The document presents a seminar on classifying induction motor bearing health conditions using machine learning algorithms. It introduces the topic, discusses electric motors and bearings, and reviews several studies that classify bearing faults using techniques like adaptive deep convolutional neural networks, k-nearest neighbors, general-purpose graphics processing units, convolutional neural networks, and random forests. The studies are compared based on their classification accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. The conclusion is that researchers are making progress toward achieving perfect classification accuracy and developing an online bearing fault detection module.
![A Presentation on
Induction Motor Bearing Health Condition
Classification Using Machine Learning Algorithms
[Seminar Presentation]
Niloy Sikder
Student ID: MSc 190221
Year: 1st, Term: I
CSE Discipline
Khulna University, Khulna
niloysikder333@gmail.com
Presented by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-1-2048.jpg)

![2
Introduction
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
Electric motors are the driving force of our industrial world.
They power approximately 85% of all rotating machines[1].
Robust device but not entirely fault-proof.
More vulnerable to the internal faults than the external ones.
Among the internal faults, bearing faults are the most frequent ones.
Their effects range from low-pitched sounds to hard motor breakdowns.
The contemporary advancements in the fields of DSP & ML allow us to detect
faults and figure out their origins.
Which enables us to take measures against motor breakdowns.
An effective solution is to investigate the motor’s vibration information.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-3-2048.jpg)
![3
The Electric Motor and It’s Bearings
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
Electric motors uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy.
Two major types – dc motors & ac motors.
Two major components – rotor (rotates around an axis) & stator (the body).
The bearings allow the rotor to revolve around its axis .
Bearings are responsible for about 50% of all motor faults[2].
Bearing faults can be classified into – inner raceway fault (IRF), ball raceway
fault (BRF) and outer raceway fault (ORF)[3].
Fig. 1. Cross-section of an electric motor[4] Fig. 2. Rotating motor bearings[5] Fig. 3. Various types of bearing faults[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-4-2048.jpg)
![4
A Brief Background
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
Researches have been working with the motor bearing fault data supplied by the
CWRU Lab for quite some time now[7].
Most of the methods involve a DSP technique to preprocess the fault signal and
then an ML technique to analyze, learn and predict future faults.
So far, Fourier Transform, Hilbert Transform , singular spectrum analysis,
complex envelope spectrum, wavelet packet analysis, Cyclic Spectrum Map etc.
signal processing techniques have been used to preprocess fault signals.
And Hidden Markov Modeling, Support Vector Machine, 𝑘-nearest neighbor
classifier, feed forward neural network, Convolutional Neural Network etc. ML
techniques that have been used to classify bearing faults.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-5-2048.jpg)
![5
Fig. 4. Test rig used by CWRU for collecting motor fault data[3]
Load 0 – 3 hp
Fault Seeder EDM
Diameter 0.007-0.021 inch
Collection rate 12000, 48000
samples/sec
rpm 1730, 1750, 1772, 1797
Table I: Available datasets in CWRU Lab website[7]
CWRU Lab’s Bearing Fault Data
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-6-2048.jpg)
![6
Literature Reviews
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
The method was proposed by Manjurul Islam and Jong-Myon Kim in 2018[9].
It uses 2D Cyclic Spectrum Map to preprocess the raw vibration signal.
Then Adaptive Deep Convolutional Neural Network to classify bearing faults.
Attempts to classify the four bearing states HBC, BRF, IRF & ORF.
The method is tested on the motor bearing fault data provided by CWRU lab.
The 2D CSM is that it is capable of highlighting the valuable information about
how rotating components are distributed within the vibration spectrum.
Once the 2D CSM of the raw signal is obtained using an improved
cyclostationary analysis, they used the ADCNN for multi-fault classification and
obtain the results.
Motor Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using ADCNN
[9] M. M. M. Islam and J.-M. Kim, “Motor Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using Deep Convolutional Neural
Networks with 2D Analysis of Vibration Signal,” Springer, Cham, pp. 144–155, 2018.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-7-2048.jpg)
![7
Fig. 5. An overall structure of the ADCNN-based method for bearing fault diagnosis[9]
Methodology
Results
The method is able to classify the 4 bearing faults with 95.75% accuracy.
