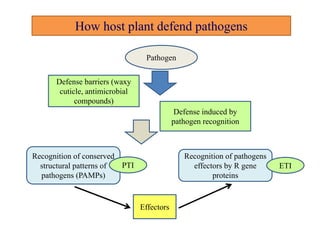
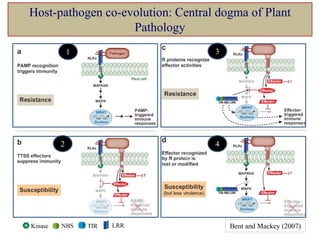
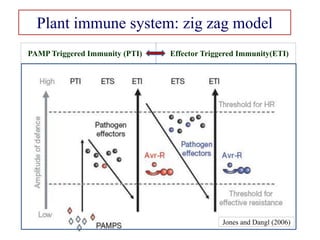
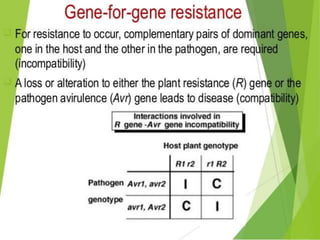
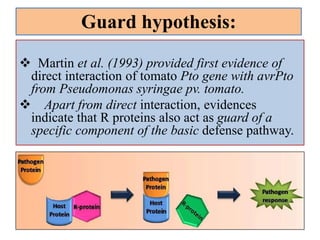
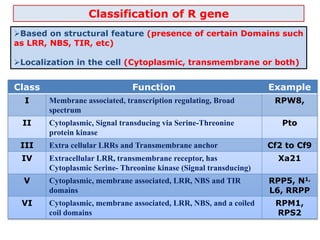
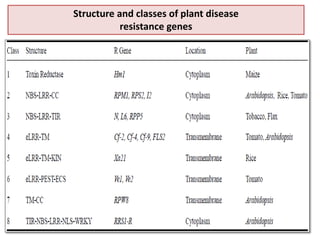
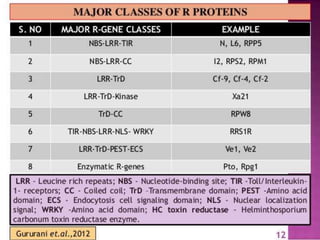
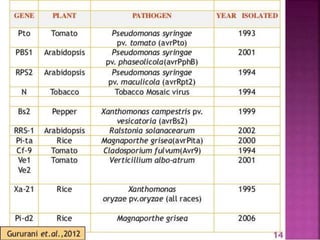
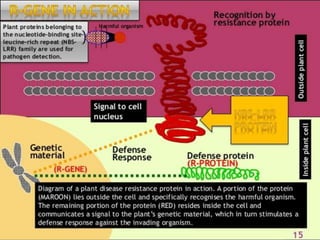
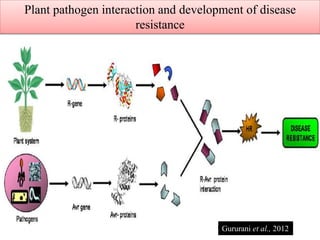
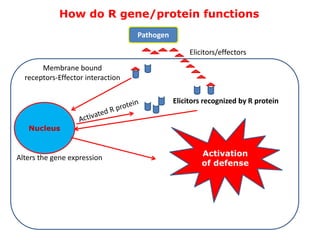
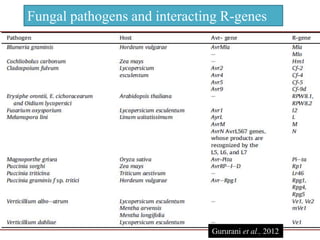
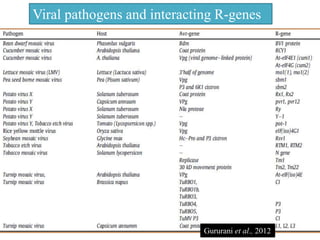
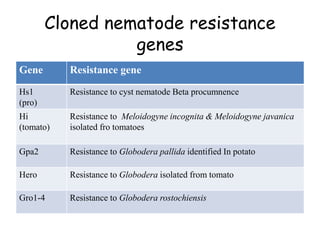
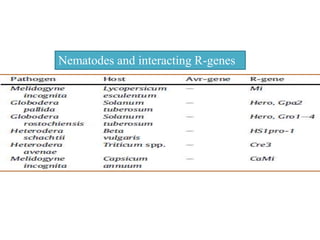
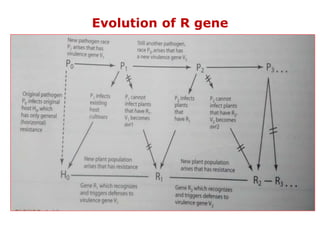
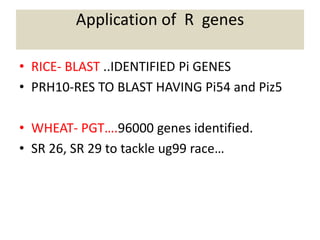
This document discusses genes in plants that provide disease resistance. It begins by outlining the plant immune system and the zig-zag model involving PAMP-triggered immunity and effector-triggered immunity. It then describes different classes of plant resistance genes based on their structural features and domains. The document also discusses the functions of resistance genes in signaling plant defenses, and provides examples of resistance genes that have been cloned and provide resistance against various pathogens like fungi, viruses, nematodes, and more.