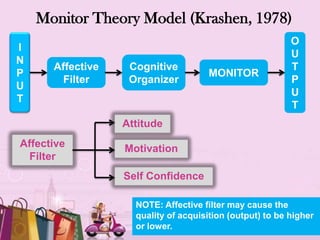
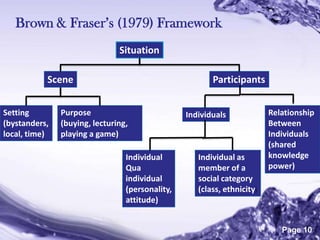
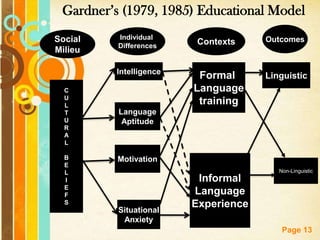
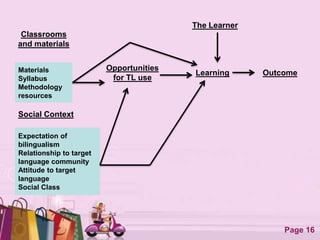
The document discusses several models of individual differences and their relationship to language learning:
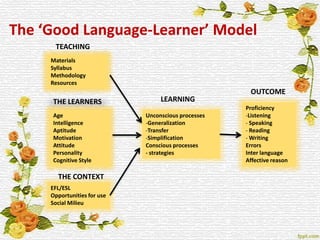
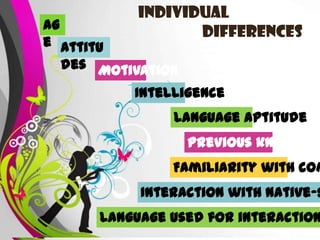
1. Models with independent learner variables like the "Good Language Learner" model which links three independent variables (learner, teaching, context) directly to learning outcomes.
2. Models with interdependent learner variables like Gardner's educational model which highlights the interrelationship between social, individual, and context variables influencing language learning outcomes.
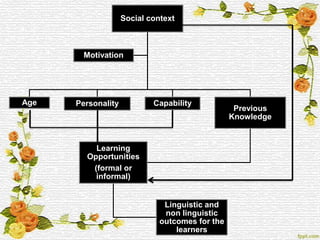
3. Spolsky's model of second language learning examines individual differences resulting from restricted conditions of social context and the learner. The models aim to understand how learner variables interact and affect language learning outcomes.