The claim is supported by providing the confusion matrix and average sensitivity
of various classes.
In comparison with two similar methods this method improves the classification
performance from 8.25% to 13.75% in terms of accuracy.
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-8-2048.jpg)
![8May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
Thomas Rauber et al. conducted this study in 2015[10].
Their study involves three different feature extraction and selection techniques,
and three different classifiers to categorize motor bearing faults .
They have used complex envelope spectrum, statistical time and frequency-
domain parameters, and wavelet packet analysis to extract features
simultaneously from the raw vibration signal.
The statistical features considered in the study are the root mean square, the square
root of the amplitude, kurtosis value, skewness value, peak-to-peak value, crest
factor, impulse factor, margin factor, shape factor, and kurtosis factor.
The classification then was performed by k-NN, a feed-forward network, & SVM.
Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using 𝒌-NN
This method also aims to classify the four bearing states (HBC, BRF, IRF,
ORF) using multiple datasets from the CWRU lab repository.
[10]T. W. Rauber, F. De Assis Boldt, and F. M. Varejão, “Heterogeneous feature models and feature selection
applied to bearing fault diagnosis,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 637–646, 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-9-2048.jpg)
![9
Fig. 6: Computational intelligence framework for bearing fault diagnosis. (a) Generic model. (b) Instantiated model[10]
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-10-2048.jpg)
![10May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
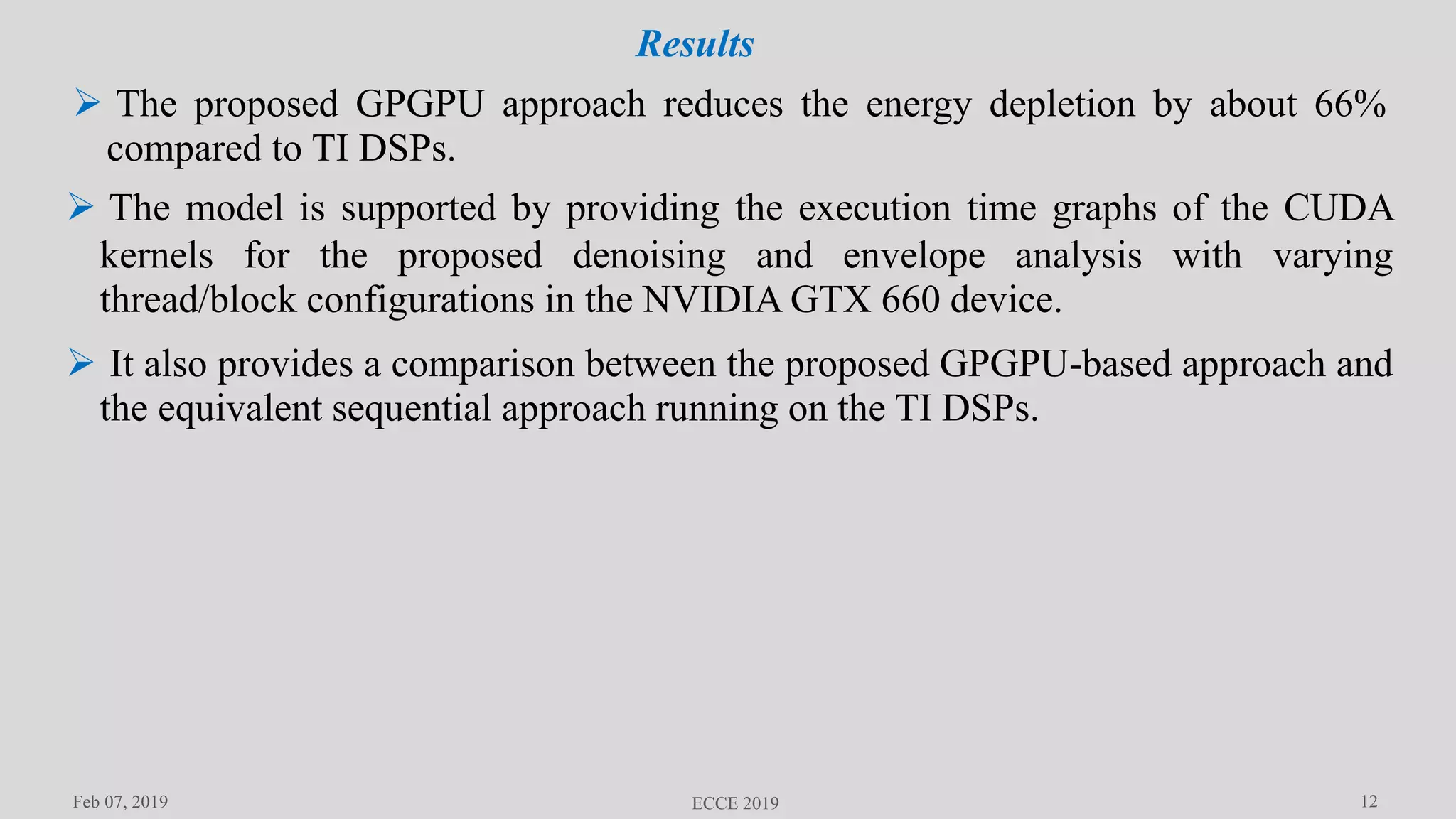
Myeongsu Kang et al. proposed this useful envelope analysis based
methodology for machine condition monitoring in 2015[11].
The methodology includes signal denoising to improve the SNR using a soft-
thresholding technique, signal preprocessing using a 2-D visualization technique
that depends on the improved residual frequency component-to-peak ratios.
The proposed method describes an efficient parallel implementation on a
General Purpose Graphics Processing Unit (GPGPU) by taking advantage of the
memory hierarchy and the massive parallelism.
The technique aims to classify the four bearing states in real-time while
reducing the energy consumption of the system and validates its efficacy by
identifying classes with 1-s acoustic emission (AE) signals sampled at 1 MHz.
