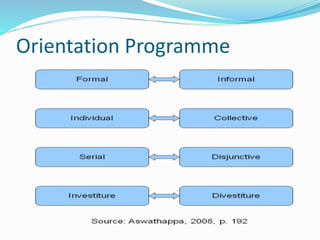
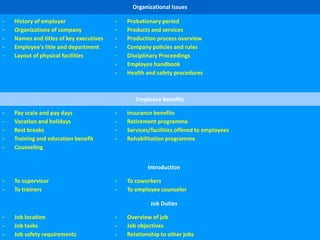
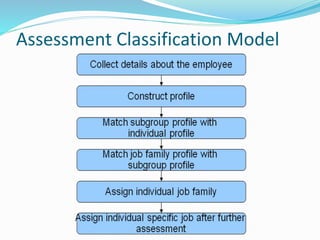
The document discusses employee orientation and onboarding. Orientation aims to help new employees adjust to their new roles and work environments by providing information about company policies, objectives, daily routines, and introducing them to colleagues. It covers organizational issues, employee benefits, the employee's job duties and placement within the company. Orientation can be formal or informal, individual or collective, and is important for relaxing and acclimating new hires to their new roles and workplaces.