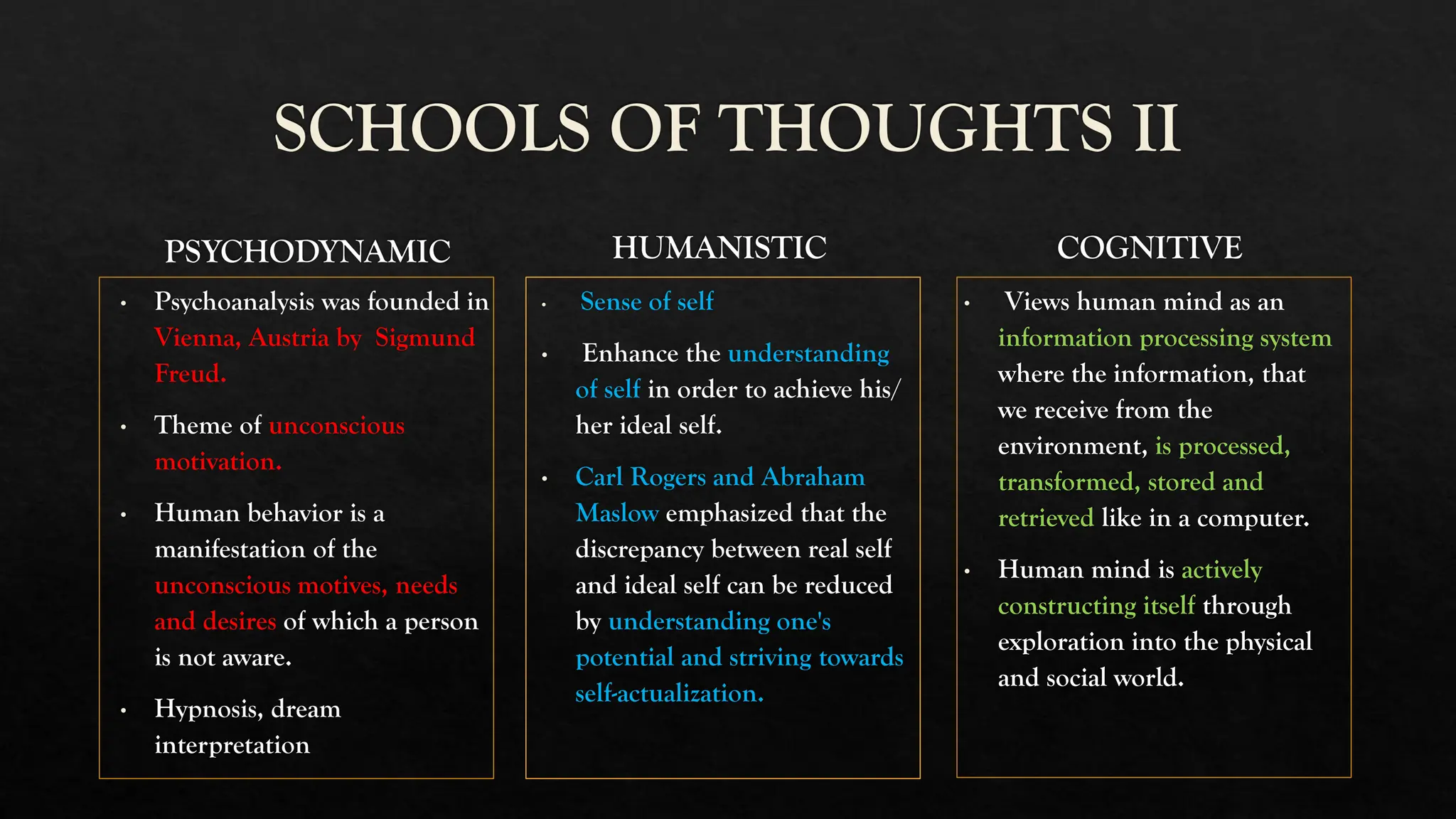
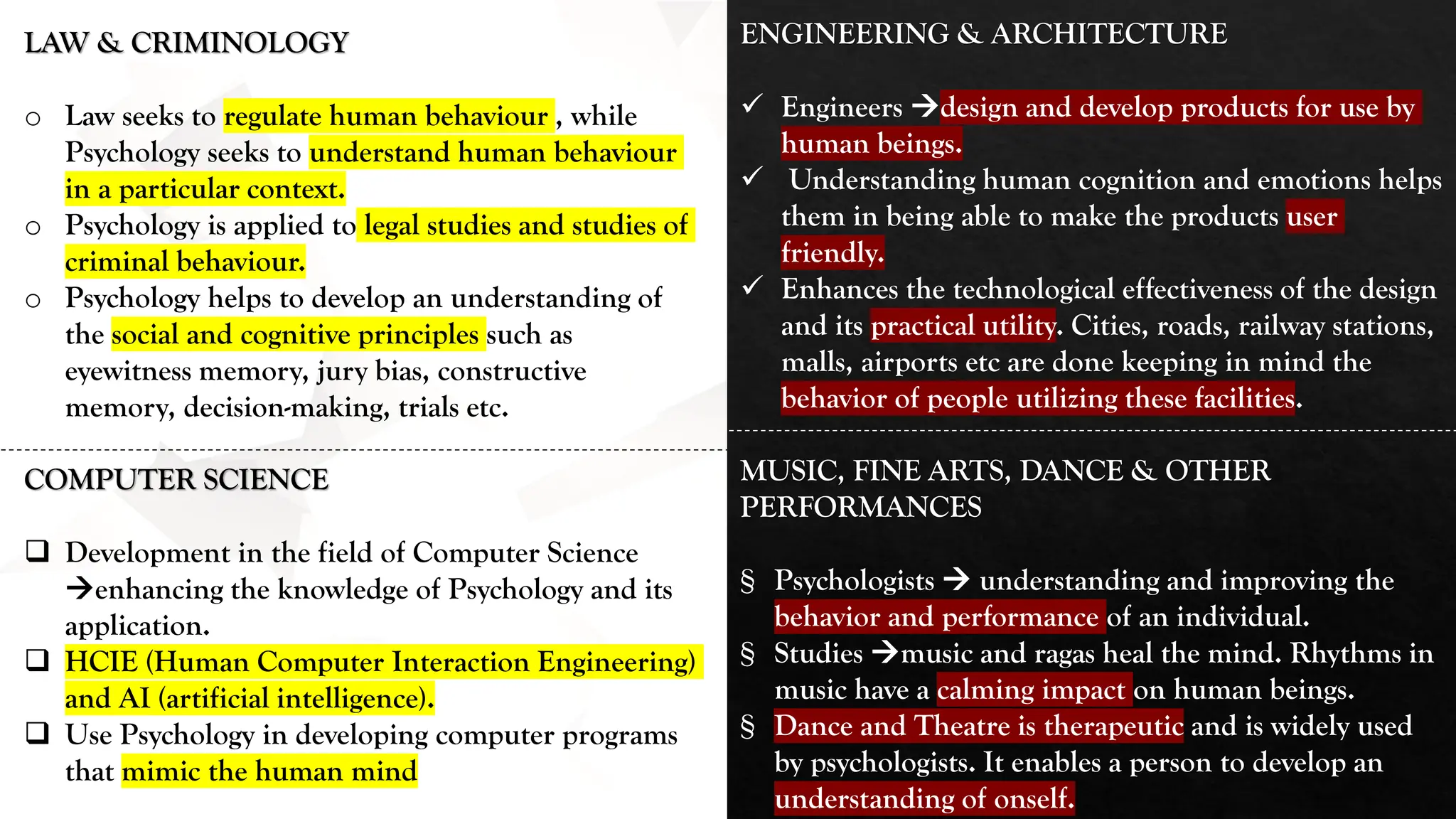
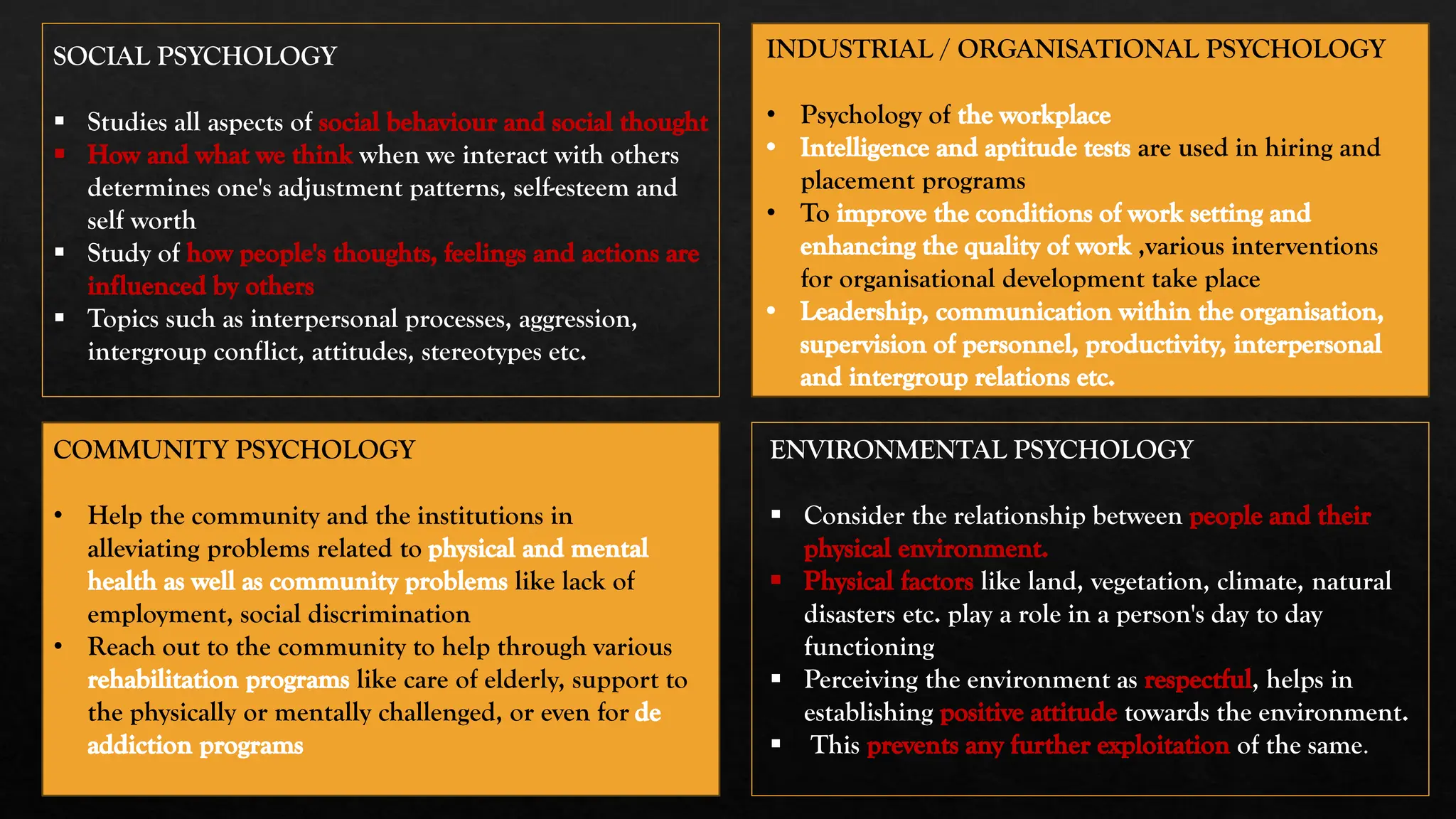
The document provides a comprehensive overview of psychology, detailing its evolution, various schools of thought, and its application as both a social and natural science. It emphasizes the importance of understanding human behavior, cognition, and emotions within various contexts influenced by culture and environment. Additionally, it highlights the diverse subfields within psychology, including clinical, counseling, developmental, and social psychology, as well as its intersections with other disciplines such as sociology, economics, and medicine.