Motor Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using GPGPU
[11] M. Kang, J. Kim, and J. Kim, “High-Performance and Energy-Efficient Fault Diagnosis Using Effective
Envelope Analysis Processing Unit,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 30, no. 05, pp. 2763–2776, 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-11-2048.jpg)
![11
Fig. 7. Structure of the GPGPU -based method for bearing fault diagnosis[11]
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-12-2048.jpg)
![13May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
Olivier Janssens et al. proposed this method for Rotating Machinery in 2018[12].
The specialty of this study is that it introduces a learning model to automatically
learn useful features for bearing fault detection from the signal itself .
Sparse coding has been used as the feature learning technique to represent a
signal using a linear combination of a few bases from a dictionary.
The methodology has two steps.
The final fault classification is performed using two pipelines.
Motor Bearing Fault Classification Using CNN
The first step consists of constructing the bases of the dictionary.
The second step consists of determining the sparse coefficients which can be
calculated using greedy pursuit algorithms or iterative shrinking algorithms.
[12]O. Janssens, V. Slavkovikj, B. Vervisch, K. Stockman, M. Loccufier, S. Verstockt, R. V. D. Walle, and S.
V. Hoecke, “Convolutional Neural Network Based Fault Detection for Rotating Machinery,” Journal of
Sound and Vibration, vol. 377, pp. 331–345, 2016.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-14-2048.jpg)
![14
Fig. 8. High-level representation of the architecture employed in[12]
Results
The method has achieved a 93.61% classification accuracy among various
bearing faults considered in the paper.
The paper also outlines the precision, recall and f1-score values that are
important for performance evaluation.
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-15-2048.jpg)
![15May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
Te Han and Dongxiang Jiang proposed this method in 2016[13].
This method is based on variational mode decomposition (VMD) and
autoregressive (AR) model parameters.
First of all, the authors employed VMD to decompose the vibration signals in
order to obtain stationary components of them.
Then, AR model was to establish each component model and analyze the
characteristic fault vectors.
Motor Bearing Fault Classification Using RF
And finally, random forest (RF) classifier is used to recognize the pattern
underlying beneath rolling bearing vibration signals.
