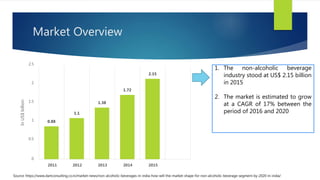
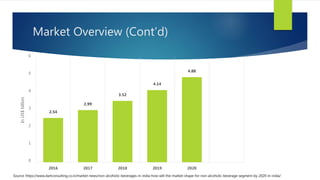
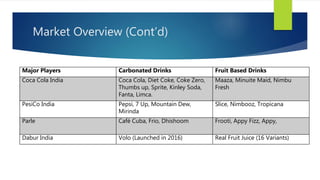
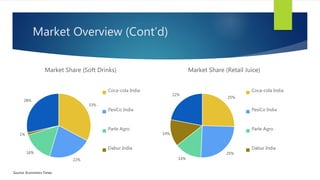
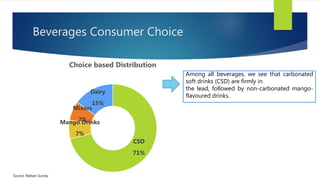
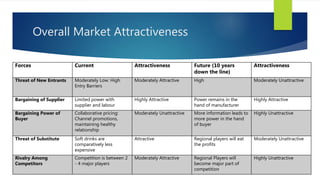
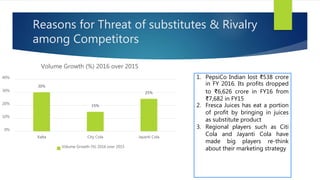
The Indian cold beverage market, valued at $2.15 billion in 2015, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17% from 2016 to 2020. Major players include Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, with carbonated drinks dominating consumer choices. Competitive forces reveal high barriers to entry, moderate power dynamics among suppliers and buyers, and a rising threat from substitute products, particularly from emerging regional brands.