[13]T. Han and D. Jiang, “Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnostic Method Based on VMD-AR Model and Random
Forest Classifier,” Shock Vib., vol. 2016, pp. 1–11, 2016.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-16-2048.jpg)
![16
Fig. 9. High-level representation of the architecture employed in[13]
Methodology
Results
The method has achieved an accuracy of 100%
Although the performance might vary depending on various parameters such as
the number of training and test samples and the employed samples.
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-17-2048.jpg)
![17
Comparison of the Acquired Results
May 08, 2019 CSE, KU
Due to the variety of the parameters based on which the performances of these
methods are measured, it is a perplexing task to compare them uniformly.
Paper/
Parameters
Maximum
Accuracy (%)
Precision
(%)
Recall
(%)
F1-Score
(%)
[10] 99.96 - - -
[12] 93.61 94.52 93.6 94.06
[9] 95.75 95.83 95.86 95.85
[13]
100 (location) 98.63
(severity)
- - -
“-” denotes that the information is not specified in the associated paper.
Table II: Comparison of the Results Acquired in the Reviewed Papers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-18-2048.jpg)

![References
[1] E. Cabal-Yepez, M. Valtierra-Rodriguez, R. Romero-Troncoso, A. Garcia-Perez, R. Osornio-Rios, H. Miranda-Vidales, and R. Alvarez-Salas, “FPGA-based entropy
neural processor for online detection of multiple combined faults on induction motors,” Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, vol. 30, pp. 123–130, 2012.
[2] M. E. H. Benbouzid, “A review of induction motors signature analysis as a medium for faults detection,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 47, no. 5,
pp. 984–993, 2000.
[3] W. A. Smith and R. B. Randall, “Rolling element bearing diagnostics using the Case Western Reserve University data: A benchmark study,” Mechanical Systems and
Signal Processing, vol. 64-65, pp. 100–131, 2015.
[4] “Why electric motors fail,” Flow Control Network, 06-Apr-2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.flowcontrolnetwork.com/why-electric-motors-fail/. [Accessed:
08-Jan-2019].
[5] “Bearing (mechanical),” Wikipedia, 03-Dec-2018. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bearing_(mechanical). [Accessed: 08-Jan-2019].
[6] A. Boudiaf, A. Moussaoui, A. Dahane, and I. Atoui, “A Comparative Study of Various Methods of Bearing Faults Diagnosis Using the Case Western Reserve
University Data,” J. Fail. Anal. Prev., vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 271–284, 2016.
[7] Bearing Data Center. [Online]. Available: https://csegroups.case.edu/. [Accessed: 08-Jan-2019].
[8] H. Ocak and K. A. Loparo, “A new bearing fault detection and diagnosis scheme based on hidden Markov modeling of vibration signals,” ICASSP, IEEE Int. Conf.
Acoust. Speech Signal Process. - Proc., vol. 5, pp. 3141–3144, 2001.
[9] M. M. M. Islam and J.-M. Kim, “Motor Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks with 2D Analysis of Vibration Signal,” Springer,
Cham, 2018, pp. 144–155.
[10] T. W. Rauber, F. De Assis Boldt, and F. M. Varejão, “Heterogeneous feature models and feature selection applied to bearing fault diagnosis,” IEEE Trans. Ind.
Electron., vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 637–646, 2015.
[11] M. Kang, J. Kim, and J. Kim, “High-Performance and Energy-Efficient Fault Diagnosis Using Effective Envelope Analysis Processing Unit,” IEEE Trans. Power
Electron., vol. 30, no. 05, pp. 2763–2776, 2015.
[12] O. Janssens, V. Slavkovikj, B. Vervisch, K. Stockman, M. Loccufier, S. Verstockt, R. V. D. Walle, and S. V. Hoecke, “Convolutional Neural Network Based Fault
Detection for Rotating Machinery,” Journal of Sound and Vibration, vol. 377, pp. 331–345, 2016.
[13] T. Han and D. Jiang, “Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnostic Method Based on VMD-AR Model and Random Forest Classifier,” Shock Vib., vol. 2016, pp. 1–11, 2016.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarmsc190221-190620123032/75/Induction-Motor-Bearing-Health-Condition-Classification-Using-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-20-2048.jpg)